Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
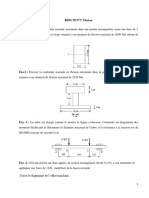
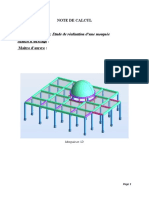
Analyse D'une Coupole
Transféré par
AbdouTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Analyse D'une Coupole
Transféré par
AbdouDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
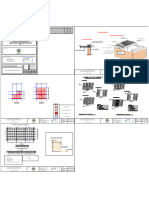
Analyse d’une coupole sphérique( )
Données de conception :
Hauteur de la coupole (h)=5 m
Diamètre de la coupole(L)=15.5 m
Epaisseur de la coupole (e)=0.15m
γc poids unitaire du béton =25KN/m3
Résistance du béton à la compression (c)=25 Mpa
Limite d'élasticité des armatures en acier (Fy)=400 Mpa
Evaluation des Charges :
Charge permanente (KN/m2)
Poids propre de la coupole……………………… 0.15*25=3.75
Etanchéité (Bitume)………………………………… 0.02*11=0.22
Mortier du ciment ………………………………….. 0.02*20=0.40
Isolation (Liège)…………………………………..….. 0.02*3=0.06
Enduit de plâtre ……………………………………… 0.02*0.15=0.3
G= 4.73KN/m2
Sur Charge Q=1KN/m2
Neige avec altitude H=500m …… Sn= 0.07*500+15/100 = 0.5KN/m 2
External( )force القوة الخارجية1.3.1(
1. Calcul le poids propre de la coupole(P.p) et la charge d’
(S.C): WDL = e*γc + Q = 0.1 × 24 + 0.5 = 2.9 KN/m2
2. Calculation of 𝐖𝐋𝐋:
.تم فرض قيمة الحمل الحي على القبة
WLL=0.5 KN/m 2
3. Calculation Radius of Sphere
(R):
L2
+ h2 13.22 2
R= 4 +5
4
2h = 2×5
= 6.856 m
4. Calculate semi central angle (∅):
∅ at f = 0
Where: f=Rise of the dome.
R−f 6.856−0
∅ = cos−1 = cos−1 =0
R 6.856
∅ at f=5 m
∅ = cos−1 R−f
= cos−1 6.856−5 = 74.29°
R 6.856
( 2.3.1القوة الداخلية Internal( )Force
تأثير 𝟏𝐓 𝟐𝐓& على القبة. شكل ()3-1
1. Meridian force (𝐓𝟏):
لتوضيح خطوات و طريقة الحل سنقوم بحساب T1و T2عند:
Ø = 74.29° and f = 5m
شكل ) (1-4يوضح ( )S.A&P.Aعلى القبة.
r =R sin∅ = 6.856 × sin 74.29=6.6 m
Surface Area (S.A) = 2πRf = 2π × 6.856 × 5 = 215.38 m2
Projected Area (P.A) = πr2 = π × 6.62 = 136.84 m2
Total load on dome at ∅=74.29°
W∅ = WDLS. A + WLLP. A
W∅ = 2.9 × 215.38 + 0.5 × 136.84 = 963.022 KN
W∅ 693.022
T1 = = = 17.36 KN/m′ (comp. )
πr sin ∅ 2π×6.6 sin 74.29
2. Ring force (𝐓𝟐)
𝑍 = WDL cos ∅ + WLL cos ∅2
:حيث
. محصلة القوى الخارجية العمودية على وحدة المساحات من السطحZ:
)Z(. ( يوضح محصلة القوى1-5) شكل
z = 2.9 cos 74.29 + 0.5 cos 74.292 = 0.542 KN/m2
T2 = (Z × R) − T1 = (0.542 × 6.856) − 17.36 = −13.63 KN/m′
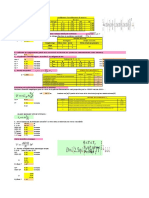
Table 1-2 show meridian and ring force due to (DL, LL).
