Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Les Pronom Personnels
Transféré par
Shiv RawatTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Les Pronom Personnels
Transféré par
Shiv RawatDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
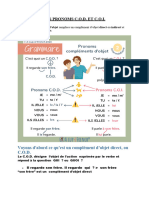
Les pronom personnels
Types of pronom personnel
1. Pronom sujet
2. COD
3. COI
4. Y
5. En
6. Pronom tonique
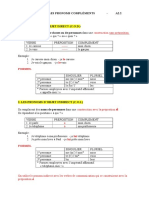
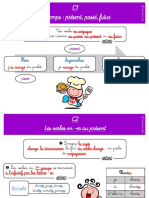
Objet direct (COD)
📝 Les copains (sujet) achetent (verb) ces cadeaux (objet)
—> sujet + verb + objet
ces cadeaux —> becomes les, placed BEFORE the verb
Les copains les achetent
the articles (les, la, le, l’) replace the objet in this case. We use this according to the gender & quantity of the object
(ex : nous - les, le livre - le, les copains - les)
the placement of le,la,les depends on the tense of the sentence [below]
Marie regarde la télé —> Marie la regarde
Elle ouvre son sac à dos. - Elle l’ouvre
In objet direct, we can ask the question “qui (who)” or “quoi (what)”
Les pronom personnels 1
Je lis le livre - i read the book
→ Je lis quoi? - what am i reading? = the book (le livre)
COD : Je le lis
Nous aimons nos amis.
COD : Nous les aimons
💡 adjectif posessifs dont change the formation of COD, they along with the object, are taken as a whole
objet direct can never be followed by prepositions and articles definis and partitifs
negation : Rahul n’aime pas les jeux-vidéos —> Il ne les aime pas (cod is added to the verb)
Placements according to the tenses
The placement of pronoms in COD, COI, Y’, En are the same :
Present tense - above example, pronoun before verb
Future proche
Elle va regarder la télévision—> Elle va la regarder
pronoun will be after the verb aller
Imperatif
Regarder la television! —> Regarder-la!
negation : ne le regarde pas ! [le regarde is taken as a unit]
pronoun will be after the verb with a hyphen
in affirmitive imperatif, le/la/les/l’ is placed after the verb
2 verbs
Elle veut faire le travail —> Elle veut le faire
if the sentence has two verbs, the COD is placed between the two verbs.
Passé composé
Elle a regardé la télévision —> Elle l'a regardée
negation : elle ne l’a pas regardée
here a is an auxilliare not a verb, so the pronoun will be placed before a
Excercise
1. Je vais manger la pomme. - Je vais la manger
2. Tu chanteras la chanson. - Tu la chanteras
3. Elle ont acheté les bananes. - Elle les ont achetés
Les pronom personnels 2
4. Corrigez les tests! - Corrigez-le!
5. Vous oubliez vos manteaux. - Vous les oubliez
Objet indirect (COI)
In COI, the subject does an action to the object
il offre à son amie - il lui offre
It answers to the question “à qui” (to who/whom?) or “à quoi” (to what?), but also to “de qui” (of who/whom?) or
“de quoi” (of what), depending on the preposition used after the verb.
(à/à la/au/à l’/aux)+ personne
pronouns for COI
il/elle —> lui [m/f/s]
nous & vous —> stays the same
ils/elles —> leur [m/f/p]
à moi —> me, m’
à toi —> te, t’
Examples :
Je donne les jouets aux enfants
Here we have both COD (les jouets) & COI (aux enfants)
COD : les jouets —> les
COI : aux enfants —> leur
📝 IMP - Order of pronom personnel in sentences : COD, COI, Y, En (BUT when me, te is used COI comes
before COD)
to replace both objects - je les leur donne
only COI : je leur donne les jouets
Examples - PPT
Il va offrir une bague á sa femme. - Il va lui offrir une bague.
