0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
91 vues9 pagesExemples de code Java pour exercices pratiques
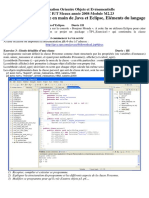
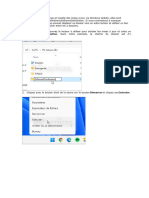
Le document décrit plusieurs exercices de programmation en Java avec des classes et méthodes. Les exercices couvrent des sujets comme la chaîne de caractères, les tableaux, les dates et les magasins.
Transféré par
bannouromar54Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Nous prenons très au sérieux les droits relatifs au contenu. Si vous pensez qu’il s’agit de votre contenu, signalez une atteinte au droit d’auteur ici.
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez aux formats DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
91 vues9 pagesExemples de code Java pour exercices pratiques
Le document décrit plusieurs exercices de programmation en Java avec des classes et méthodes. Les exercices couvrent des sujets comme la chaîne de caractères, les tableaux, les dates et les magasins.
Transféré par
bannouromar54Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Nous prenons très au sérieux les droits relatifs au contenu. Si vous pensez qu’il s’agit de votre contenu, signalez une atteinte au droit d’auteur ici.
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez aux formats DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd