Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Type of Number: Arithmetic
Transféré par
Munawwar ZafriDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Type of Number: Arithmetic
Transféré par
Munawwar ZafriDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
4/18/12
TYPE OF NUMBER
Click to edit Master subtitle style
ARITHMETIC
4/18/12
THE REAL NUMBER SYSTEM
The real number system evolved over time by expanding the notion of what we mean by the word number. At first, number meant something you could count, like how many sheep a farmer owns. These are called the natural numbers, or sometimes the counting numbers. real number also known as R
The
4/18/12
THE REAL NUMBER LINE
A
line with real number with each number is called a real number line. to the right are greater than points to the left.
Points
4/18/12
THE REAL NUMBER R
REAL NUMBER SYSTEM
Classification
4/18/12
of number NAME SYMBOL Natural Number N Whole Number Integers Rational Number W Z Q
Irrational Number
EXAMPLE 1,2,3,4,5,6,7, . 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, . ,-3,-2,1,0,1,2,3, _4,1 7 2 4 = 0.8 5 = 3.141592654 3=
4/18/12
ARITHMETIC
ARITHMETIC OPERATION
Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/18/12
ARITHMETIC OPERATION
The
basic arithmetic operation that can be known. SYMBOL OPERATION + ADDITION _ * / SUBSTRACTION MULTIPLICATION DIVISION
4/18/12
FACTOR AND MULTIPLES
Factor.
- The number you multiple to get the product. the product of 36 have a several
Example,
factor. 1x36 = 36 2x18 = 36 3x12 = 36 4 x 9 = 36 6 x 6 = 36
4/18/12
FINDING FACTOR
Start
with 1x the number. Try several number such as 2,3,4. you get double (4x4), mean you are
Then, If
the number are repeat, cross it out.
When
done.
4/18/12
WHAT ARE THE FACTOR OF 36 ?
1 x 36 2 x 18 3 x 12 4x9 5 x ??? 5 is not the factor, so, cross it out. 6 x 6 double = done the factor of 36 is 1,2,3,4,6,9,12,18,36.
4/18/12
FACTORS AND MULTIPLES
Multiples.
with
- is formes by multiplying a given number counting number. - the counting number are such as 1,2,3,4,5,6,7, etc.
4/18/12
EXAMPLE : LIST THE MULTIPLE OF 6 :
1x6=6 2 x 6 =12 3 x 6 = 18 4 x 6 = 24 5 x 6 = 30 6 x 6 = 36 7 x 6 = 42 counting numbers. - so, the multiple of 6 are 6,12,18,24,30,36,42, etc.
4/18/12
WHAT THE FIRST 6 MULTIPLES OF 12 ?
1 x 12 = 12 2 x 12 = 24 3 x 12 = 36 4 x 12 = 48 5 x 12 = 60 6 x 12 = 72 - So, the first 6 of multiples of 12 is 12,24,36,48,60,72.
4/18/12
ARITHMETIC
PRIME AND COMPOSITE FACTOR
Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/18/12
PRIME AND COMPOSITE FACTOR
Composite
number have more than two factor.
- example : 10, 24, 30, 60, 120
Prime
factor. One and the number itself. -example : 3, 5, 7, 11, 31
factor are the number that have two
4/18/12
ARITHMETIC
PRIME FACTOR
Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/18/12
PRIME FACTOR
Use
the factor tree to help you to find PRIME FACTOR.
WRITE 24 AS THE PRODUCT OF ITS PRIME FACTOR.
24 6 3 2 2 4 2
4/18/12
24 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 prime factor !!!
WRITE 80 AS THE PRODUCT OF PRIME FACTOR.
80 8 4 2 5 10 2
4/18/12
80 = 2 x 2 x 4 x 5 prime factor !!!
4/18/12
ARITHMETIC
HIGHEST COMMON FACTOR & LOWEST COMMON FACTOR
Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/18/12
FIND THE HCF AND LCM OF 36 & 90.
36 9 3 3 9 3 2 4 2 5 10 2 3 90
- Prime factor are now have been found.
4/18/12
FACTOR TREES.
Prime
factor :
36 = 3 x 3 x 2 x 2 90 = 2 x 3 x 3 x 5 - Now, we need to find HCF & LCM. (Highest Common Factor) & (Lowest Common Multiple)
4/18/12
HIGHEST COMMON FACTOR (HCF)
To
find HCF: - Do the factorization of each integer. - List them in column. - Find the full column.
4/18/12
HIGHEST COMMON FACTOR (HCF)
Example
: Find the HCF of 12, 14, 20 2 2 2 2 2 5 2 3 7
12 14 20 HCF
So,
the HCF of 12, 14 and 20 is 2.
4/18/12
LOWEST COMMON MULTIPLE (LCM)
To
find LCM:
- Do the prime factorization of each integer. - List them in column. - For each column, write down the value of the factor, then multiply it to get LCM.
4/18/12
LOWEST COMMON MULTIPLE (LCM)
Example:
Find the LCM of 8, 16, 22. 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 11 11
8 16 22 LCM
So,
the LCM of 8, 16, and 22 is 176.
4/18/12
ARITHMETIC
ORDER OF OPERATION (BEDMAS)
Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/18/12
ORDER OF OPERATION (BEDMAS)
What
is BEDMAS ? BEDMAS is: B = Bracket E = Exponent D = Division M = Multiple A = Addition S = Substraction
4/18/12
ORDER OF OPERATION
Example
(8 - 5) x (4 + 2) / 3 = ? - How to solve it? - By using BEDMAS - In this case, we must identify it first.
4/18/12
ORDER OF OPERATION (BEDMAS)
Solution
(8 5) x (4 +2 ) / 3 = 3x6/3 = 3x2 =6 -So, by using BEDMAS, we can solve the operation easily and get the correct answer.
4/18/12
ARITHMETIC
DECIMAL NUMBER
Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/18/12
DECIMAL NUMBER
Dividing We
the numerator by the denominator. the decimal point. : Number 3.456 Operation x 10 Answer 34.56
convert the fraction to decimal.
Shifting
Example
Shift one places to the right Shift two places to the right Shift three
789.432
x 100
78943.2
18.934
x 1000
18934
4/18/12
RECURRING DECIMAL
Some
division will end exactly and produce more number. : 53 / 22 = 2.363636364
Example
In
other case, the division will never work, the number after decimal will go on without end. In this case we called it RECURRING DECIMAL. : 4 / 3 = 1.333333 3 / 111 = 0.027027027027
Example
4/18/12
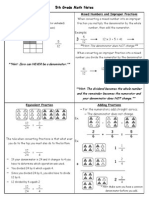
ADDING / SUBTRACTING DECIMAL
Align Bring
the decimal
the decimal down with the correct line of decimal. : 123.456 + 12.34 = ? : 123.456 + 12.34 135.796
Example Solution
By
using the correct method, we can solve the operation easily and get the corret answer.
4/18/12
MULTIPLYING DECIMAL
Multiply Count
normally.
factor.
the number decimal spaces in both
Move
your answer decimal this number of spaces. : 7.63 x 0.4 = ? : 7.63 x .4 3052. ( 2 decimal) ( 1 decimal) 3.052 ( 3
Example
Solution
4/18/12
DIVIDING DECIMAL (LONG DIVISION)
Move
the divisor decimal enough spaces so that will become whole number. move the decimal point. : 643.22 / 0.2 321.61 2 ) 643.22
Dont
Example Solution
4/18/12
DIVIDING DECIMAL (FRACTION)
Count
the number of decimal spaces in the numerator and the denominator. the larger of these value. : Move each decimal 3 places.
Choose Reduce
123.456 = 123456 = 61728 = 30864 = 10288 0.3 300 150 75 25 * The only prime factor of 25 is 5, since 10288 is not available in 5, the operation is done.
4/18/12
TYPE OF FRACTION
TYPE OF FRACTION PROPER FRACTION DEFINITION Numerator < denominator EXAMPLE 5 , 6 , 13 8 14 19
IMPROPER FRACTION MIXED FRACTION
Numerator = or > denominator Whole number plus fraction
7 , 13 , 3 4 9 1 4 6+ 9 = 6 4 9
4/18/12
CONVERSION
Convert Divide
improper to mixed.
