Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Correction - Devoir - Les Amplificateurs PDF
Correction - Devoir - Les Amplificateurs PDF
Transféré par
Tarik Mlilas0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
11 vues72 pagesTitre original
Correction_devoir_les amplificateurs.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
11 vues72 pagesCorrection - Devoir - Les Amplificateurs PDF
Correction - Devoir - Les Amplificateurs PDF
Transféré par
Tarik MlilasDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 72
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions Page 5-1
CHAPTER 5
Problem 5.1-01
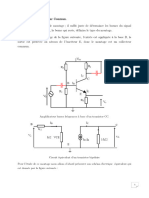
Assume that M2 in Fig. 5.1-2 is replaced by a 10kQ resistor. Use the graphical technique
illustrated in this figure to obtain a voltage transfer function of M1 with a 10k load
resistor. What is the maximum and minimum output voltages if the input is taken from
OV to SV?
[OMEWORK SOLUTIONS
Solution
A computer generated plot of this problem is shown below,
5
Vous (V)
0 1 2 3 4 5
Vin(V) Fig. $5.1-01
‘The maximum output is obviously equal to SV. The minimum output requires the
following calculation assuming that M1 is in the active region.
5-Yout
6. 2
110x10°2[(5-0.T pug ~ 0.5% pu] = ToC
S-¥out
43 Vout- Vou = 322 > Voui= — 9.5 Voyr + 4-504 =
This gives,
Vous (Min) = 4.254.2945 = 0.5V
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions Page 5-2
Problem 5.1-02
Using the large-signal model parameters of Table 3.1-2, use sv
Eqs. (1) and (5) to calculate the values of voyrp(max) and fw tum
Vourmin). Compare with the results shown on Fig. 5.1-2 on LF
the voltage transfer function curve. (oe
Solution
From Eq, (5.1-1), Foy (max) can be calculated as vour
FS wi _2um
vy | Ly 7 1um
43V -
Viug(max) = Voy
Fig. $5.1-02
From Eq, (5.1-5), Vous (min) can be calculated as,
Vu (it) = Vpp ~Pr ~L0D="2)
fi Be
a
(5-0.7)
Va (tnin)) = § — 0.7 -—
oo 7, So)
\*G10)6)
Problem 5.1-03,
‘What value of f,/B, will give a voltage swing of 70% of Vp sv
if Vp is 20% of Vy? What is the small-signal voltage gain
corresponding to this value of f,/B,?
Solution
Given Vr =0.2V pp and Coys (max) —Voys (min))= 0.7¥ pp ML
From Eq. (5.1-1) and (5.1-5)
Cop-"r)
Vout (19x) — Voyp (min) =
or, 0.7 pp =¥20-92¥ pp) _, (+
hho Be
\ &
‘The small-signal voltage gain can be given by
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions
Problem 5.1-04
What value of V,, will give a current in the active load
inverter of LOMA if Wy/Ly = Sum/1pm and W,/L, =
2pm/1ym? For this value of V;,, what is the small-signal
voltage gain and output resistance?
Solution
‘Assuming Mj is operated in saturation
rele)
Vv, -0.7)" |
2
or, 100= won 3 Vj, = 1303V
8m __ | (Ku)
The small-signal gain can be given by A, =—
Ba \ (Kp)
‘The output resistance can be given by
Problem 5.1-05
Repeat Ex. 5.1-1 if the drain current in M1 and M2 is SOA.
Solution
From Eqs. (5.1-1) and (5.
vour(max) = 4.3V.