Il vient d’offrir une bague á sa femme. - Il vient de lui offrir une bague. (vient de - just, not a verb)
Pronom Y
The pronoun “Y” is used to replace places in a sentence. The place is usually accompanied by á/ a preposition
even though de can be used as a preposition we do not use y, we use en instead.
Les pronom personnels 3
Ex:
Ne va pas à la plage toute seule (alone) —> N’y va pas toute seule
Je mets les cles dans le sac - J’y mets les cles/Je les y mets
Y can also replace a thing (never a person) introduced by “à, au, aux, à l’, à la”
ils se sont opposés à ce mariage - ils s'y sont opposes
NOTE : when the following verbs are followed by an object (not a person) we use y
penser à
croire à
s'intéresser à
reflechir à
Ex :
je pense à mon travail - j'y pense
ma fille s'intéresse a la peinture - ma fille s'y intéresse
NOTE : If you are asked to replace the sujet which is in the beginning of the sentence use il/elle. (L’enfant
mange une pomme —> l’enfant will become il)
Pronom En
Used ONLY for de - as a preposition and for articles partitifs and also expressions of quantity
Ex:
Je viens du cinema - J’en viens
Je bois du cafe - J’en bois
Elle boit trois litres d’eau - Elle en boit trois litres (negation : elle n’en boit pas [when we negate expressions
of quantity, you don't have to repeat the measure of the quantity])
for verbs besoin de (need of) & s’occuper de (take care of) —>
J’ai besoin de l’argent - J’en ai besoin
pronom tonique - nb
Les pronom personnels 4
Les pronom personnels 5
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- La grammaire: Devenez incollable sur les règles linguistiques de la langue françaiseD'EverandLa grammaire: Devenez incollable sur les règles linguistiques de la langue françaisePas encore d'évaluation
- Notes - Class 04Document10 pagesNotes - Class 04Manupa PereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms Personnels Exercices ExpliquDocument8 pagesLes Pronoms Personnels Exercices ExpliquPetite TaengPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms Cod:CoiDocument12 pagesLes Pronoms Cod:CoiAlicia DelepoullePas encore d'évaluation
- Résumé FR LangueDocument5 pagesRésumé FR Languetouati souad0% (1)
- Les Verbes Pronominaux Au Passé ComposéDocument6 pagesLes Verbes Pronominaux Au Passé ComposéirePas encore d'évaluation
- Les Doubles PronomsDocument2 pagesLes Doubles Pronomsvclonda100% (1)
- Francais A2Document5 pagesFrancais A2nguyen.ngocanh.291005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pronoms PersonnelsDocument5 pagesPronoms PersonnelssellcoksPas encore d'évaluation
- FRA - Les Parties Du Discours 4 (Les Pronoms)Document4 pagesFRA - Les Parties Du Discours 4 (Les Pronoms)Carolina di domenicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dzexams Docs 4am 904940Document23 pagesDzexams Docs 4am 904940sohaib houdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Accord Du Participe PasseDocument5 pagesAccord Du Participe PasseDiana Maria Torres RestrepoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours sur les pronoms - UFMC1 - TraductionDocument16 pagesCours sur les pronoms - UFMC1 - Traductionidirbenadjina00Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pronoms Cod-Coi ExplicationDocument3 pagesPronoms Cod-Coi ExplicationpolgarapPas encore d'évaluation
- Impératif ProfessionnelleDocument20 pagesImpératif ProfessionnelleTarik ChouaibisPas encore d'évaluation
- Théorie Pronoms PersonnelsDocument6 pagesThéorie Pronoms Personnelscris2737Pas encore d'évaluation
- Révision EnglaisDocument3 pagesRévision Englaistalhaoui faresPas encore d'évaluation
- La Conjugaison en Anglais More English PDFDocument4 pagesLa Conjugaison en Anglais More English PDFziedPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabulaire:: Les Homophones GrammaticauxDocument7 pagesVocabulaire:: Les Homophones Grammaticauxussef00Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cours - Les PronomsDocument7 pagesCours - Les PronomsMathis DelattrePas encore d'évaluation
