Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
01 Fiche Sur Les Equations Irrationnelles
Transféré par
Sadibou DiakhateCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
01 Fiche Sur Les Equations Irrationnelles
Transféré par
Sadibou DiakhateDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
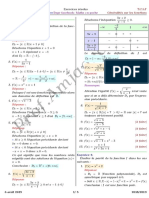
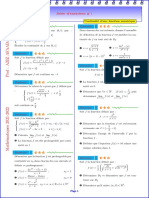
Équations irrationnelles
√ √
1 Équation du type A(x) = B(x).
Pour que cette équation soit définie, il faut que :
A(x) > 0 et B(x) > 0
Cela nous donne donc l’ensemble de définition D f de l’équation.
Pour résoudre, on élève au carré, en ayant soin de dire que x ∈ D f
Exemple : Soit l’équation suivante :
√ √
4x − 1 = 3 − x
On détermine l’ensemble de définition D f
1
( " #
4x − 1 > 0 x> 1
Df = ; 3
⇐⇒ 4 d’où
3−x>0
x63
4
On élève au carré :
x ∈ Df et 4x − 1 = 3 − x
5x = 4
4
x=
5
( )
4 4
∈ Df donc S =
5 5
√
2 Équation du type A(x) = B(x).
Pour que cette équation soit définie, il faut que :
A(x) > 0 et B(x) > 0
En fait la première condition est superflue car si l’on élève au
carré l’équation, on obtient :
A(x) = [B(x)]2
Si l’égalité est vérifiée alors A(x) est nécessairement positif ou nul.
Conclusion : l’équation est équivalente à : B(x) > 0 et A(x) = [B(x)]2
Paul Milan 1 sur 2 Première S
Exemple : Soit l’équation suivante :
√
x2 − 1 = x + 2
On détermine l’ensemble de définition :
x + 2 > 0 donc x > 2 soit D f = [−2; +∞[
On élève au carré
x ∈ Df et x2 − 1 = (x + 2)2
x2 − 1 = x2 + 4x + 4
−4x = 5
5
x=−
4
( )
5 5
− ∈ Df donc S = −
4 4
Paul Milan 2 sur 2 Première S
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- LC 21-080Document4 pagesLC 21-080Simon HoudePas encore d'évaluation
- Minhaj SalafiDocument18 pagesMinhaj SalafisososopiPas encore d'évaluation
- Avoir Des Loisirs Dans Un Espace UrbainDocument2 pagesAvoir Des Loisirs Dans Un Espace UrbainonerPas encore d'évaluation
- Livre de L'interne - HématologieDocument738 pagesLivre de L'interne - HématologieMed100% (1)
- 01 Cours Equation IrrationnellesDocument3 pages01 Cours Equation Irrationnellesaaron mufukPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Cours Equation IrrationnellesDocument3 pages01 Cours Equation IrrationnellesadilPas encore d'évaluation
- AleaFonctionS1 1Document1 pageAleaFonctionS1 1Sanae SanonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours Chapitre de RappelsDocument10 pagesCours Chapitre de Rappelslarbaouiabdelmajid475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Les Fonctions Numériques (Exercices Résolus)Document3 pagesLes Fonctions Numériques (Exercices Résolus)Said AmjaouchPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Ctrle 16 10 2017 CorrectionDocument3 pages01 Ctrle 16 10 2017 Correctionbonel dafonsecaPas encore d'évaluation
- KS 1Document2 pagesKS 1Sami BEN AISSIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercices Corrigés Chapitre 7Document1 pageExercices Corrigés Chapitre 7Emma GALESPas encore d'évaluation
- DS Fcts Limites CDocument2 pagesDS Fcts Limites Csamriboubacar69Pas encore d'évaluation
- Devoir D 1 s1 (2BAC) PDFDocument2 pagesDevoir D 1 s1 (2BAC) PDFEnim SsayPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre - Mathématique - Différentielle de FonctionDocument8 pagesChapitre - Mathématique - Différentielle de FonctionHumble Art100% (1)
- 1C 1D2T 23 24 CorrectionDocument16 pages1C 1D2T 23 24 CorrectionCherif AdeossiPas encore d'évaluation
- NOM/Prénom: Amphi Et Groupe de TD:: CO Estion Xamen ArtielDocument4 pagesNOM/Prénom: Amphi Et Groupe de TD:: CO Estion Xamen Artieldjerambete saint alfredPas encore d'évaluation
- Etude G en Erale Des Fonctions: CFI Ann Ee Scolaire 2017 2019 DE TorokoroDocument9 pagesEtude G en Erale Des Fonctions: CFI Ann Ee Scolaire 2017 2019 DE TorokoroDaouda SangarePas encore d'évaluation
- DM5 Corr RDDocument3 pagesDM5 Corr RDhamdimioPas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0010.Document2 pagesWa0010.yassmine akkiouiPas encore d'évaluation
