Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
TYREgtr 04 03e
Transféré par
anleyedemeTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
TYREgtr 04 03e
Transféré par
anleyedemeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Working Document No.
: TYREgtr-04-03
VIN and TIN
Vehicle Identification Number
(VIN)
and
Tyre Identification Number
(TIN)
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
• The VIN is a nearly universally accepted 17 digit alphanumeric code (which
does not use the letters I, O or Q) that uniquely identifies a vehicle.
• It is based on the ISO Standards 3779 and 3780. The former describes the
composition of the VIN and the latter describes the codification system
which identifies the manufacturer, the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI).
• The WMI is managed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) based
in the US.
• The VIN is composed of 3 sections, which identify the manufacturer,
describe the vehicle characteristics, and uniquely identify the vehicle
sequence number.
– WMI = World Manufacturer Identifier (places 1 through 3)
– VDS = Vehicle Descriptor Section (places 4 through 9)
– VIS = Vehicle Identification Section (places 10 through 17)
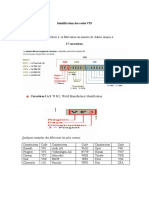
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
WMI VDS VIS
Manufacturer Vehicle Attributes Check Digit Model Plant Code Sequential Number
Identifier Year
Managed by SAE Managed by Calculated Code Managed by manufacturer
manufacturer value given in
ISO
3779
28 SEPTEMBER 2007 TYRE INDUSTRY GTR WORKING GROUP 2/5
Tyre Identification Number (TIN)
• The TIN is defined by the US NHTSA and is required on all tyres
sold in the US (cf. 49 CFR §574.5 and 574.6). It uses a 12 digit
alphanumeric code (excluding the letters G, I, O, Q, S and Z)
composed of the following elements:
– The factory code is a 2 character alphanumeric code unique to each
manufacturing facility. The codes are assigned and managed by
NHTSA.
– The size code (2 characters) is maintained by the manufacturer and
must allow the identification of the size of the tyre.
– The optional tyre type code (3 or 4 characters) is used to identify other
tyre characteristics and the brand of tyre. The records of the codes used
are kept by the manufacturer.
– The date code (4 digits) is a simple combination of the week number of
fabrication and the last 2 digits of the year of manufacture. The starting
day of the week is defined as Sunday. (For information, ISO standard
8061 specifies Monday as the first day of the week.)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Factory Code Tyre Size Code Tyre Type Code (Optional) Date Code
Managed by NHTSA Managed by manufacturer Managed by manufacturer No management required
28 SEPTEMBER 2007 TYRE INDUSTRY GTR WORKING GROUP 3/5
Comparison of TIN and VIN
TIN
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Factory Code Tyre Size Code Tyre Type Code (Optional) Date Code
Managed by NHTSA Managed by manufacturer Managed by manufacturer No management required
Weekly production
Product lot identity
Manufacturer
description
identity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
WMI VDS VIS
Manufacturer Vehicle Attributes Check Digit Model Plant Code Sequential Number
Identifier Year
Managed by SAE Managed by Calculated Code Managed by manufacturer
manufacturer value given in
ISO
3779
Individual product
identity
VIN
28 SEPTEMBER 2007 TYRE INDUSTRY GTR WORKING GROUP 4/5
Conclusions / Questions
• The TIN is seen by the global tyre industry as a
satisfactory way of uniquely identifying its products
• The similarities with the VIN are reassuring
– The only major difference is that the TIN allows identification of a
specific product's weekly production lot, while the VIN allows
identification of an individual vehicle
• Who should manage the list of factory codes (currently
NHTSA, but could be WP.29, for example)?
• Should the TIN date code be aligned with ISO 8601?