R F Ø R S.A P.A WØ T1 Z T2
(m) (m) (m) (𝐦𝟐) (𝐦𝟐) (KN) 𝐊𝐍 𝐊𝐍 (KN/m’)
(𝐦′) (𝐦𝟐)
6.856 0 0 0 0 0 0 11.65 3.4 11.65
6.856 0.5 22.01 2.57 21.53 20.756 72.83 12.03 2.40 4.44
6.856 1 31.33 3.56 43.07 39.93 144.898 12.43 2.40 4.06
6.856 1.5 38.62 4.27 64.61 57.54 216.16 12.87 2.57 4.76
6.856 2.5 50.55 5.29 107.69 88.05 356.34 13.87 2.24 1.54
6.856 2.7 53.20 5.49 118.46 94.70 390.89 14.14 2.06 0.018
6.856 3 55.77 5.66 129.23 100.95 425.25 14.43 1.31 -5.41
6.856 3.5 60.69 5.97 150.77 112.28 493.38 15.06 1.47 -4.94
6.856 4 65.38 6.23 172.31 122.04 560.72 15.74 1.56 -5.05
6.856 4.5 69.90 6.43 193.84 130.23 627.27 16.51 0.54 -12.75
6.856 5 74.29 6.6 215.38 136.84 693.04 17.36 0.53 -13.66
)DL,LL(. ( مخطط قوى الضغط الشد على القبة نتيجة1-7) شكل
in Stress for (Check )Concrete التحقق من إجهادات الضغط و الشد3.3.1(
compression
يتم التحقق من إجهادات الضغط والشد لتحديد إذا ما كانت الخرسانة تستحمل ال
method limits .Ultimate المؤثرة عليها باستخدام طريقةstresses
o From table 1-2
The maximum meridian force (T1) = 17.36 KN/m′
The maximum ring force (T2) = −13.66 KN/m′
1. compression stresses:
Actual ultimate limit comp. stresses in concrete:
1.5T1 1.5×17.36
ts = 1000×0.1 = 0.2604 mpa
Allowable ultimate limit comp. stresses:
0.4 fc′ = 0.4 × 20 = 8 mpa
:مالحظه
allowable. لألسطح القشرية نأخذ نصف قيمةBuckling حتى نضمن عدم حدوث
8
= 4 mpa
2
∴ Allowable Ultimate Limit comp. stresses =4mpa > Actual ultimate
limit comp. stresses=0.2604mpa
2. Tensile stresses:
Actual tensile ring stresses in concrete= 1.5×13.66
= 0.205 mpa
1000×0.1
Allowable tensile stresses in concrete = 0.5√fc′ = 2.23 mpa
∴Allowable tensile stresses= 2.23 mpa > Actual tensile stresses= 0.205 mpa
∴Use ts =100mm
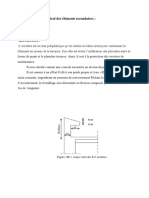
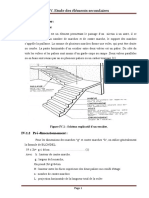
Ring of Analysis (Structure )Beam التحليل اإلنشائي الكمرة الحلقية5.1(
Ring on Loads (Calculating )Beam األحمال على الكمرة الحلقية1.5.1(
From table 1-2 Maximum compression force T1 = 17.36 at ∅ = 74.29°
KN
m′
شكل ) (1-9المركبة األفقية والرأسية.
نقوم بتحليل ( )T1الى مركبتين رأسية ( )Vومركبة افقيه ()Hكما هو مبين في شكل(1-9).
1.المركبة الرأسية )V(:
beam verticalوتصمم على كل من المربكة الرأسية لقوة ( )T1تنتقل الى
).(torsion,shear,B.M
V = T1 sin ∅ = 17.36 sin 74.29 = 16.72 KN/m
2.المربكة االفقية )H(:
المركبة االفقية لقوة ( )T1نت تقل الى beam horizontalوتصمم على tension) .(normal
H = T1 cos ∅ = 17.36 cos 74.29 = 4.7 KN/m
3.تحديد الطول الصافي للكمر الحلقية )L(:
=L
πD , n=8
n
π × 13.2
=L = 5.18 m
8
Where:
n: number of supports for the ring beam.
L: clear span between dome supports.
(Minimum Depth of Ring أقل عمق للكمرة الحلقية2.5.1(
Beam)
. متر وهي مستمرة من االتجاهين5..8 الطول الصافي للكمرة الح قل ية هو
From Table B-2:
Table B-2 Minimum Thickness of Beams and One-Way Slabs.