- Pronoms Y-EnDocument2 pagesPronoms Y-EnNicoBirminghamukPas encore d'évaluation
- Doubles PronomsDocument10 pagesDoubles PronomsCarlota Vázquez EstebanPas encore d'évaluation
- Only in Imperative Affirmative FormDocument3 pagesOnly in Imperative Affirmative FormSandroz CavniPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms PersonnelsDocument18 pagesLes Pronoms Personnelswehodo3908Pas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms RelatifsDocument15 pagesLes Pronoms RelatifsEvelin CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms Compléments COD COI IDIOMASDocument4 pagesLes Pronoms Compléments COD COI IDIOMASRosblackPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours Les Pronoms Personnels Compléments-PR. ARIF SAMIRADocument11 pagesCours Les Pronoms Personnels Compléments-PR. ARIF SAMIRANour EddinePas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms EN Et YDocument2 pagesLes Pronoms EN Et YMajito RichterPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms EN Et YDocument3 pagesLes Pronoms EN Et YIsaPas encore d'évaluation
- La PronominalisationDocument21 pagesLa PronominalisationOlga Aycardi100% (1)
- L'accord U Participe PasséDocument5 pagesL'accord U Participe PasséAmy SullivanPas encore d'évaluation
- L Impératif Et PronomsDocument20 pagesL Impératif Et PronomsAngie CallejonPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram2 les pr relatifsDocument4 pagesGram2 les pr relatifsKim Hye RinPas encore d'évaluation
- Faire + InfinitifDocument5 pagesFaire + InfinitifMinh TrietPas encore d'évaluation
- Cod - CoiDocument3 pagesCod - CoiaadhyatallapareddyPas encore d'évaluation
- OU, DontDocument4 pagesOU, DontamouPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms EN Et YDocument4 pagesLes Pronoms EN Et Ylau1985Pas encore d'évaluation
- French Grammar Pre-Board IDocument19 pagesFrench Grammar Pre-Board Isriharib035Pas encore d'évaluation
- Accord Du Participe Passe IiDocument6 pagesAccord Du Participe Passe Iisony sonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Accord Du Participe Passe IiDocument6 pagesAccord Du Participe Passe Iisony sonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms ComplémentsDocument13 pagesLes Pronoms ComplémentsIngrid IslabãoPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiche Les Pronoms Cod Coi en yDocument1 pageFiche Les Pronoms Cod Coi en yAngela Salvador BrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Francais - Revision FinaleDocument12 pagesFrancais - Revision FinaleStefaniaIvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms RelatifsDocument8 pagesLes Pronoms RelatifsHeidy Teresa MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Le PronomDocument11 pages4 Le PronomAit ichou ahmad100% (2)
- Pronom BLDocument14 pagesPronom BLSoulaimane BelaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Pronoms PersoDocument3 pagesPronoms Persosandaogos444Pas encore d'évaluation
- Séance 2Document6 pagesSéance 2Hà Nguyễn NgọcPas encore d'évaluation
- Accord Du Participe PasséDocument8 pagesAccord Du Participe PasséYoussoupha DiakhatePas encore d'évaluation
- Cod CoiDocument3 pagesCod CoiDương Thị Mỹ HạnhPas encore d'évaluation
- FSF2D French Exam NotesDocument4 pagesFSF2D French Exam NotesA Square ChickenPas encore d'évaluation
- CV Pronoms ComplementsDocument8 pagesCV Pronoms Complementssplendini8028Pas encore d'évaluation
- L - Emploi Des PronomsDocument7 pagesL - Emploi Des PronomsSid ahmed Zerrouki sbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Faire Causatif NotesDocument9 pagesFaire Causatif NotesMaximwell MaxPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview 1Document3 pagesOverview 1h8vkkvphkrPas encore d'évaluation
