Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Exercices Corrigés Logique Combinatoire Bac Technique en Tunisie
Transféré par
Hayder KassebiCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Exercices Corrigés Logique Combinatoire Bac Technique en Tunisie
Transféré par
Hayder KassebiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Laboratoire génie électrique 4Stech Correction de la série N°1 Logique combinatoire Page 1/8
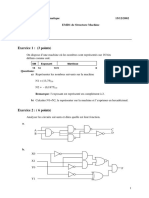
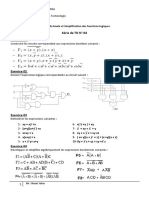
Exercice N°1 :
R2
10k
1°) S = a b ; R = a.b aA1 U1:A SA
1 R3
3
2
b
B1 74HC386
220
2°) C’est un demi additionneur (Half adder) a R1
10k
U2:A RB
1 R4
Exercice N°2 : 2
3
220
7408
1°/
½ Add
a
b
½ Add
rin S
Rout
2-1°/ Schéma d’un additionneur complet ( Full adder)
Report 1 1
1 1 1 0
+ 1 0 1 1
Résultat 1 1 0 0 1
2-2°/
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0
1 1 1 0
+ + + +
Exercice N°3 : 1 0 0 1
A= (1001)2 ; B= ( 0101)2 ;
S= (1110)2
Prof : Borchani hichem et Hammami mourad www.seriestech.com
Laboratoire génie électrique 4Stech Correction de la série N°1 Logique combinatoire Page 2/8
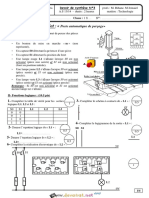
Exercice N°4 :
A = 11001(2) et B = 11110(2)
1°)
1 1 1 1 0
+
1 1 0 0 1
=1 1 0 1 1 1
2°)
0V
5V 0V +
+5V U1 S1
5 10
A1 S1
9
8 6
V 3
A2 S2
2
A3 S3
1 15 S2
A4 S4
11
B1
7
B2
4
B3
16 S3
B4
13 14
C0 C4
7483
S4
U1
10 9
A1 S1
8 6
A2 S2 S5
3 2
A3 S3
1 15
A4 S4
11
B1
7 S6
B2
4
B3
16
B4
13 14
C0 C4
7483
Exercice N°5- Etude d’un additionneur BCD :
Soit X une sortie logique qui occupera le niveau haut seulement quand la somme est supérieure à 1001
1°) Equation de X. B3 B2 B1 B0
Représentation codée BCD
X = S4 + S3.(S2+S1) C0 : report fourni par l’additionneur
C4 Additionneur du rang inférieur
S4 S3 S2 S1 S0 parallèle de 4 bits
10 0 1 0 1 0 (ex : CI 7483)
11 0 1 0 1 1 S4 S3 S2 S1 S0 A3 A2 A1 A0 Représentation codée BCD
12 0 1 1 0 0
13 0 1 1 0 1
14 0 1 1 1 0
15 0 1 1 1 1
16 1 0 0 0 0
17 1 0 0 0 1
18 1 0 0 1 0
2°) Schéma du montage
Additionneur Additionneur
de la
Report appliqué parallèle de 4 bits correction
à l’additionneur (ex : CI 7483)
BCD suivant X Σ3 Σ2 Σ1 Σ0
Somme BCD
Prof : Borchani hichem et Hammami mourad www.seriestech.com
Laboratoire génie électrique 4Stech Correction de la série N°1 Logique combinatoire Page 3/8
Exercice N°6 :
A= (1001)BCD ; B= ( 0101)BCD ;
S= ( 0001 0100)BCD
Exercice N°7 : Addition BCD de trois digits
A = 286 et B = 973
U1
3 U2 U3
1
15 13 15 13 15 13
0 A1 S1 0 0 A1 S1 1 0 A1 S1 1
1 12 1 12 1 12
1 A2 S2 1 0 A2 S2 0 1 A2 S2 0
3 11 3 11 3 11
0 A3 S3 0 0 A3 S3 1 1 A3 S3 0
5 10 5 10 5 10
0 A4 S4 0 1 A4 S4 0 0 A4 S4 1
14
1 14 14
B1 1 B1 1 B1
2 2 2
0 B2 1 B2 1 B2
0
4 4 4
B3 1 B3 0 B3
1
6 6 6
B4 0 B4 0 B4
71 19 70 19 7 9
CI CO CI CO CI CO 0
4560 4560 4560
Exercice N°8 :
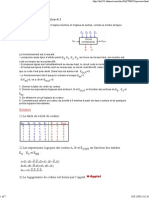