مستمر من جهة
بسيطة اإلرتكاز مستمرة من الجهتين
واحدة كابولي
Member Simply ends Both
One end Cantilever
supported continuous
continuou
s
Beams
or Ln Ln Ln Ln
ribbed 16 18.5 21 8
one-way
slabs
Solid Ln Ln Ln Ln
one- way 20 24 28 10
slabs
Fy
+ (0.4 ) لغير ذلك يتم ضرب القيم فيFy=420، Fy( )mpa هذه القيم هي إلجهاد حديد
700
(Both
h ends continuous)
span L 5.18×103
min = 24
= 24
= 215 mm
For vertical beam (Bv) use: depth (h) =450 mm and width (b) =300 mm
For horizontal beam (Bh) use: depth (h) =250mm and width (b) =550mm
on (Loads )Beams األحمال على الكمرات3.5.1(
1. loads on vertical beam (𝐁𝐯):
Weight of beam (Bv)= b × h × γc = 0.45 × 0.3 × 24 = 3.24 kN/m′
Weight of beam (Bh)= b × h × γc = 0.25 × 0.25 × 24 = 1.5 kN/m′
W = O. W. Bv + O. W. Bh + V = 3.24 + 1.5 + 16.72 = 21.46 KN/m′
P = W × 2πr = 21.46 × 2π × 6.6 = 890 KN
2. loads on Hor. beam (𝐁𝐇):
تؤثر علىnormal( )force على شكل.Horz( Bh ) Beam ) تنتقل الىT1( ) لقوةH( المركبة االفقية
.قطاع الكمرة
H = T1cosθ = 17.36 cos74.29 = 4.7 KN/m
Normal tension force on Bh:
T = H × r = 4.7 × 6.6 = 31.02 KN
Table B-3 Force and moment on ring beam.
Max.
Central
Load Max. Max. Bending Moment Torsional
No. of angle
on each Shearin Moment
supports
suppor g Force At C.L of At C.L of
t Span column
n R Qmax M+Ve M−Ve Mt max θ
4 P/4 P/8 0.0176 Pr − 0.0322 Pr 0.0053 Pr 19° 21`
6 P/6 P12 0.0075 Pr − 0.0148 Pr 0.0015 Pr 12° 44`
8 P/8 P/16 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟒𝟐 𝐏𝐫 − 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟖𝟑 𝐏𝐫 𝟎. 𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟔 𝐏𝐫 𝟗° 𝟑𝟑`
10 P/10 P/20 0.0032 Pr − 0.0052 Pr 0.0004 Pr 7° 36`
12 P/12 P/24 0.0019 Pr − 0.0037 Pr 0.0002 Pr 6° 21`
3. maximum bending moment:
From Table B-3 : using number of supports n=8
Max. M+ve = 0.0042 × p × r = 0.0042 × 890 × 6.6 = 24.7 KN. m
Max. M−ve = 0.0083 × p × r = 0.0083 × 890 × 6.6 = 48.8 KN. m
4. maximum torsional moment:
From Table B-3:
Max. Mt = 0.0006 × p × r = 0.0006 × 890 × 6.6 = 3.6 KN. m
5. maximum shearing
force: From Table B-3:
Load on each support= P = 890 = 112 KN
n 8
6. Calculation of corresponding (Q):
التي يتم بها تصميمmax( )torsion عند النقطة التي يوجد بهاshear( )force
وهي قيمة ال
Qmax
force) torsion and .(Shear الكانات لمقاومة كل من
P 890
= = = 55.63 KN
16 16
Central angle ∅ = 9.55°
π
X = r∅ π
= 6.6 × 9.55 × = 1.1 m
180
180
Qcorr = Qmax − W × X = 55.63 − (21.46 × 1.1) = 32.1 KN
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapitre 5Document36 pagesChapitre 5Walid MelikPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre6 ExoDocument13 pagesChapitre6 ExoMacrem MacremPas encore d'évaluation
- Etude NervureDocument15 pagesEtude NervureMalekMsakni100% (1)
- Exercices d'optique et d'électromagnétismeD'EverandExercices d'optique et d'électromagnétismeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Attachment 1Document41 pagesAttachment 1Sarah BhmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Acrotere + Plancher (Corrigé)Document9 pagesAcrotere + Plancher (Corrigé)Idir MoslemPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul Des PannesssssDocument17 pagesCalcul Des Pannesssssamal100% (1)
- VERIFICCATION - TraverseDocument41 pagesVERIFICCATION - TraverseHp MacPas encore d'évaluation
- TD5 Flexion (1)Document12 pagesTD5 Flexion (1)Malak BouhadidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercices d'intégrales de lignes, de surfaces et de volumesD'EverandExercices d'intégrales de lignes, de surfaces et de volumesPas encore d'évaluation
- TD Effort TranchantDocument10 pagesTD Effort TranchantStéphane FotsingPas encore d'évaluation
- Radier General 03Document13 pagesRadier General 03medsonic005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre 03Document58 pagesChapitre 03Ahmed InfirmierPas encore d'évaluation
- Note de Calcul RadierDocument2 pagesNote de Calcul RadierFATMA0% (1)
- MAT - Indices de Performances - Comportement Des Poutres en FlexionDocument13 pagesMAT - Indices de Performances - Comportement Des Poutres en FlexionJunior BoumPas encore d'évaluation
- Exemple de Calcul de RadierDocument6 pagesExemple de Calcul de RadierRita Nour71% (7)