) we get
=5-07-——2
Your(min) = 5- 0.7 - Fo T7102)
From Eq, (5.1-7) we get,
Your mi 148.3,
y,
From Eq. (5.1-8) we get,
1 10°
R ZOFTS + TOT = 13.296 KD
‘out = Bast Bds2* md
The zero is at,
Smi_ _ 148.3pS
1=Cyai = Osi = 2. 966x101! rads/sec —> 47.2 GHz
The pole is at,
1 1
Page 5-3
vour
(L
( (rr),
in = Bdst*8as2*Bm2 = 20% 2.54 70.71 ==LSI2VIV
Wi _5um
Ly 71pm
Fig. $5.1-04
PL = O38 = Rk Chdl+Cpag*Cga*C) ~ (13.296KQ)(1.0225pF)
73,555x108 rads/sec, > 11.71 MHz
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions Page 5-4
Problem 5.1-06
Assume that W/L ratios of Fig. P5.1-6 are W/L, = Vpp
2pumn/1 pm and W o/Ly = Wy/Ly = Wall,
Ijmn/pm. Find the de value of V , that will give a
dc current in M1 of 110A. Calculate the small
signal voltage gain and output resistance of Fig.
P5.1-6 using the parameters of Table 3.1-2.
Solution 1002
Assuming all transistors are in saturation and ideal
current mirroring
© \ : ¥,) }
or, = M0" = twos
The small-signal voltage gain can be given by
elle)
where, [ps =Ip,=100 WA, and 1,, =10 MA.
A
‘The output resistance can be given by
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions Page 5-5
Problem 5.1-07
Find the small-signal voltage gain and the -34B frequency in Hertz for the active-load
inverter, the current source inverter and the push-pull inverter if W, = 2um, Ly
W, = lum, Ly = 1m and the de current is SOWA. Assume that yy, = 4fF, Cy.
Cyaz = AIP, Cyqy = 108F and C,
Yop
PMOS Load Source Load
Inverter Inverter i Inverter
Figure 5.1-1 Various types of inverting CMOS amplifiers.
Solution
1. Active load inverter
The output resistance can be given by
1 1
tet giana
Bmx 2650H))(50 pn)
‘The total output capacitance can be given by
Cou = Cy, + Cys + Cogn + Oya: + Cyas = 1029 DE
The -3 dB frequency can be given by
Sosa =
<= 10.9 MHz
2aR,,.C,
2. Current-source inverter
‘The output resistance can be given by
1 1
Ray =——— = = 222.22 kQ
Bint Baa Ip (Ay + Ay)
The total output capacitance can be given by
HCL + Cy, t Cyn + Oya + Cyn= L028 DE
4B frequency can be given by
Sosa == = 9.697 MH,
2aR,,,C,
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions Page 5-6
Problem 5.1-07 - Continued
3. Push-pull inverter
‘The output resistance can be given by
1 1
Bint Ban Ip (Ay + Ay) mn22kO
‘The total output capacitance can be given by
20, + Cyan + Cusn + Cyan + C= LODB DE
‘The -3 dB frequency can be given by
—1 _
2AR...C,
fsa =
Problem 5.1-08
‘What is the small-signal voltage gain of a current-sink
inverter with W, = 2m, Ly = lum, W) =o = 1 uum at Ip
=0.1, 5 and 100 1A? Assume that the parameters of the
devices are given by Table 3.1-2.
1. Ip =0.1 pa
fn 01H) _ sag us
Bm =
“nV, (2.5)(26m)~
Sri Sm
Oaths) Toy te
3. Ip =100 wa
Bei 28 (tn 14142 ws
A,=-7—Se_ = -__8mt__ asi viv
To(dy +p)
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions
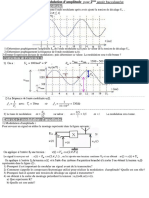
Problem 5.1-09
ACMOS amplifier is shown. Assume M1 and M2 operate in
the saturation region. a.) What value of Vgc gives 100A,
through M1 and M2? b.) What is the DC value of vyy? ¢.)
‘What is the small signal voltage gain, Vow/Vin, for this,
amplifier? d.) What is the -34B frequency in Hz of this
amplifier if Cga = Cga = SOP, Che = Coa = 30fF, and Cy, =
500mF?