1- Table de vérité 2- Equations logiques de S1, S2 et S3
b1 b0 a1 a0 S1 S2 S3
b1b0 00 01
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 a 1a 0 11 10
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 00 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 1 0 01 0 1 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 1 0 11 0 0 1 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 1 10 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 1 1 0 0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 S1 = a1.a0 .b1 .b0 + a1.a0 .b1.b0 + a1.a0 .b1.b0 + a1.a0 .b1.b0
0 1 1 1 0 1 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 0 1 0 0 b1b0 b1b 0
00 01 11 10 00 01 11 10
1 0 1 1 0 1 0 a 1a 0 a 1a 0
1 1 0 0 0 0 1 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 1 1 1
1 1 0 1 0 0 1 01 1 0 0 0 01 0 0 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 0 1 11 1 1 0 1 11 0 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 10 1 1 0 0 10 0 0 1 0
S2= a1.b1 + a0 .b1.b0 + a1.a0 .b0 S3= a1.b1 + a1.a0 .b0 + a0 .b1.b0
Prof : Borchani hichem et Hammami mourad www.seriestech.com
Laboratoire génie électrique 4Stech Correction de la série N°1 Logique combinatoire Page 4/8
3°) +5V
U1
10
a0 12
A0
A1
13
a1 15
A2
A3
9
b0 11
B0
S1 S2 S3
B1
b1 14
B2
1
B3
2 7
A<B QA<B
3 6
A=B QA=B
4 5
A>B QA>B
7485
0V
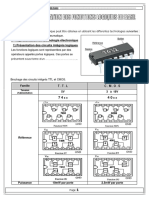
Exercice N°9 :
Entrées sorties
A B cascadables
A<B A=B A>B A<B A=B A>B
1100 0111 0 1 0 0 0 1
1100 1111 0 0 0 1 0 0
1100 1100 0 1 0 0 1 0
1100 1100 0 0 0 1 0 1
1100 0100 1 0 0 0 0 1
1101 1101 1 0 0 1 0 0
Exercice N°10 :
1°)
a) F= (A0 B0). (A1 B1). (A2 B2). (A3 B3)
b) F= 1 lorsque A=B
2°) La référence du circuit est le 7485
A0
0
B0
0
A1
0
B1
0
A2 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 F
0
B2
7485
0
A3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
B3
0
+5V
0V
Prof : Borchani hichem et Hammami mourad www.seriestech.com
Laboratoire génie électrique 4Stech Correction de la série N°1 Logique combinatoire Page 5/8
Exercice N°11 :
fs = fs2+fe2.fs1 ; fi = fi2+fe2.fi1 ; fe = fe2.fe1
fi2
A2 fs
Comparateur fe2
B2 1bit fs 2
fe
fi1
A1
Comparateur fe1 fi
B1 1bit fs 1
Exercice N°12 :
a3 a2 a1 a0
0V +5V 0V +5V
14
11
15
13
12
10
14
11
15
13
12
10
4
3
2
1
4
3
2
1
9
7485
U1
7485
U1
A>B
A=B
A<B
B3
B2
B1
B0
A3
A2
A1
A0
A>B
A=B
A<B
B3
B2
B1
B0
A3
A2
A1
A0
QA>B
QA=B
QA<B
QA>B
QA=B
QA<B
5
6
7
5
6
7
Prof : Borchani hichem et Hammami mourad www.seriestech.com
Laboratoire génie électrique 4Stech Correction de la série N°1 Logique combinatoire Page 6/8
Exercice N°13 : S0 Z0
1°) Tables de vérités relatives au circuit suivant : 0 I0
1 I1
I3 I1 MUX Z1
I2 I0 S S1 S0 Z0 Z1 Z
I1 MUX Z 0 0 I0 I2 I0
I0 S 0 1 I1 I3 I1
I1 I1 MUX Z0 1 0 I0 I2 I2
I0 I0 S 1 1 I1 I3 I3
S0 S1
2°) la fonction réalisée par ce circuit : un multiplexeur 4 vers1.
