Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
98-Civ-A4 - Version Anglaise - Mai 2011
Transféré par
chivo760 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
7 vues3 pagesEXAMEN OIQ
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentEXAMEN OIQ
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
7 vues3 pages98-Civ-A4 - Version Anglaise - Mai 2011
Transféré par
chivo76EXAMEN OIQ
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 3
ORDRE DES INGENIEURS DU QUEBEC
MAY 2011 SESSION
Open-book examination
Calculators : only authorized models
Duration: 3 hours
It is mandatory to return the questionnaire with answers.
98-CIV-A4 GEOTECHNICAL MATERIALS AND ANALYSIS.
Problem 1. (15 pts)
An undisturbed sample of moist sand was obtained fiom the base of an excavation, In the
undisturbed state, the sample had a mass of 884g and a volume of 478 cm’. After oven-drying,
the mass of the sample was found to be 829g. Given that the gravity of the sand particles was
2.67, calculate:
a) The dry density and void ratio. (5 pts)
b) Water content and the degree of saturation of the moist sand in its in situ conditions. (5
pts)
©) The relative density of the sand deposit, knowing that the maximum and minimam void
ratios for the sand are €ymx=0.98 and eyxi=0.34 (Spi).
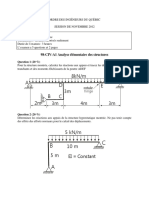
Problem 2 (20 pts)
A rigid square footing 2m x2 m is to be constructed at a depth of 2 m in a clayey sand deposit of
total thickness 6 m. The average force due to the dead load of the structure and the footing is
1000 KN. The water table is at a depth of 3m. Calculate the total and effective vertical stresses at
depths of 2.5, 3.5, 4.5 and 5.5 m for the conditions (y=18 KN/m*)
a) Before construction, (10 pts)
b) A long time after construction. (10 pts)
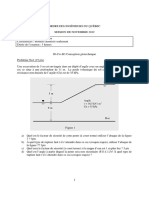
Problem 3 (15 pts)
‘The assembly of figure 1 is used to evaluate the permeability of coarse sand, The volume of flow
is 0,05 m? over a period of 20 minutes.
a) Knowing that the cross-section of the sample is 1 m’, evaluate the coefficient of
permeability (k). (5 pts)
») Evaluate the risk of drive of the particles at the exit of the flow by calculating the safety
factor (y=18 kN/m?). (5 pts)
Figure 1 Problem 2
©) How much would be necessary to decrease the water level to avoid any risk of drive of the
Particles (safety factor of 3)? (5 pts)
Problem 4. (25 pts)
A sample of saturated clay, taken from a depth of 5 m, was tested in a conventional ocdometer.
The table 1 gives the vertical stress and the corresponding thickness recorded during the test
‘The water content at the end of the test was 40% and the initial height was 20 mm (G,=2.7).
a) Plot a graph of void ratio versus 0”, (log scale) using figure 2. (5 pts)
b) Determine C, and C,.(5 pts)
©) Determine my between o°/=400 kPa and o”,=500 kPa. (5 pts).
4) Determine o°p, using Casagrande’s method. (5 pts).
©) Determine the over consolidation ratio (OCR) by considering a water table at the surface
and y=17 kg/m’. (5 pts)
Table 1. Ocdometric test measurement
oy (kPa) 109 2004008001600 800—«400~—«100
h (mm) 19.2190 17,0148 12,6 si T—=ida3 159
08
0.78
07
2065
06
0.55
os
1 10 100 1000
(kPa)
Figue2 Problem 4
Problem 5 (25 pts)
Three samples of loose sand were tested under consolidated undrained conditions (CU). The
failure stresses and excess porewater pressures for each sample are given below
Sample No (Gs); (kPa) (c1-03)¢ Au;(kPa)
1 210 123 2
2 360 252 162
3 685 448 323
a) Plot Mobr’s citcle of effective stress from these data. (5 pts)
b) Determine the friction angle for each test. (5 pts)
©) Determine the orientations of (1) the failure plane and (2) the plane of maximum shear
stress to the horizontal for Test 2. (5 pts)
4) Determine the failure stresses for Test 1. (Spts)
©) Is the failure shear stress the maximum shear stress? Give reasons.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 14-EC-3 - Version Française - Novembre 2014Document2 pages14-EC-3 - Version Française - Novembre 2014chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-B3 - Version Française - Novembre 2012Document6 pages98-Civ-B3 - Version Française - Novembre 2012chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-A3 - Version Française - Mai 2013Document3 pages98-Civ-A3 - Version Française - Mai 2013chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-B3 - Version Française - Mai 2013 PDFDocument3 pages98-Civ-B3 - Version Française - Mai 2013 PDFchivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14-CI-A3 - Mai 2015 - Version FrançaiseDocument3 pages14-CI-A3 - Mai 2015 - Version Françaisechivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-A1 - Version Française - Novembre 2012Document2 pages98-Civ-A1 - Version Française - Novembre 2012chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-B7 - Version Française - Mai 2013Document1 page98-Civ-B7 - Version Française - Mai 2013chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-B7 - Version Française - Novembre 2012Document1 page98-Civ-B7 - Version Française - Novembre 2012chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-A3 - Version Française - Mai 2013Document3 pages98-Civ-A3 - Version Française - Mai 2013chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-A2 - Version Française - Mai 2012Document4 pages98-Civ-A2 - Version Française - Mai 2012chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-B7 - Version Française - Mai 2013Document1 page98-Civ-B7 - Version Française - Mai 2013chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-B7 - Version Française - Novembre 2012Document1 page98-Civ-B7 - Version Française - Novembre 2012chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-B3 - Version Anglaise - Mai 2011Document4 pages98-Civ-B3 - Version Anglaise - Mai 2011chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14-CI-A7 - Version Française - Novembre 2014Document6 pages14-CI-A7 - Version Française - Novembre 2014chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-A2 - Version Française - Mai 2012Document4 pages98-Civ-A2 - Version Française - Mai 2012chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-A3 - Version Française - Mai 2012Document4 pages98-Civ-A3 - Version Française - Mai 2012chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-A4 - Version Française - Novembre 2012Document6 pages98-Civ-A4 - Version Française - Novembre 2012chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14-CI-B2 - Version Française - Novembre 2014Document5 pages14-CI-B2 - Version Française - Novembre 2014chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 98-Civ-B3 - Version Française - Mai 2013Document3 pages98-Civ-B3 - Version Française - Mai 2013chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14-CI-A4 - Version Française - Novembre 2014Document6 pages14-CI-A4 - Version Française - Novembre 2014chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation
- 14-CI-B3 - Version Française - Novembre 2014Document6 pages14-CI-B3 - Version Française - Novembre 2014chivo76Pas encore d'évaluation