Solution
a) Veg =Vr2 + Vicar
21,
=V,,+ |e 205
») Vi, =Voo
y,
°) A=
® fuaé (8a: * 812) 51 Mi
I (Cur* Cyt Cu* Our *E,
Page 5-7
Figure P5.1-9
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions Page 5-8
Problem 5.1-10
A current-source load amplifier is shown. (a.) If Cppy +Vop
=Capp = 1001, Copy =Copp = SOI, Cgsy = Cosp =
100ff, and C= IpF, find the -34B frequency in Hertz, M3-|-——[-M2
(b.) If Boltzmann’s constant is 138x103 Joules/°K, find
the equivalent input thermal noise voltage ofthis amplifier“) 004A, [em T*
at room temperature (ignore bulk effects, 7) = 0). + =
AILWIL'
Solutions Yin aia 10 $
(a) The -3dB frequency is equivalent to the magnitude of —
the output pole which is given as =
Fig. P5.1-10
1
7 = 5198 = 1IKA
“edt *Char*Cyaa'*CoaatCy, = 0.05 + 0.05 +0.1 + 0.1 +1 pF = 1.3pF
.923x10° radsisec. > | Fagp = 1-102 MHz
(b.) The noise voltage at the output can be written as,
—,(_ Smt —,(_ 8m»
= Fm" \Basi*8aca) * €n2 (Bacr*8ac2)
Reflecting this noise voltage back to the input gives the equivalent input noise as,
8kT.
(S02 (én (Sm 38m af Sn
emt * Bm BEY * Bm
Bm
CMOS Analog Circuit Design (2° Ed.) - Homework Solutions Page 5-9
Problem 5.1-11
Six inverters are shown. Assume that Ky’ = 2Kp' and that y= Ap, and that the de bias
current through each inverter is equal. Qualitatively select, without using extensive
calculations, which inverter(s) has/have (a.) the largest ac small signal voltage gain, (b.)
the lowest ac small signal voltage gain, (c.) the highest ac output resistance, and (d.) the
lowest ac output resistance. Assume all devices are in saturation.
Yop
Circuit 1 Circuit 2 Circuit3 Circuit 4 Circuit $
Figure P5.1-11
Solution
Circuit 1 | Circuit2 [| Cireuit3 [ Circuit4 [Circuit 5 [ Circuit 6
8m [Bmn=N2 &mp]_— SmP_—_|Bmn=V2 8m] SmP_—_Bav=V2 Bmp] Sm
1 1 1 1
1 1
Rou |"Sm+8mbn |" SmP+8mbP | ~ BP ~8mN | Sent Bas | Baan Baar
0.707 0.707 = =
F SmP* SmbP “emp |—1 _J__1 _
sace1+V2) |gage1+V2)
V2 8mp 8mP
in|] _SmP mb vb
sacp(1+V3) |Sace(1+V2)
B8mP+8mbP | &mP*SmbP
(a) Circuit 5 has the highest gain.
(b.) Circuit 4 has the lowest gain (assuming normal values of §_/8mb)
(©) Circuits 5 and 6 have the highest output resistance.