- AcrotèreDocument9 pagesAcrotèreAhmad BabiPas encore d'évaluation
- L'acrotéreDocument9 pagesL'acrotéreAbdelali SolPas encore d'évaluation
- Etude de La PileDocument17 pagesEtude de La PileFousma SmailPas encore d'évaluation
- Etude de La PileDocument3 pagesEtude de La PileFaTima Aries SlaKta100% (1)
- Compte Rendu TP4 Pendule Elastique PDFDocument5 pagesCompte Rendu TP4 Pendule Elastique PDFOussama hartley100% (1)
- Calcul Du Voile PériphériqueDocument8 pagesCalcul Du Voile Périphériquemadjid tighiltPas encore d'évaluation
- De CopoleDocument17 pagesDe Copolefazialgc96% (24)
- AcrotereDocument22 pagesAcrotereMourad Taj71% (7)
- Calcule Des Charge EsquisseDocument15 pagesCalcule Des Charge Esquisseaymenmizouni13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cours Radier GeneralDocument20 pagesCours Radier GeneralAhmad ZreikPas encore d'évaluation
- Pou UtreDocument8 pagesPou Utrelaila lougaghi100% (1)
- Etude Des Éléments Secondairess123 ADocument29 pagesEtude Des Éléments Secondairess123 AAhmed HAMIDPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Elements EcondairesDocument37 pages4 Elements EcondairesmidouPas encore d'évaluation
- Exemple CisaillementDocument10 pagesExemple Cisaillementafaf sadranePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre 4 Applications Poteau À TreillisDocument26 pagesChapitre 4 Applications Poteau À TreillisAmir Mohammed el amine AmriPas encore d'évaluation
- Exemples Patrick PaultreDocument41 pagesExemples Patrick Paultremostefaoui mohammed100% (1)
- Ferr VOILDocument8 pagesFerr VOILAhmed HAMIDPas encore d'évaluation
- Series de TD S5Document22 pagesSeries de TD S5abdelhak AouadiPas encore d'évaluation
- TD Chapitre-08Document6 pagesTD Chapitre-08Francis Zenwan Asouan DessoignyPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul Des Dalles MixtesDocument7 pagesCalcul Des Dalles MixtesYounes TaoufikPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications Poteau À Treillis Pour Envoie en LigneDocument26 pagesApplications Poteau À Treillis Pour Envoie en Ligne5pzpz7tm2pPas encore d'évaluation
- Étude 2eme Variante de ViaducDocument78 pagesÉtude 2eme Variante de ViaducSam BenPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Examen BlancDocument11 pagesSolution Examen BlancChristina SawdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensionnement Des Voiles - CopieDocument5 pagesDimensionnement Des Voiles - CopiechaoukiPas encore d'évaluation
- Etude N°11Document10 pagesEtude N°11Ngoné MbayePas encore d'évaluation
- Bloc D'angle R+6Document31 pagesBloc D'angle R+6farid RezigPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini-Projet BP 3ITDocument87 pagesMini-Projet BP 3IThasna zahriPas encore d'évaluation
- Note de Calcul Reservoir 1000 m3Document17 pagesNote de Calcul Reservoir 1000 m3azddine100% (1)
- Dalle PleineDocument10 pagesDalle PleineMohamed Taher JebariPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPITRE II TRACTION Et COMPRESSIONDocument8 pagesCHAPITRE II TRACTION Et COMPRESSIONCapitno PhilipPas encore d'évaluation
- Problèmes BAEL Poutres (Corrigé)Document8 pagesProblèmes BAEL Poutres (Corrigé)lferdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre - 3-Les Éléments SecondairesDocument81 pagesChapitre - 3-Les Éléments SecondairesAbdelhak GuettiPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul Des DallesDocument18 pagesCalcul Des Dallesmadjid tighiltPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-Plancher 11Document25 pages4-Plancher 11ca va bienPas encore d'évaluation
- M''BDocument17 pagesM''BMourad GcvPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul D'acrotèreDocument8 pagesCalcul D'acrotèreWarda JoryPas encore d'évaluation
- Support Melody Eurocode 8 Initiation 1jDocument68 pagesSupport Melody Eurocode 8 Initiation 1jBayari ArPas encore d'évaluation