Exercice N°14 :
74153
Chronogrammes de A, B et S.
A
0
CLK CLK Compteur 0
B 1 G 3
modulo 4
t
1G EN MUX
A 1C0
0
1C1
t 1C2
1
2
1Y
S
B 1C3 3
2G
t 2C0
+Vcc 2Y
2C1
S 2C2
t 2C3
Exercice N°15 :
On désire réaliser une fonction logique S à trois variables en utilisant
un multiplexeur 8 vers 1 « 74151 »
Table de vérité et équation logique de la sortie S :
c b a S
0 0 0 0
ba 0 0 1 1
c 00 01 11 10 0 1 0 1
0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1
1 0 1 1
S c.a c. b b.a 1 1 0 1
1 1 1 0
Exercice N°16 :
Fonction NAND à deux entrées à l’aide d’un multiplexeur 4 vers 1
de référence 74153
b a S
0 0 1
0 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 0
Prof : Borchani hichem et Hammami mourad www.seriestech.com
Laboratoire génie électrique 4Stech Correction de la série N°1 Logique combinatoire Page 7/8
Exercice N°17 : G2A
t
A
t
B
t
C
t
74138 Y0
t
DMUX
A (1)
0 0
(15) Y0 Y1
B (2) G 0 1
(14) Y1 t
7
C
(3) 2 2
(13) Y2 Y2
+Vcc 3
(12) Y3 t
4
(11) Y4 Y3
G1 (6)
5
(10) Y5 t
(4)
G2A
(5)
6 (9) Y6 Y4
G2B 7
(7) Y7 t
Y5
t
Y6
t
Y7
t
Exercice N°18 :
1°)
Entrées
Sortie active
A3 A2 A1 A0
0 0 0 0 Y0
2°) Fonction réalisée : Démultiplexeur 1 vers 16. 0 0 0 1 Y1
0 0 1 0 Y2
0 0 1 1 Y3
0 1 0 0 Y4
0 1 0 1 Y5
0 1 1 0 Y6
0 1 1 1 Y7
1 0 0 0 Y8
1 0 0 1 Y9
1 0 1 0 Y10
1 0 1 1 Y11
1 1 0 0 Y12
1 1 0 1 Y13
1 1 1 0 Y14
1 1 1 1 Y15
Prof : Borchani hichem et Hammami mourad www.seriestech.com
Laboratoire génie électrique 4Stech Correction de la série N°1 Logique combinatoire Page 8/8
Exercice N°19 :
1-
Entrée de
A B F
sélection M Cn Opération réalisée
A3A2A1A0 B3B2B1B0 F3F2F1F0
S3S2 S1 S0
1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 F = A + A et B 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 1 1 X 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 F = non (A ou B) 0 0 1 0
0 1 0 1 1 X 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 F = non B 1 0 0 1
0 1 1 0 1 X 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 F = A xor B 1 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 F = (A ou B) + A 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 F = (A et (non B)) - 1 0 0 1 1
0 1 0 0 1 X 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 F = non (A et B) 1 1 1 0
1 0 1 1 1 X 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 F = A et B 1 0 0 0
1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 F=A 1 1 0 0
2 – Si (S3 S2 S1 S0) = (1 0 0 1) ; et M=1 écrire l’équation de F0 en fonction de A0 et B0 avec des
opérateurs NAND à deux entrées.