(Gd) Circuit 1 has the lowest output resistance.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 4pages-Tersystem BticinoDocument4 pages4pages-Tersystem BticinoHassan CHAFYQPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPITRE 2 Circuit Integret HajarDocument11 pagesCHAPITRE 2 Circuit Integret Hajarel bekkary HajarPas encore d'évaluation
- Moteur À Courant Continu À Excitation Séparée Alimenté Par Un Hacheur SérieDocument1 pageMoteur À Courant Continu À Excitation Séparée Alimenté Par Un Hacheur Sériebrinley boonePas encore d'évaluation
- Suites Transistor Bipolaire en Regime DynamiqueDocument10 pagesSuites Transistor Bipolaire en Regime DynamiqueHamza El HadaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Iec 60107-8-1997Document114 pagesIec 60107-8-1997Mohamed Fahhad CoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exposé Sur L'exploitation D'une Chaîne de Production Automatisée Sana OuferkachDocument19 pagesExposé Sur L'exploitation D'une Chaîne de Production Automatisée Sana Ouferkachsana ouferkachPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapporte de Stage Tunisie Telecom AyariDocument41 pagesRapporte de Stage Tunisie Telecom AyariSouha RiguenPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation D'un Convertisseur Matriciel de Type Direct Avec Les Deux Stratégies de Modulation de VenturiniDocument5 pagesSimulation D'un Convertisseur Matriciel de Type Direct Avec Les Deux Stratégies de Modulation de Venturinitayeb dePas encore d'évaluation
- 113-22 Rapport 11Document12 pages113-22 Rapport 11Houdhayfa Ben KhlilPas encore d'évaluation
- Tp1 Presentation Materiel Utilise TP Traitement Signal PDFDocument13 pagesTp1 Presentation Materiel Utilise TP Traitement Signal PDFFatma BelabedPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap1-Sys Monophasé Et TriphaséDocument18 pagesChap1-Sys Monophasé Et TriphasémahdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercices Corrigées Modulation D'amplitude Sujets Bac SC Mathématique PDFDocument14 pagesExercices Corrigées Modulation D'amplitude Sujets Bac SC Mathématique PDFZolly X666Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exercice 1Document5 pagesExercice 1atika smarraiPas encore d'évaluation
- PIC16F877 Onduleur MultiniveauxDocument71 pagesPIC16F877 Onduleur MultiniveauxabfstbmsodPas encore d'évaluation
- Analogique ExoDocument5 pagesAnalogique ExosaaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronique Analogique 1Document138 pagesElectronique Analogique 1Yynn FerdinandPas encore d'évaluation
- FP - INGELEC - LUMINAIRES - LED - Panels Slim Backlit Optima - VA - 0Document3 pagesFP - INGELEC - LUMINAIRES - LED - Panels Slim Backlit Optima - VA - 0Clovis BounouPas encore d'évaluation
- Brodeuse Brother 700e IIDocument6 pagesBrodeuse Brother 700e IIPhilippe CANPas encore d'évaluation
- Youssef RiahiDocument1 pageYoussef RiahiYoussef RiahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Corrigés Travaux Dirigés D'automates Programmables Industrels LPU GEII 2021-2022Document25 pagesCorrigés Travaux Dirigés D'automates Programmables Industrels LPU GEII 2021-2022mohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ms Eln Mezouagh+BoulenouarDocument74 pagesMs Eln Mezouagh+BoulenouarDONIA JBELIPas encore d'évaluation
- Boudjella CIE2009 OranDocument8 pagesBoudjella CIE2009 OranOussama Mohammad MessadiPas encore d'évaluation
- DOSSIER TECHNIQUE. Souris Informatique. Souris Informatique Dossier Technique 1 - 6Document6 pagesDOSSIER TECHNIQUE. Souris Informatique. Souris Informatique Dossier Technique 1 - 6Fongho Eric SinclairPas encore d'évaluation
- Amplificateur de PuissanceDocument5 pagesAmplificateur de PuissancenounouNu50% (2)
- Protection Contre La FoudreDocument4 pagesProtection Contre La FoudrebuiidkgtPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours PPT - MX Pour Le Solaire - PV2 - 2020Document100 pagesCours PPT - MX Pour Le Solaire - PV2 - 2020Jalal TiYalPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod 2 3 OnduleursDocument17 pagesMod 2 3 OnduleursNader AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Complément Du TP5 - Réalisation Des Exercices Du TP5Document5 pagesComplément Du TP5 - Réalisation Des Exercices Du TP5Hamoudi BatnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sujet Option B 2007Document73 pagesSujet Option B 2007Riham abPas encore d'évaluation
- M-ELE.SY.TE 4 فيها تصويرة البولاريزاسيو PDFDocument96 pagesM-ELE.SY.TE 4 فيها تصويرة البولاريزاسيو PDFissam HadjhamdiPas encore d'évaluation