- Coefficient RDocument3 pagesCoefficient RAbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Etude Au vent-RNV2013rev01Document11 pagesEtude Au vent-RNV2013rev01AbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Noeud Poteau-PoutreDocument2 pagesNoeud Poteau-PoutreAbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Mini LogicielDocument12 pagesMini LogicielAbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- FerraillageDocument1 pageFerraillageMoh LahPas encore d'évaluation
- NOTE DE CALCUL - MosquéeDocument72 pagesNOTE DE CALCUL - MosquéeAbdou100% (2)
- Etudes Sismique 12Document10 pagesEtudes Sismique 12AbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul Des Charge de Vent Pour Un Bâtiment Rectangulaire À Toiture À Deux Versant Selon RNV99Document32 pagesCalcul Des Charge de Vent Pour Un Bâtiment Rectangulaire À Toiture À Deux Versant Selon RNV99Civil Abdou0% (1)
- Note de CalculDocument34 pagesNote de Calculmohamed senoussiPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul Des Coeficient de Maoration DynamiqueDocument12 pagesCalcul Des Coeficient de Maoration DynamiqueAbdou100% (1)
- Poutre Rectangulaire - Justification À L'effort TranchantDocument1 pagePoutre Rectangulaire - Justification À L'effort Tranchantmakakk100% (1)
- Minaret FacebookDocument3 pagesMinaret FacebookOussama AMARIPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - Poutre Continue M-CaquotDocument1 page3 - Poutre Continue M-CaquotSaloua Zinouch100% (4)
- Minaret FacebookDocument3 pagesMinaret FacebookOussama AMARIPas encore d'évaluation
- Poutre Rectangulaire ELSDocument1 pagePoutre Rectangulaire ELSBrahim MabasPas encore d'évaluation
- Semelles IsoDocument1 pageSemelles IsoAMINAPas encore d'évaluation
- Conception Et Calcul Dun PontDocument118 pagesConception Et Calcul Dun PontAbdou100% (1)
- CH 2 Etude Au VentDocument16 pagesCH 2 Etude Au VentHamou MelloulPas encore d'évaluation
- Poutreent Els EluDocument4 pagesPoutreent Els EluSaid JabirPas encore d'évaluation
- Poutre Rectangulaire ELUDocument3 pagesPoutre Rectangulaire ELUSadok KzadriPas encore d'évaluation
- Semelle Fillante Fille 3Document5 pagesSemelle Fillante Fille 3mustaphaPas encore d'évaluation
- ComplementDocument15 pagesComplementAbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Radier DDDocument8 pagesPDF Radier DDAbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Etude Comparative Entre La Methode Statique Et Model SpectralDocument104 pagesEtude Comparative Entre La Methode Statique Et Model SpectralAbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours BAEL 91 Modifié 99 PDFDocument104 pagesCours BAEL 91 Modifié 99 PDFNaoufel Mbarki67% (3)
- Étude Comparative Entre SAP2000 Et ROBOBAT Pour Un Bâtiment en BA, en Utilisant Les Résultats Du Modèle RéduitDocument91 pagesÉtude Comparative Entre SAP2000 Et ROBOBAT Pour Un Bâtiment en BA, en Utilisant Les Résultats Du Modèle RéduitAbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Batiment IndustrielDocument42 pagesBatiment IndustrielAbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- Robot Structural 2019Document30 pagesRobot Structural 2019AbdouPas encore d'évaluation
- TP7 Mesure de La Tension SuperficielleDocument4 pagesTP7 Mesure de La Tension Superficiellehamrouni saoudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Neodyl 5.2!17!2553 Avis TechniqueDocument14 pagesNeodyl 5.2!17!2553 Avis TechniqueMohammed BelabbesPas encore d'évaluation
- Exos HydrauliquesDocument7 pagesExos HydrauliquesOualid CatibPas encore d'évaluation
- Classements Feu Reflex 60 Euroclasses PDFDocument2 pagesClassements Feu Reflex 60 Euroclasses PDFDyhia Me-laPas encore d'évaluation
- Carnet de Ferraillage Poutres VoilesDocument7 pagesCarnet de Ferraillage Poutres VoilesNQT2430% (1)
- B1 Resistance Au Glissement Boulons HR 2Document2 pagesB1 Resistance Au Glissement Boulons HR 2lecaudeydidierPas encore d'évaluation
- TP 3Document2 pagesTP 3medjnahePas encore d'évaluation
- Proposition de These 2023Document4 pagesProposition de These 2023Benoit KougbiPas encore d'évaluation
- TD de Rupture Fatigue FluageDocument7 pagesTD de Rupture Fatigue Fluagesalah mohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Curs3 PDFDocument0 pageCurs3 PDFAlexandru TofanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre 04 - Poutres ContinuesDocument15 pagesChapitre 04 - Poutres ContinuesrabehiPas encore d'évaluation
- Importance de La Géotechnique Et Contrôle de Qualité Des Matériaux Dans L'acte de Construire - Hanane EL BOUZAKRI EL IDRISSIDocument35 pagesImportance de La Géotechnique Et Contrôle de Qualité Des Matériaux Dans L'acte de Construire - Hanane EL BOUZAKRI EL IDRISSIouattara.o.madinaPas encore d'évaluation
- La Methode de Cross Et Le Calcul Pratique Des Constructions Hyperstatiques P. GharonDocument5 pagesLa Methode de Cross Et Le Calcul Pratique Des Constructions Hyperstatiques P. Gharonfedor remyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluviale v2Document179 pagesFluviale v2Amin TahriPas encore d'évaluation
- Batiment Version Finale PDFDocument49 pagesBatiment Version Finale PDFHamzaBftl100% (4)
- Série 1Document2 pagesSérie 1Med ElyoubiPas encore d'évaluation
- Stage 2 Éme FinaleDocument52 pagesStage 2 Éme FinaleAly AyouniPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul Simsmique Pour Construction en Feuille ExcelDocument8 pagesCalcul Simsmique Pour Construction en Feuille ExcelHicham BadisPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre I Ecoulement A Surface LibreDocument5 pagesChapitre I Ecoulement A Surface LibreNoureddine MerahPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapport TakuDocument18 pagesRapport TakumarthialprofPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapport de Stage de Fin D'études PDFDocument71 pagesRapport de Stage de Fin D'études PDFMahdaoui MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Étude Des Aciers PDFDocument10 pagesÉtude Des Aciers PDFHassineMarwenePas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete XzaDocument3 pagesConcrete XzadfghjkPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrogeologie 1Document91 pagesHydrogeologie 1maroua boudaliPas encore d'évaluation
- NDC MS-02Document11 pagesNDC MS-02Med El Hadi AbidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Plan D'intervention Batisse 10 Rass Jnan-ObjetDocument1 pagePlan D'intervention Batisse 10 Rass Jnan-ObjetSadiki NabilPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel de Calcul de Dalle Pleine BaelDocument12 pagesExcel de Calcul de Dalle Pleine BaelBilel ChaabenPas encore d'évaluation
- Conditions RemblaiDocument19 pagesConditions RemblaiWissal ElbarkaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Partie BDocument153 pagesPartie BSimon DubePas encore d'évaluation
- PV de Chantier D'octobreDocument3 pagesPV de Chantier D'octobrecivil ingénieur learningPas encore d'évaluation
- Le logement contemporain: Entre confort, désir et normes (1995-2012)D'EverandLe logement contemporain: Entre confort, désir et normes (1995-2012)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revue des incompris revue d'histoire des oubliettes: Le Réveil de l'Horloge de Célestin Louis Maxime Dubuisson aliéniste et poèteD'EverandRevue des incompris revue d'histoire des oubliettes: Le Réveil de l'Horloge de Célestin Louis Maxime Dubuisson aliéniste et poèteÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (3)
- Gestion des déchets solides urbains: aperçu, concepts, applications et perspectivesD'EverandGestion des déchets solides urbains: aperçu, concepts, applications et perspectivesPas encore d'évaluation
- Comment on construit une maison: Histoire d'une maison illustrée de soixante deux dessins par Viollet-le-DucD'EverandComment on construit une maison: Histoire d'une maison illustrée de soixante deux dessins par Viollet-le-DucPas encore d'évaluation
- Med-chains & Covid -19: Solutions innovantes pour les pandémiesD'EverandMed-chains & Covid -19: Solutions innovantes pour les pandémiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Architecte et architecture: Les Grands Articles d'UniversalisD'EverandArchitecte et architecture: Les Grands Articles d'UniversalisPas encore d'évaluation
- Poterie: Les Grands Articles d'UniversalisD'EverandPoterie: Les Grands Articles d'UniversalisPas encore d'évaluation