F0 A0 B0 = A0 B0 A0 B0
F0 = (A0 / B0) / (A0 / A0) / (B0 / B0)
Prof : Borchani hichem et Hammami mourad www.seriestech.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Logique CombinatoireDocument9 pagesLogique CombinatoireRouaissi Ridha100% (1)
- Exercices Logique Combinatoire Du Bac Technique en TunisieDocument9 pagesExercices Logique Combinatoire Du Bac Technique en TunisieOussama MezriguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Addit 1174 PDFDocument11 pagesAddit 1174 PDFSimoBal-ghaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- TD2 Combinatoire PT 2019-2020Document7 pagesTD2 Combinatoire PT 2019-2020Maha Bouattour100% (1)
- SERIE - 2 - TDs - Logique CombinatoireDocument5 pagesSERIE - 2 - TDs - Logique CombinatoireAnge nolwenPas encore d'évaluation
- Série Corrigée de Révision N°1 - Technologie - 1ère AS (2011-2012) MR Amjed SaddemDocument4 pagesSérie Corrigée de Révision N°1 - Technologie - 1ère AS (2011-2012) MR Amjed SaddemSABRINE KHPas encore d'évaluation
- Logique Combinatoire Et MultiplexageDocument15 pagesLogique Combinatoire Et MultiplexagePhenix PhenixPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercices Avec Corrigés (CA1, CA2, SVA, IEEE 754)Document8 pagesExercices Avec Corrigés (CA1, CA2, SVA, IEEE 754)You CefPas encore d'évaluation
- Upload - Série D'exercices N°2-3tech-Systèmes Combinatoires-2013-2014 PDFDocument6 pagesUpload - Série D'exercices N°2-3tech-Systèmes Combinatoires-2013-2014 PDFyassine zitouniPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebre de Boole Exercice CorrigéDocument4 pagesAlgebre de Boole Exercice CorrigéZAKARIA100% (1)
- Cours Electronique Numerique-3Document141 pagesCours Electronique Numerique-3ibouPas encore d'évaluation
- TD3 2011 CorrigeDocument8 pagesTD3 2011 CorrigeBa Chir100% (3)
- TD Systèmes Logiques-ConvertiDocument69 pagesTD Systèmes Logiques-ConvertijemaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Logique Combinatoire-P1Document13 pagesLogique Combinatoire-P1Mohamed LaliouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Examen Sys Logique Iit 2016 - Principal - CorrigéDocument6 pagesExamen Sys Logique Iit 2016 - Principal - CorrigéabderrahmenPas encore d'évaluation
- Logique SéquentielleDocument6 pagesLogique SéquentielleAhmed HabboutiPas encore d'évaluation
- Algébre de Boole Exrecice CorrigéDocument10 pagesAlgébre de Boole Exrecice CorrigéAhmat Sale100% (1)
- Devoir de Synthèse N°3 - Technologie Fonctions Logiques de Base+ Liaisons Mecaniques Poste Automatique de Perçage - 1ère AS (2013-2014) MR Zouhaier Rihane PDFDocument4 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°3 - Technologie Fonctions Logiques de Base+ Liaisons Mecaniques Poste Automatique de Perçage - 1ère AS (2013-2014) MR Zouhaier Rihane PDFKamel Tayahi100% (1)
- TD4 SLDocument5 pagesTD4 SLRomualde Nunue100% (1)
- TD Numeration LogiqueDocument4 pagesTD Numeration LogiqueAdhem NaijiPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation Des Fonctions Logiques de BaseDocument2 pagesSimulation Des Fonctions Logiques de Basemekki100% (1)
- Systeme de NumérationDocument79 pagesSysteme de NumérationGuerbai100% (5)
- Corre Ction TD1 SuiteDocument5 pagesCorre Ction TD1 SuiteBeyaz ÇiçekPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPITRE I Circuits Logiq Combinatoires PDFDocument28 pagesCHAPITRE I Circuits Logiq Combinatoires PDFTimble PuteurPas encore d'évaluation
- Série D'exercices N°2-3tech-Systèmes Combinatoires-2013-2014 - CorrectionDocument7 pagesSérie D'exercices N°2-3tech-Systèmes Combinatoires-2013-2014 - CorrectionAymen ladhari100% (1)