• If a need for 3 digit factory codes exists, it should be
considered rapidly to allow time for adoption
– 2 digit codes may be depleted shortly
– Recycling old, no-longer-used codes can help (10 years after
factory shutdown, for example)
28 SEPTEMBER 2007 TYRE INDUSTRY GTR WORKING GROUP 5/5
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Computer Science Paper 2 HLDocument21 pagesComputer Science Paper 2 HLSONGI CHAI100% (1)
- Contrôle Technique Périodique 05/08/2022 22207973Document1 pageContrôle Technique Périodique 05/08/2022 22207973Jimmy DumontPas encore d'évaluation
- BMW f11 French Owner ManualDocument375 pagesBMW f11 French Owner ManualDaniel GigelPas encore d'évaluation
- FR FR XM 2000 PDFDocument231 pagesFR FR XM 2000 PDFLuc Mutombo MukuluPas encore d'évaluation
- CR Vin 01042011Document3 pagesCR Vin 01042011assahili100% (1)
- APQPDocument50 pagesAPQPmoez100% (2)
- Liste Descodes Secrets Et Leur Fonctionnement Pour Samsung Codes Secrets Et Leur Fonctionnement Pour SamsungDocument2 pagesListe Descodes Secrets Et Leur Fonctionnement Pour Samsung Codes Secrets Et Leur Fonctionnement Pour Samsungkonate ichiakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Le Guide de La Reparation Des PneumatiquesDocument36 pagesLe Guide de La Reparation Des Pneumatiquesmounaimbz31Pas encore d'évaluation
- Identification Du Véhicule: PrésentationDocument5 pagesIdentification Du Véhicule: Présentationsebastien dardeauPas encore d'évaluation
- Isotech Catalogue Plaquettes de Frein PLDocument156 pagesIsotech Catalogue Plaquettes de Frein PLJero MilPas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogue Hitachi-Zw180Document334 pagesCatalogue Hitachi-Zw180SMITIPas encore d'évaluation
- Fia, Elemento de Competición Homologado.Document3 pagesFia, Elemento de Competición Homologado.Locossueños Crazy carsPas encore d'évaluation
- MY17 SB Many Models 000 0055 43 Ed B FRNDocument46 pagesMY17 SB Many Models 000 0055 43 Ed B FRNAlfaro GustavoPas encore d'évaluation
- Véhicules UtilitairesDocument364 pagesVéhicules UtilitairesjaleovideoPas encore d'évaluation
- Citroën C4 Picasso SpaceTourer (B78) 2015 Module de Commande de Carrosserie BSI - Calculateur Carrosserie 2024.01.14 17.58.23Document1 pageCitroën C4 Picasso SpaceTourer (B78) 2015 Module de Commande de Carrosserie BSI - Calculateur Carrosserie 2024.01.14 17.58.23layadimohamed60Pas encore d'évaluation
- FR FR c4 2004 (1159) PDFDocument412 pagesFR FR c4 2004 (1159) PDFPas CalPas encore d'évaluation
- Manuel D'Entretien: DÉBARDEUR 632E/635GDocument626 pagesManuel D'Entretien: DÉBARDEUR 632E/635GmecanicsamPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Motor Xsara FR 2001Document394 pagesManual Motor Xsara FR 2001paul2002cm100% (1)
- Véhicules Utilitaires: Dexc/Dps/Apv/Mtd Méthodes Techniques DocumentationDocument106 pagesVéhicules Utilitaires: Dexc/Dps/Apv/Mtd Méthodes Techniques DocumentationmaximePas encore d'évaluation
- Caractéristiques Des Véhicules Automobiles PDFDocument45 pagesCaractéristiques Des Véhicules Automobiles PDFKhalid Bel67% (3)
- PM 05 16 FR PDFDocument44 pagesPM 05 16 FR PDFYounes MouhoubPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiche2 Orga SecteurDocument2 pagesFiche2 Orga SecteurMed HOUDPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie 6 Code VINDocument5 pagesSerie 6 Code VINAya Mlm100% (2)
- Récapitulatif Des Anti DémarragesDocument19 pagesRécapitulatif Des Anti DémarragesMikaël OXoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mr362espace0 PDFDocument60 pagesMr362espace0 PDFyassine123Pas encore d'évaluation
- RC152 Trailer Hitch Harness Recall - FRDocument7 pagesRC152 Trailer Hitch Harness Recall - FRbigkarimlive.frPas encore d'évaluation
- Exposé Sur Un Référentiel SectorielDocument4 pagesExposé Sur Un Référentiel SectorielMODELCO SARLPas encore d'évaluation