N by D as far as possible and express any remainder as a proper fraction. : Express 13 as a mixed number. 6 Solution : 2 6 ) 13 - 12 1
1
Example
answer : 6
4/18/12
CONVERSION
Mixed
to improper
Multiply
the whole number by D, add N. Place the total over N. : 3 3 2 (3 x 3) + 2 3 11 3
Example
4/18/12
ARITHMETIC
RATIO AND PROPORTION
Click to edit Master subtitle style
4/18/12
RATIO AND PROPORTION
Ratio
: It is a comparison of two objects. Often express as a fraction. : There are 3 Indian for every 15 student.
Example
Solution
: 3 : 15 or 3 15
4/18/12
RATIO AND PROPORTION
Proportion
: - An equation that states two ratio are equal. : There are 3 Indian for every 9 student. How many Indian are there are 27 student ? :
Indian Student 3 9 x 27
Example
there if
Solution
4/18/12
HOW TO SOLVE ???
Using
(MPE)
the Multiplication Property of Equality : 3 27 3 9 x 27 27
Solution
3(3)=x 9 Indian = x
4/18/12
HOW TO SOLVE ???
Cross
multiplication. : 3 = 9 x 27 cross multiply
Solution
27 ( 3 ) = 9 (x) 81 = 9x 9 Indian = x
4/18/12
THANK YOU
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Practical Shop Math: Simple Solutions to Workshop Fractions, Formulas + Geometric ShapesD'EverandPractical Shop Math: Simple Solutions to Workshop Fractions, Formulas + Geometric ShapesÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Number Sense and DecimalsDocument20 pagesNumber Sense and Decimalsapi-238442866Pas encore d'évaluation
- HESI A2 Math Practice Tests: HESI A2 Nursing Entrance Exam Math Study GuideD'EverandHESI A2 Math Practice Tests: HESI A2 Nursing Entrance Exam Math Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- FractionsanchorchartDocument3 pagesFractionsanchorchartapi-262892674Pas encore d'évaluation
- Term Paper Module 1Document18 pagesTerm Paper Module 1fortxtonly80Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - Order of Operations, GCF & LCMDocument16 pages3 - Order of Operations, GCF & LCMJessa Mae BanquirigPas encore d'évaluation
- RD Sharma Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational NumbersDocument54 pagesRD Sharma Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational NumbersKavita Dhoot0% (1)
- Example 1: Find The Least Common Multiple of 3 and 5Document3 pagesExample 1: Find The Least Common Multiple of 3 and 5AAMCPas encore d'évaluation
- Least Common MultipleDocument13 pagesLeast Common MultipleAASFI Private SchoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan - Multiple and Factors - PPT - V 3Document35 pagesLesson Plan - Multiple and Factors - PPT - V 3kavitagrover5718Pas encore d'évaluation
- Number Property TheoryDocument6 pagesNumber Property TheoryprabindraPas encore d'évaluation
- GCF FoaDocument16 pagesGCF FoaPrecious Kim Pascua SamboPas encore d'évaluation
- Integers, Powers and RootsDocument28 pagesIntegers, Powers and RootsLehleh HiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil ServiceDocument12 pagesCivil ServiceRaquel disomimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Highway Math ManualDocument75 pagesBasic Highway Math ManualdpxPas encore d'évaluation
- The Decimal Method of Comparing FractionsDocument2 pagesThe Decimal Method of Comparing FractionsadleenshazPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 UNIT - I Number SystemDocument39 pages1 UNIT - I Number SystemAkash KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Math Questions That Appear inDocument2 pages10 Math Questions That Appear inKenneth Cantil LisboPas encore d'évaluation
- SurdsDocument27 pagesSurdsSha Mercs100% (1)
- 1.2 Powers and RootsDocument2 pages1.2 Powers and RootsjkgsfPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson17: Addition & Subtraction of FractionsDocument2 pagesLesson17: Addition & Subtraction of FractionsAagam JainPas encore d'évaluation
- SURDSDocument27 pagesSURDSPemungut Hasil100% (2)
- How To Get The Greatest Common Factor of Numbers (GCF)Document12 pagesHow To Get The Greatest Common Factor of Numbers (GCF)MijiPas encore d'évaluation
- CS Math ReviewerDocument84 pagesCS Math ReviewerJohn Rafael SordanPas encore d'évaluation
- LCM and LCDDocument12 pagesLCM and LCDHeather Bailey ParryPas encore d'évaluation