- Exercices Logique Séquentielle CorrigésDocument6 pagesExercices Logique Séquentielle CorrigésDr. Chekir Amira100% (1)
- Sc3a9rienc2b03 STRM Mi Avril 2014Document8 pagesSc3a9rienc2b03 STRM Mi Avril 2014remy stephane ETOA ETOA0% (1)
- Exam - ARCHITECTURE - Jan - 2021-V3 - CorrigéDocument2 pagesExam - ARCHITECTURE - Jan - 2021-V3 - CorrigéGANG SHOOTPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercices de CompteursDocument22 pagesExercices de CompteursRad PAMBUPas encore d'évaluation
- TD4 CorrectionDocument15 pagesTD4 CorrectionistaitosPas encore d'évaluation
- TD - Systeme Numeration (Correction)Document2 pagesTD - Systeme Numeration (Correction)yasminePas encore d'évaluation
- Le Circuit Integre Ne555Document4 pagesLe Circuit Integre Ne555Sami Mahjoubi100% (1)
- Correction Oscillateur ColpittsDocument5 pagesCorrection Oscillateur Colpittsayman lamzouri100% (1)
- Lcs Devoir1Document1 pageLcs Devoir1Arwa RoraPas encore d'évaluation
- TD N 2 FpgaDocument4 pagesTD N 2 FpgaLE BARON0% (1)
- Corrigé de TD2Document9 pagesCorrigé de TD2Hocine BePas encore d'évaluation
- Chap6-Circuit ArithmetiquesDocument8 pagesChap6-Circuit ArithmetiquesAhmed Gourine100% (2)
- TD 2Document6 pagesTD 2ESIPas encore d'évaluation
- CorrigéExamen 2020-2021Document3 pagesCorrigéExamen 2020-2021Moujahed GassoumiPas encore d'évaluation
- Logique Combinatoire (TP Automatisme ... Adder 4 Bits Soustracter 4bits Multiplieur 4 Bits .....Document37 pagesLogique Combinatoire (TP Automatisme ... Adder 4 Bits Soustracter 4bits Multiplieur 4 Bits .....Soufiane El AoufiPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie de TD N02Document4 pagesSerie de TD N02Yasser Safar Batti100% (3)
- Corrigé TD 154Document3 pagesCorrigé TD 154MBADJOUN Daniel100% (1)
- TD3 en 2019 2020Document2 pagesTD3 en 2019 2020Mahdi LahdiliPas encore d'évaluation
- TP 2Document3 pagesTP 2Kadri Mongi100% (1)
- Exo Ensl CoDocument14 pagesExo Ensl CoAnonymous DZg1vCRdj50% (2)
- Chapitre 4 - Les Compteurs SynchronesDocument40 pagesChapitre 4 - Les Compteurs SynchronesBaha HermassiPas encore d'évaluation
- Examens, Exercices, Astuces Tous Ce Que Vous Voulez Tableaux de KARNAUGH cours-exercices-corriges-TP-solution PDFDocument15 pagesExamens, Exercices, Astuces Tous Ce Que Vous Voulez Tableaux de KARNAUGH cours-exercices-corriges-TP-solution PDFBabacarDiago50% (2)
- TP Portes Logiques ISISDocument9 pagesTP Portes Logiques ISISMinh Quang TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours APM 02 PDFDocument13 pagesCours APM 02 PDFLeroy Lionel SonfackPas encore d'évaluation
- TD Ire + Sequentiel+CorrectionDocument18 pagesTD Ire + Sequentiel+CorrectionKamal Mef67% (3)
- Codeur DecodeurDocument7 pagesCodeur DecodeurAntonio SabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie N1Document9 pagesSerie N1khalifakarouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Université Mohamed KHIDER..Document5 pagesUniversité Mohamed KHIDER..soniabetta2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3814200a00 PDFDocument2 pages3814200a00 PDFzizouhichePas encore d'évaluation
- TP1 Oscillateurs IsisDocument3 pagesTP1 Oscillateurs IsisAnas FarhaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Corriges Mécanique Lève Moto EtDocument2 pagesCorriges Mécanique Lève Moto EtDavid Jay100% (1)
- Upload - Série D'exercices N°11-3tech-Microcontrôleur-2013-2014-CorrectionDocument14 pagesUpload - Série D'exercices N°11-3tech-Microcontrôleur-2013-2014-CorrectionOumaima AbdelwahedPas encore d'évaluation
- EXEL3 11juin2009Document2 pagesEXEL3 11juin2009Gray AbPas encore d'évaluation