- LES PRONOMS PERSONNELSDocument7 pagesLES PRONOMS PERSONNELSCarmen HCPas encore d'évaluation
- ملخص الفرنسية sh dDocument17 pagesملخص الفرنسية sh dhappy oum FirasPas encore d'évaluation
- Libro Frances AVANZADODocument94 pagesLibro Frances AVANZADODouglas Santisteban HernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- Remédiation LinguistiqueDocument13 pagesRemédiation Linguistiqueإسلا ميات100% (1)
- Pronom Tonique P.T - GracDocument2 pagesPronom Tonique P.T - GracShiv RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Pronom Tonique P.T - GracDocument2 pagesPronom Tonique P.T - GracShiv RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Term 1 - AllDocument20 pagesTerm 1 - AllShiv RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Letters - Grade 9Document3 pagesLetters - Grade 9Shiv RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- La Classe Des MotsDocument16 pagesLa Classe Des MotsDahir Nezar LahcenPas encore d'évaluation
- 9VG - Verben - DossierDocument28 pages9VG - Verben - DossierAdeline Carlin UlrichPas encore d'évaluation
- Modaux Cours Et ExoDocument6 pagesModaux Cours Et ExoMark HollingsworthPas encore d'évaluation
- Cartes Mentales ConjugaisonnDocument4 pagesCartes Mentales ConjugaisonnSaidi As Youcef100% (1)
- Le Passé Composé GénéralDocument41 pagesLe Passé Composé GénéralGuillermo Gómez VecinoPas encore d'évaluation
- 76 Phrasal Verbs À Connaître en Anglais - ISpeakSpokeSpokenDocument27 pages76 Phrasal Verbs À Connaître en Anglais - ISpeakSpokeSpokenAimé IkoyobPas encore d'évaluation
- La Conjugaison Des Verbes Au Preesent CompletDocument4 pagesLa Conjugaison Des Verbes Au Preesent CompletJorge David Bolognesi Ballivian100% (1)
- Decomposition Decimaux 1Document1 pageDecomposition Decimaux 1ahmed22gouda22Pas encore d'évaluation
- French InsultsDocument5 pagesFrench InsultsAlex D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ce2 Evaluation 3eme Groupe PresentDocument2 pagesCe2 Evaluation 3eme Groupe PresentMOKRANI LEILA50% (2)
- Grammaire NeerlandaiseDocument65 pagesGrammaire NeerlandaiseBn Lmit100% (2)
- Les Lecons de Conjugaison PDFDocument17 pagesLes Lecons de Conjugaison PDFSaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Conjugacion FrancesDocument5 pagesConjugacion FrancesmopliqPas encore d'évaluation
- GRAMMAIRE 4eDocument61 pagesGRAMMAIRE 4eSamuel Kouassi100% (1)
- Islcollective Worksheets Comptent c2 Dbutant Pra1 Elmentaire A1 Intermdiaire b1 Intermdiaireavanc b2 Printermdiaire A2 L 77064533555330aaea2a119 68543581Document5 pagesIslcollective Worksheets Comptent c2 Dbutant Pra1 Elmentaire A1 Intermdiaire b1 Intermdiaireavanc b2 Printermdiaire A2 L 77064533555330aaea2a119 68543581Anne BeauvoirPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammaire AnglaiseDocument23 pagesGrammaire AnglaiseSalemon DiedhiouPas encore d'évaluation
- Binaire Et HexadécimalDocument11 pagesBinaire Et Hexadécimalirie100% (1)
- +les Verbes Et Leurs Prepositions (CLE. 2007) PDFDocument117 pages+les Verbes Et Leurs Prepositions (CLE. 2007) PDFSamir Wehebb100% (1)
- Anglais PDF TotalDocument50 pagesAnglais PDF TotalAnne PicochePas encore d'évaluation
- Grammaire Française Pour Les FinniphonesDocument538 pagesGrammaire Française Pour Les Finniphonesfrancophile86100% (1)
- Extrait en Vacances Avec Les Cours Legendre AllemandDocument20 pagesExtrait en Vacances Avec Les Cours Legendre AllemandZiguissom SoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Apprendre Les Verbes Irréguliers Anglais FacilementDocument22 pagesApprendre Les Verbes Irréguliers Anglais FacilementEnricoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercice Verbe Etre Et Avoir - Google SearchDocument1 pageExercice Verbe Etre Et Avoir - Google SearchWafa DridiPas encore d'évaluation