- (Aptitude) LCM, HCF, GCD - Basic Concept, Calculation, Applications Explained MrunalDocument14 pages(Aptitude) LCM, HCF, GCD - Basic Concept, Calculation, Applications Explained MrunalVenkata Ramesh SirigiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Fraction NotesDocument5 pagesFraction Notesapi-272836036Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Ed Math 2021Document13 pagesGen Ed Math 2021Jeric Sebastian GanaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen MathDocument4 pagesGen MathbonganaymaltePas encore d'évaluation
- 1.0 Whole Numbers-Math 100Document30 pages1.0 Whole Numbers-Math 100ShanayaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.0 WHOLE NUMBERS-Math 100Document30 pages1.0 WHOLE NUMBERS-Math 100ShanayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adding-Subtracting Fractions-Mixed Numbers PDFDocument7 pagesAdding-Subtracting Fractions-Mixed Numbers PDFJoseph BalasinghamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ema Emits College Philippines: Greatest Common Divisor and Euclid's AlgorithmDocument5 pagesEma Emits College Philippines: Greatest Common Divisor and Euclid's AlgorithmMaria Teresa OndoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fractions - Class VIDocument28 pagesFractions - Class VIAngelica Garcia100% (2)
- Math 5 Module and Worksheet 2Document9 pagesMath 5 Module and Worksheet 2Elah Grace ViajedorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Multiples FactorsDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Multiples Factorssandhya srinivasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra I PDFDocument240 pagesAlgebra I PDFGeofreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathreview PDFDocument29 pagesMathreview PDFTrang LêPas encore d'évaluation
- GRE Math ReviewDocument61 pagesGRE Math ReviewJosé María EgúsquizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Simplified Basic Algebra and Coordinate Geometry Algebra, Lines and Conic Section For High Schools and Colleges (Kingsley Augustine) (Z-Library)Document327 pagesSimplified Basic Algebra and Coordinate Geometry Algebra, Lines and Conic Section For High Schools and Colleges (Kingsley Augustine) (Z-Library)Kelvin IgbodikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gat A: Formula SheetDocument14 pagesGat A: Formula SheetHashim BugtiPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer CSCDocument22 pagesReviewer CSCChristopher CocalPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra Basics: For Friends .AdarshDocument11 pagesAlgebra Basics: For Friends .AdarshAdarsh RonPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.GCF and LCMDocument6 pages6.GCF and LCMMariane DominguianoPas encore d'évaluation
- FractionsDocument4 pagesFractionsJosé Antonio Luque LamaPas encore d'évaluation
- MODULE 1 - Business Math: Fundamental Operations On Fractions, Decimals, and PercentageDocument6 pagesMODULE 1 - Business Math: Fundamental Operations On Fractions, Decimals, and PercentageAaron Balsa100% (1)
- Fractions Study GuideDocument2 pagesFractions Study GuidePorsh RobrigadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Simplification Approximation PDFDocument176 pagesSimplification Approximation PDFsaketPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Summaryapi-194648813Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Math ReviewerDocument44 pagesBasic Math ReviewerJerald NgPas encore d'évaluation
- MR - 1 Working With NumbersDocument27 pagesMR - 1 Working With NumbersNicolas DiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Fraction Unit NotesDocument15 pagesFraction Unit Notesapi-210303377Pas encore d'évaluation
- Technology and Livelihood Education Smaw Nci: Quarter 1 Module Week 5-6Document8 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education Smaw Nci: Quarter 1 Module Week 5-6Ceasar Ryan AsuncionPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics - Ratio - Equivalent and ReducingDocument2 pagesMathematics - Ratio - Equivalent and ReducingPoopPas encore d'évaluation
- LCM, GCF, GCDDocument6 pagesLCM, GCF, GCDGemine Ailna Panganiban NuevoPas encore d'évaluation