- GPCDOC X Cbe 26680 Key 140007507896 201302112210Document3 pagesGPCDOC X Cbe 26680 Key 140007507896 201302112210gbadziPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiche Synthese Conformite Montage Des Pneus Poids Lourd TNPFDocument3 pagesFiche Synthese Conformite Montage Des Pneus Poids Lourd TNPFMustapha CarripPas encore d'évaluation
- Rattrapage LusDocument1 pageRattrapage Lushousniredouane83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Identification Du Véhicule: PrésentationDocument4 pagesIdentification Du Véhicule: Présentationtoni13021302100% (1)
- 02 Syh FRDocument7 pages02 Syh FRMed Ben AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Glossaire AbreviationsDocument48 pagesGlossaire AbreviationsalyPas encore d'évaluation
- MINI Notice+d'utilisation 01402917348Document232 pagesMINI Notice+d'utilisation 01402917348didier lalyPas encore d'évaluation
- Prospectus Afri-Parc AutoDocument2 pagesProspectus Afri-Parc AutoBenjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini PDFDocument306 pagesMini PDFGatyen RatiarisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Controle Technique Nissan 2Document1 pageControle Technique Nissan 2ricardomarquesalpendrejasmim100% (1)
- Book Nov DesDocument32 pagesBook Nov DesLuluk KusniatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide de Capitalisation Pour La Caracterisation Et La Mesure Des Etats de Surface en Complement A La Normalisation IsoDocument27 pagesGuide de Capitalisation Pour La Caracterisation Et La Mesure Des Etats de Surface en Complement A La Normalisation IsoMiguel QueirosPas encore d'évaluation
- Controle Technique NissanDocument1 pageControle Technique NissanricardomarquesalpendrejasmimPas encore d'évaluation
- Automated PCB Labelling Brochure Europe FrenchDocument16 pagesAutomated PCB Labelling Brochure Europe Frenchtoumi aminePas encore d'évaluation
- Repair Manual d7f EngineDocument46 pagesRepair Manual d7f EnginePedroPas encore d'évaluation
- MOTEUR (Essence) 4 Cylindres Fonte: Types VéhiculesDocument46 pagesMOTEUR (Essence) 4 Cylindres Fonte: Types VéhiculesJd DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- AYEL Jean - Lubrifiants Pour Moteurs Thermiques - Specifications Des ConDocument8 pagesAYEL Jean - Lubrifiants Pour Moteurs Thermiques - Specifications Des ConYodaScribdPas encore d'évaluation
- 02Document4 pages02HACHMINATOUPas encore d'évaluation
- Repair Manual d7f EngineDocument49 pagesRepair Manual d7f EngineBlaise MakPas encore d'évaluation
- Tarif Voirie 2017Document48 pagesTarif Voirie 2017frederic wilfred FabrePas encore d'évaluation
- TXB NavigatorDocument32 pagesTXB NavigatorOnian HassanePas encore d'évaluation
- Contrôle Technique Périodique 04/04/2024 24222845Document1 pageContrôle Technique Périodique 04/04/2024 24222845akhmdchmaevPas encore d'évaluation
- Document Technique Saxo 15dDocument207 pagesDocument Technique Saxo 15dbenz53 amdPas encore d'évaluation
- Genie gth4016 - SRDocument177 pagesGenie gth4016 - SRbruno di matteoPas encore d'évaluation
- Audi A3 CarosserieDocument37 pagesAudi A3 CarosserieRodolfo Diaz0% (1)
- Conti TechDocument62 pagesConti TechcouscousriderPas encore d'évaluation
- Verif EPI Bloqueur Suivi FRDocument1 pageVerif EPI Bloqueur Suivi FRCristian camilo Castiblanco RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Gla Classmanual6515540743finalDocument414 pages2015 Gla Classmanual6515540743finalVasile ContiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Exo Master Schedule-101208Document1 pageExo Master Schedule-101208adrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Utilisation KDS (SCANNER)Document34 pagesUtilisation KDS (SCANNER)Hamou Bouabida100% (2)
- Livret D'Entretien 318D Et 320D Chargeur CompactDocument21 pagesLivret D'Entretien 318D Et 320D Chargeur CompactLAURA XIMENA PEREZ QUINTANAPas encore d'évaluation