- TD N°10 (Dérivabilité) - 1Document2 pagesTD N°10 (Dérivabilité) - 1Salma FarjymPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Ctrle 22 11 2012Document2 pages04 Ctrle 22 11 2012Lima MariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre 6 Fonctions Du 2nd DegrDocument4 pagesChapitre 6 Fonctions Du 2nd Degrmayeulg2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Déterminer Le Nombre de Solutions D'une Équ : AccueilDocument8 pagesDéterminer Le Nombre de Solutions D'une Équ : AccueilGuina GueyePas encore d'évaluation
- TD-N-1-limites-conti Serie 1 2SM-1 - 230924 - 114121Document6 pagesTD-N-1-limites-conti Serie 1 2SM-1 - 230924 - 114121RcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Des Exercices - Limites Et Continuité-Ts - SunudaaraDocument19 pagesSolution Des Exercices - Limites Et Continuité-Ts - SunudaaraJule BaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Fonctions1 CoursDocument5 pages2 Fonctions1 Courskeassemon danielle mondesirPas encore d'évaluation
- Fonction de Reference - Correction PDFDocument4 pagesFonction de Reference - Correction PDFabdlkarimPas encore d'évaluation
- DC2 3SC Mme KHANFIR 2015 11Document2 pagesDC2 3SC Mme KHANFIR 2015 11Chokri BesbesPas encore d'évaluation
- DS04 Correction TSpeDocument5 pagesDS04 Correction TSpewilldavidtchiakpe0Pas encore d'évaluation
- DLSM 1Document2 pagesDLSM 1thisisarwa77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Devoir DL Tan CorrectionDocument5 pagesDevoir DL Tan CorrectionDJIL BENPas encore d'évaluation
- Corriges Maths S 02-2Document4 pagesCorriges Maths S 02-2Manar BahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercice 01Document1 pageExercice 01Zakaria EzziyadiPas encore d'évaluation
- LogarithmeDocument12 pagesLogarithmeOthnielPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie Fonctions NumeriquesDocument3 pagesSerie Fonctions Numeriquesymvffvrqq2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Équations Et Inéquations Du Premier DegreDocument2 pagesÉquations Et Inéquations Du Premier Degrebeebac20090% (1)
- Limite Et Continuité - CorrectionDocument7 pagesLimite Et Continuité - CorrectionmohamedechchbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Correction RévisionDocument3 pagesMaths Correction Révisionclotildelaboury0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes Calcul Differentiel 5Document10 pagesNotes Calcul Differentiel 5assanediaibndjibydiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Devoir N1 Semestre 1 Maths 2eme Bac Sciences PC Word Modele - 2Document1 pageDevoir N1 Semestre 1 Maths 2eme Bac Sciences PC Word Modele - 2abdellah faqdaniPas encore d'évaluation
- TD1 AnalyseNumeriqueDocument3 pagesTD1 AnalyseNumeriqueFreddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bac Blanc 2021 CorrigéDocument5 pagesBac Blanc 2021 Corrigésemroud dahbiaPas encore d'évaluation
- BTS Devoirs 2 LimitesDocument3 pagesBTS Devoirs 2 LimitesPuaimana IOANEPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronique de BaseDocument4 pagesElectronique de BaseHOUDAPas encore d'évaluation
- MATH1Document5 pagesMATH1Moulay CherifPas encore d'évaluation
- Series 1 FRDocument1 pageSeries 1 FRSanae Sanona100% (1)
- Cours Équation Inéquation 1er DegréDocument7 pagesCours Équation Inéquation 1er Degréfire robotPas encore d'évaluation
- Continuité D'une Fonction NumeriqueDocument2 pagesContinuité D'une Fonction NumeriqueMarouaneRimo100% (1)
- Corrige Caledonie j2 27 10 2022 DVDocument6 pagesCorrige Caledonie j2 27 10 2022 DVfan ClubPas encore d'évaluation
- Modèle MathématiqueDocument4 pagesModèle MathématiqueNizar KAOUACHIPas encore d'évaluation
- Dérivées Exercices Corrigés 03Document3 pagesDérivées Exercices Corrigés 03Louis FrançoisPas encore d'évaluation
- Limites Et Continuité (C) - 3ème Math - Série 1 (Nov) - 2020.2021Document4 pagesLimites Et Continuité (C) - 3ème Math - Série 1 (Nov) - 2020.2021Petra ShelbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepa Saint Jean: Analyse 1 Chapitre 3: Limites Et Continuit eDocument2 pagesPrepa Saint Jean: Analyse 1 Chapitre 3: Limites Et Continuit eMiguel AngePas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul de LimitesDocument2 pagesCalcul de LimitesClément AdandéPas encore d'évaluation
- All Lim ContinuiteDocument4 pagesAll Lim ContinuitetorkitaherPas encore d'évaluation
- DS4201920201M3 CorrectionDocument2 pagesDS4201920201M3 Correctionmelissa azrouPas encore d'évaluation
- 9-11-2020 - GR E-F Travaux Dirigés Corrigés Analyse MathématiqueDocument67 pages9-11-2020 - GR E-F Travaux Dirigés Corrigés Analyse Mathématiqueelouche yassine RafaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Suivi TomporelDocument2 pagesSuivi TomporelJamila LHMPas encore d'évaluation
- Série 1 PDFDocument9 pagesSérie 1 PDFZvyneebPas encore d'évaluation
- Série 1Document3 pagesSérie 1Oussema SKPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie D'exercices Limites D'une FonctionDocument4 pagesSerie D'exercices Limites D'une Fonctionmohmed elbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Homographique 2 1415Document1 pageHomographique 2 1415AbdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Leçons sur les séries trigonométriques : professées au Collège de FranceD'EverandLeçons sur les séries trigonométriques : professées au Collège de FrancePas encore d'évaluation
- Axtem Mag PRINTEMPS 2012Document16 pagesAxtem Mag PRINTEMPS 2012MTS_47Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rapport2 G2Document8 pagesRapport2 G2ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Sikadur® Injection LP: Fiche ProduitDocument3 pagesSikadur® Injection LP: Fiche Produitabdelali baaddouchPas encore d'évaluation
- Investir Dans Le Secteur Fruits Et Legumes Du MaliDocument23 pagesInvestir Dans Le Secteur Fruits Et Legumes Du MaliGregory MaigaPas encore d'évaluation
- RapportDocument25 pagesRapportMolka Ayechi100% (1)
- La DouleurDocument14 pagesLa DouleurSamantha Francisco RossettiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction À La Prothèse Partielle FixeDocument42 pagesIntroduction À La Prothèse Partielle FixeBit CoyinPas encore d'évaluation
- CAT EASY Catalogue e Sy PDFDocument20 pagesCAT EASY Catalogue e Sy PDFReda NariPas encore d'évaluation
- Charles Lancelin - Comment On Meurt-Coment On Nait (Les Deux Pôles de La Vie) (FR) PDFDocument101 pagesCharles Lancelin - Comment On Meurt-Coment On Nait (Les Deux Pôles de La Vie) (FR) PDFViviane Tjiovas100% (1)
- Eurocode 5 BASE DE DONNEESDocument10 pagesEurocode 5 BASE DE DONNEEScabreraPas encore d'évaluation
- Perception Et IllusionDocument3 pagesPerception Et IllusionSelma AddaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Épreuve 02 - Le SéismeDocument3 pages2 - Épreuve 02 - Le SéismeLįllÿ LįllÿPas encore d'évaluation
- BAROKA Mémoire Tourisme 2016Document127 pagesBAROKA Mémoire Tourisme 2016Josué BAROKA100% (1)
- Essai SPT Arvor 2010Document1 pageEssai SPT Arvor 2010Seif EddinePas encore d'évaluation
- TD Solution SYSTEME ENDOMEMBRANAIREDocument2 pagesTD Solution SYSTEME ENDOMEMBRANAIREahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Td2 Trans StatiqueDocument5 pagesTd2 Trans Statiquesara100% (1)
- MQS Science XIthDocument127 pagesMQS Science XIthKrishna KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - CCTP Ouvrage Oued GabesDocument14 pages3 - CCTP Ouvrage Oued GabesqsegaqgPas encore d'évaluation
- Mat2777 Examen Final H2020Document9 pagesMat2777 Examen Final H2020fahfaPas encore d'évaluation
- TD 03 CorrigéDocument5 pagesTD 03 CorrigéTaimocha FatiPas encore d'évaluation
- RB SCCDDocument36 pagesRB SCCDsirovic90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Le ZahirDocument3 pagesLe Zahirmounirnet100% (1)
- Gestion Des Déchets 22223 1 PDFDocument101 pagesGestion Des Déchets 22223 1 PDFbehdenna riyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manuel Qualité Agro-AlimentaireDocument16 pagesManuel Qualité Agro-AlimentaireSambouPas encore d'évaluation
- Pancreatite ÉemDocument8 pagesPancreatite ÉemInfirmier Santé PubliquePas encore d'évaluation
- Preuve Ponctuelle Obligatoire Eps - Bac GT - Livret Candidat - Tennis de Table - 2024 15860Document6 pagesPreuve Ponctuelle Obligatoire Eps - Bac GT - Livret Candidat - Tennis de Table - 2024 15860moussaidiabdouPas encore d'évaluation