- ML Aggarwal Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Rational and Irrational NumbersDocument1 pageML Aggarwal Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 - Rational and Irrational NumbersRaunak AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- RevisionDocument15 pagesRevisionMaria IezhitsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vedic MathsDocument46 pagesVedic MathsPranshu JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- General Education SummaryDocument24 pagesGeneral Education SummaryJenna Marie TolosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation manual-HM5001 TTRDocument15 pagesOperation manual-HM5001 TTRGio CJPas encore d'évaluation
- Modbus RegisterDocument7 pagesModbus RegisterZuniiga AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Code Reason Effect: Step 1. Step 1ADocument2 pagesCode Reason Effect: Step 1. Step 1AAhmedmahPas encore d'évaluation
- Website Layout Design in Corel DrawDocument111 pagesWebsite Layout Design in Corel DrawFathoni WangsadranaPas encore d'évaluation
- SanternoDocument468 pagesSanternoFrank DicksonPas encore d'évaluation
- CAPPC Presentation 12-5-05Document46 pagesCAPPC Presentation 12-5-05rahulPas encore d'évaluation
- PlaxisDocument6 pagesPlaxisRehan HakroPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT - 1 Formula and ProcedureDocument4 pagesUNIT - 1 Formula and ProcedurevinothPas encore d'évaluation
- SB Erv Arvu123zea2 03 20Document2 pagesSB Erv Arvu123zea2 03 20Mohammed Tausif AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Bsi Bs en 1366-8 Smoke Extraction DuctsDocument40 pagesBsi Bs en 1366-8 Smoke Extraction DuctsMUSTAFA OKSUZPas encore d'évaluation
- Proceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeDocument9 pagesProceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeTanzil ZaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Re - Rockspace.local - Ap - SetupDocument6 pagesRe - Rockspace.local - Ap - SetuptrujillobresslerPas encore d'évaluation
- SVBP 223 Structural Design of RailwayDocument30 pagesSVBP 223 Structural Design of RailwayRHOWELLE TIBAYPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance of ForecastingDocument37 pagesImportance of ForecastingFaizan TafzilPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution To Q9 (Vii) Tut-Sheet 3 (By Professor Santanu Dey)Document1 pageSolution To Q9 (Vii) Tut-Sheet 3 (By Professor Santanu Dey)Prayas JainPas encore d'évaluation
- The Logic of Faith Vol. 1Document39 pagesThe Logic of Faith Vol. 1Domenic Marbaniang100% (2)
- Mech CVTDocument15 pagesMech CVTsachin guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Pumps - Api-610: Single Stage Volute Casing PumpsDocument5 pagesProcess Pumps - Api-610: Single Stage Volute Casing Pumpsmehrzad1373Pas encore d'évaluation
- Powernel1500 TDS EN 02152006Document1 pagePowernel1500 TDS EN 02152006Magoge NgoashengPas encore d'évaluation
- Kyehyun Park - Drawing and Painting Beautiful Flowers - Discover Techniques For Creating Realistic Florals and Plants in Pencil and Watercolor-Quarry Books (2022)Document334 pagesKyehyun Park - Drawing and Painting Beautiful Flowers - Discover Techniques For Creating Realistic Florals and Plants in Pencil and Watercolor-Quarry Books (2022)Krutika Sapkal94% (18)
- ACI 305 Hot Weather Concrete PDFDocument9 pagesACI 305 Hot Weather Concrete PDFCristhian MartinezPas encore d'évaluation
- StatisticsDocument2 pagesStatisticsAnish JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Cert Piping W54.5Document2 pagesCert Piping W54.5SANU0% (1)
- Fiat Bravo Training ManualDocument111 pagesFiat Bravo Training ManualJa Ja75% (4)
- Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics ProjectDimpySurya44% (25)
- Taskkill To Unlock WindowsDocument3 pagesTaskkill To Unlock WindowswebbizPas encore d'évaluation
- ICT & ICT LabDocument22 pagesICT & ICT LabM Asif 72 2MPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3Document8 pagesLab 3Muhd Nur RidzwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural SteelDocument17 pagesStructural SteelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade Beam Design CalculationDocument3 pagesGrade Beam Design CalculationArnold VercelesPas encore d'évaluation