- Present SimpleDocument6 pagesPresent SimpleKhadija ElmouhammadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Temps en Anglais - Le Guide de La Conjugaison AnglaiseDocument34 pagesLes Temps en Anglais - Le Guide de La Conjugaison AnglaiseMoussa SaboPas encore d'évaluation
- Parler Anglais en 5 Minutes Par Jour C Est MalinDocument28 pagesParler Anglais en 5 Minutes Par Jour C Est MalinIlias OmariPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Pronoms 2Document4 pagesLes Pronoms 2khulekani samuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Temps Anglais PDFDocument3 pagesLes Temps Anglais PDFMouhamed Thioub100% (1)
- Les Verbes PronominauxDocument10 pagesLes Verbes PronominauxTatiana GutuPas encore d'évaluation
- LES CHIFFRES ROMAINS DE 1 À 5.000 by TwinDocument36 pagesLES CHIFFRES ROMAINS DE 1 À 5.000 by TwinSeydou DiamoutenePas encore d'évaluation
- DELF B1 - Production Orale - 2800 mots pour réussirD'EverandDELF B1 - Production Orale - 2800 mots pour réussirÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Hypnotisme et Magnétisme, Somnambulisme, Suggestion et Télépathie, Influence personnelle: Cours Pratique completD'EverandHypnotisme et Magnétisme, Somnambulisme, Suggestion et Télépathie, Influence personnelle: Cours Pratique completÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (8)
- Le TDA/H chez l'adulte: Apprendre à vivre sereinement avec son trouble de l'attentionD'EverandLe TDA/H chez l'adulte: Apprendre à vivre sereinement avec son trouble de l'attentionPas encore d'évaluation
- Tests de grammaire française: 400 questions pour évaluer vos connaissancesD'EverandTests de grammaire française: 400 questions pour évaluer vos connaissancesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Aimez-Vous en 12 Étapes Pratiques: Un Manuel pour Améliorer l'Estime de Soi, Prendre Conscience de sa Valeur, se Débarrasser du Doute et Trouver un Bonheur VéritableD'EverandAimez-Vous en 12 Étapes Pratiques: Un Manuel pour Améliorer l'Estime de Soi, Prendre Conscience de sa Valeur, se Débarrasser du Doute et Trouver un Bonheur VéritableÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Le livre de la mémoire libérée : Apprenez plus vite, retenez tout avec des techniques de mémorisation simples et puissantesD'EverandLe livre de la mémoire libérée : Apprenez plus vite, retenez tout avec des techniques de mémorisation simples et puissantesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- Améliorer votre mémoire: Un Guide pour l'augmentation de la puissance du cerveau, utilisant des techniques et méthodesD'EverandAméliorer votre mémoire: Un Guide pour l'augmentation de la puissance du cerveau, utilisant des techniques et méthodesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Anglais Pour Les Nulles - Livre Anglais Français Facile A Lire: 50 dialogues facile a lire et photos de los Koalas pour apprendre anglais vocabulaireD'EverandAnglais Pour Les Nulles - Livre Anglais Français Facile A Lire: 50 dialogues facile a lire et photos de los Koalas pour apprendre anglais vocabulaireÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Force Mentale et Maîtrise de la Discipline: Renforcez votre Confiance en vous pour Débloquer votre Courage et votre Résilience ! (Comprend un Manuel Pratique en 10 Étapes et 15 Puissants Exercices)D'EverandForce Mentale et Maîtrise de la Discipline: Renforcez votre Confiance en vous pour Débloquer votre Courage et votre Résilience ! (Comprend un Manuel Pratique en 10 Étapes et 15 Puissants Exercices)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (28)