- Devoir de Contrôle N°3 Climatiseur D'une Voiture 2014 2015 (MR Tarek Elbazmi)Document3 pagesDevoir de Contrôle N°3 Climatiseur D'une Voiture 2014 2015 (MR Tarek Elbazmi)Ridha GouadriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours 2Document4 pagesCours 2free fire xyahiaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Thème 3 Le Cid Evaluation BilanDocument3 pagesThème 3 Le Cid Evaluation BilanYounes Larhrib100% (1)
- Cor - GEE1 - 1 La Grammaire en Exercices Cahier 1Document71 pagesCor - GEE1 - 1 La Grammaire en Exercices Cahier 1Adriano YamaokaPas encore d'évaluation
- Magir1 Devoir Ipv6 2014 2015Document3 pagesMagir1 Devoir Ipv6 2014 2015assouoPas encore d'évaluation
- PrepECN Item 90 - Infections Naso-Sinusiennes de L'adulte Et de L'enfant - Fiches de Préparation Aux ECN de MédecineDocument7 pagesPrepECN Item 90 - Infections Naso-Sinusiennes de L'adulte Et de L'enfant - Fiches de Préparation Aux ECN de MédecineAdémonla ROUFAÏPas encore d'évaluation
- Support Stratégies Des Firmes MultinationalesDocument38 pagesSupport Stratégies Des Firmes MultinationalesmariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Douville O Enfants Des RuesDocument33 pagesDouville O Enfants Des RuesJean Rigobert MbengPas encore d'évaluation
- Moi GianniDocument1 pageMoi GianniIlham BnPas encore d'évaluation
- Qâsim - Al Firansi PDFDocument6 pagesQâsim - Al Firansi PDFmac51100Pas encore d'évaluation
- Série de TD 03Document2 pagesSérie de TD 03BilaPas encore d'évaluation
- ComptabiliteDocument503 pagesComptabiliteAhmed JebariPas encore d'évaluation
- Problématique: Comment Marivaux Réussit-Il À Mettre en Abyme Les Différents Niveaux de Stratagèmes Mis en Œuvre Dans Cette Scène ?Document3 pagesProblématique: Comment Marivaux Réussit-Il À Mettre en Abyme Les Différents Niveaux de Stratagèmes Mis en Œuvre Dans Cette Scène ?Louis BoulayPas encore d'évaluation
- P 20133329Document142 pagesP 20133329andoPas encore d'évaluation
- French Writing - QuestionsDocument13 pagesFrench Writing - QuestionsSujithPas encore d'évaluation
- Interview-Bounajah Compo 1asDocument3 pagesInterview-Bounajah Compo 1asMaache Nadjet100% (1)
- Crise 2000 de La Cote D'ivoirDocument4 pagesCrise 2000 de La Cote D'ivoirballa pierre koivoguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Roto 16sept 1ed PDFDocument16 pagesRoto 16sept 1ed PDFLa_RotondePas encore d'évaluation
- Coaching Personnel IndividuelDocument2 pagesCoaching Personnel Individuelmuller senséPas encore d'évaluation
- Comment Prospecter de Nouveaux ClientsDocument10 pagesComment Prospecter de Nouveaux ClientsAyadi NizarPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Atomes MoléculesDocument3 pages4 Atomes MoléculesSidhoum SidPas encore d'évaluation
- Ichimoku Timespan Theory Nombre9Document2 pagesIchimoku Timespan Theory Nombre9san RayPas encore d'évaluation
- M01 Métier Et Formation-GE-TEMIDocument43 pagesM01 Métier Et Formation-GE-TEMIltc100% (1)
- Nouveau Rapport MLADocument20 pagesNouveau Rapport MLAzicozo012Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH 1 Analyse Financière ESGDocument8 pagesCH 1 Analyse Financière ESGOualid OunaceurPas encore d'évaluation
- AlkhawarichtiDocument2 pagesAlkhawarichtisyll.el-hadji-massePas encore d'évaluation
- MasterDocument1 pageMasterMaoukil TachPas encore d'évaluation
- La Gestion de La Paie PDFDocument96 pagesLa Gestion de La Paie PDFYacine AyatPas encore d'évaluation
- WTPW-Simon PierreDocument100 pagesWTPW-Simon Pierrekonan kouadio henri franckPas encore d'évaluation
- (Free Scores - Com) - 039 Guessan Gna Houa Jean Claude Sanctus Sainte Bernadette 75050Document2 pages(Free Scores - Com) - 039 Guessan Gna Houa Jean Claude Sanctus Sainte Bernadette 75050Edmond NIREMAPas encore d'évaluation