- Apprendre l’allemand - Texte parallèle - Collection drôle histoire (Français - Allemand)D'EverandApprendre l’allemand - Texte parallèle - Collection drôle histoire (Français - Allemand)Évaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Manipulation et Persuasion: Apprenez à influencer le comportement humain, la psychologie noire, l'hypnose, le contrôle mental et l'analyse des personnes.D'EverandManipulation et Persuasion: Apprenez à influencer le comportement humain, la psychologie noire, l'hypnose, le contrôle mental et l'analyse des personnes.Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (13)
- Vocabulaire DELF B2 - 3000 mots pour réussirD'EverandVocabulaire DELF B2 - 3000 mots pour réussirÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (34)
- La Pensée Positive en 30 Jours: Manuel Pratique pour Penser Positivement, Former votre Critique Intérieur, Arrêter la Réflexion Excessive et Changer votre État d'Esprit: Devenir une Personne Consciente et PositiveD'EverandLa Pensée Positive en 30 Jours: Manuel Pratique pour Penser Positivement, Former votre Critique Intérieur, Arrêter la Réflexion Excessive et Changer votre État d'Esprit: Devenir une Personne Consciente et PositiveÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)
- Anglais ( L’Anglais Facile a Lire ) 400 Mots Fréquents (4 Livres en 1 Super Pack): 400 mots fréquents en anglais expliqués en français avec texte bilingueD'EverandAnglais ( L’Anglais Facile a Lire ) 400 Mots Fréquents (4 Livres en 1 Super Pack): 400 mots fréquents en anglais expliqués en français avec texte bilingueÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Le Participe passé dans tous ses états: Petit traité de l'Accord du Participe passé avec être et avoirD'EverandLe Participe passé dans tous ses états: Petit traité de l'Accord du Participe passé avec être et avoirPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformez votre vie: Utilisez le pouvoir créateur qui est en vous pour construire votre vie à l'image de ce que vous voulez qu'elle soitD'EverandTransformez votre vie: Utilisez le pouvoir créateur qui est en vous pour construire votre vie à l'image de ce que vous voulez qu'elle soitÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (14)
- L'Interprétation des rêves de Sigmund Freud: Les Fiches de lecture d'UniversalisD'EverandL'Interprétation des rêves de Sigmund Freud: Les Fiches de lecture d'UniversalisPas encore d'évaluation
- Apprendre le turc - Texte parallèle (Français - Turc) Histoires courtesD'EverandApprendre le turc - Texte parallèle (Français - Turc) Histoires courtesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Les Outils Intellectuels des Génies: 40 principes qui vont vous rendre intelligent et vous enseigner à penser comme un génieD'EverandLes Outils Intellectuels des Génies: 40 principes qui vont vous rendre intelligent et vous enseigner à penser comme un génieÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Trésor des Proverbes Latino-Américains avec leurs équivalents espagnols, français, québécois et anglaisD'EverandTrésor des Proverbes Latino-Américains avec leurs équivalents espagnols, français, québécois et anglaisPas encore d'évaluation
- L’Art d’avoir toujours raison: Premium EbookD'EverandL’Art d’avoir toujours raison: Premium EbookÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Vocabulaire DELF B2 - 300 expressions pour reussirD'EverandVocabulaire DELF B2 - 300 expressions pour reussirÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (7)
- Réflexions de Bill: Une compilation unique de courtes contributions pertinentes et inspirantes du cofondateur des AA, Bill W.D'EverandRéflexions de Bill: Une compilation unique de courtes contributions pertinentes et inspirantes du cofondateur des AA, Bill W.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comment développer l’autodiscipline: Résiste aux tentations et atteins tes objectifs à long termeD'EverandComment développer l’autodiscipline: Résiste aux tentations et atteins tes objectifs à long termeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (7)