Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Calcul Trigo Resume 1
Transféré par
El Mehdi Belbacha0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
67 vues1 pageTitre original
calcul trigo resume 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
67 vues1 pageCalcul Trigo Resume 1
Transféré par
El Mehdi BelbachaDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
Prof:Belbacha
CALCUL TRIGONOMETRIQUE
Année scolaire : 2022-23
1) Formules de transformations : 5) Transformations des produits en sommes.
1)Pour tous réels 𝑥 et 𝑦 on a : Pour tous réels 𝑥, 𝑦 on a :
𝑐𝑜𝑠 (𝑥 − 𝑦) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥. 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑦 + 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥. 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑦 (1) 1
𝑐𝑜𝑠 (𝑥 + 𝑦) = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥. 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑦 − 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥. 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑦 (2) 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥. 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑦 = [𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥 + 𝑦) + 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥 − 𝑦)]
2
𝑠𝑖𝑛 (𝑥 + 𝑦) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥. 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑦 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥. 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑦 (3) 1
𝑠𝑖𝑛 (𝑥 − 𝑦) = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥. 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑦 − 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥. 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑦 (4) 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥. 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑦 = − [𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥 + 𝑦) − 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥 − 𝑦)]
Pour tout réel 𝑥 on a : 2
𝑐𝑜𝑠(2𝑥) = 2𝑐𝑜𝑠²𝑥 − 1 et 𝑐𝑜𝑠(2𝑥) = 1 − 2𝑠𝑖𝑛²𝑥 1
𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥. 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑦 = [𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑥 + 𝑦) + 𝑠𝑖𝑛(𝑥 − 𝑦)]
𝑠𝑖𝑛(2𝑥) = 2𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥. 𝑐𝑜𝑠x 2
1 cos 2 x 1 cos 2 x La linéarisation d’une expression c’est de l’écrire
cos ² x et sin ² x sous la forme d’une somme.
2 2
x x 6 ) LES EQUATIONS TRIGONOMETRIQUES.
cos x 2 cos ² 1 cos x 1 2sin ² 1) Rappelles : k
2 2
x x a) cos x cos x0 x x0 2k ou x x0 2k
sin x 2sin cos
2 2 b) sin x sin x0 x x0 2k ou x x0 2k
2) Formules de la tangente. c) tan x tan x0 x x0 k
Soient 𝑥 et 𝑦 deux réels tels que :
2) L’équation : (𝐸): 𝑎𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 + 𝑏𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥 + 𝑐 = 0
Soient 𝑎 et 𝑏 deux réels non nuls on a :
𝑥≠ + 𝑘𝜋 et 𝑦 ≠ + 𝑘𝜋 on a :
2 2 Pour tout réel 𝑥 :
tan x tan y a
1) Si (𝑥+ 𝑦) ≠ +𝑘𝜋 alors tan x y a cos x b sin x a ² b² cos x
b
sin x
2 1 tan x tan y a ² b² a ² b²
2 tan x a cos x b sin x a ² b² cos cos x sin sin x
2) si 𝑥 ≠ + 𝑘 alors : tan 2 x
4 2 1 tan ² x
où le réel 𝜑 est déterminer par :
3) Si (𝑥 − 𝑦) ≠ + 𝑘𝜋 alors : a b
2 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜑 = et 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜑 =
a ² b² a ² b²
tan x tan y
tan x y a cos x b sin x a ² b² cos x
1 tan x tan y
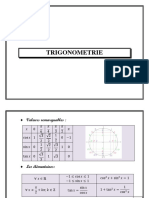
3) Les valeurs trigonométrique en fonction L’équation 𝑎𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑥 + 𝑏𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑥 + 𝑐 = 0 se ramène à :
x c
de : 𝑡 = 𝑡𝑎𝑛 ( ) 𝑐𝑜𝑠(𝑥 − 𝜑) =
2 a ² b²
Soit 𝑥 un réel tel que : 𝑥 ≠ 𝜋 + 2𝑘𝜋 On posant :
x
𝑡 = 𝑡𝑎𝑛 ( ) Si de 𝑥 ≠ + 𝑘𝜋 et 𝑥 ≠ 𝜋 + 2𝑘𝜋 on a :
2 2
1 t² 2t 2t
1) cos x 2) sin x 3) tan x
1 t ² 1 t ² 1 t²
4) Transformations des sommes en produits
Pour tous réels 𝑝 , 𝑞, on a :
pq pq
sin 𝑝 + sin 𝑞 = 2sin ( ) . 𝑐𝑜𝑠 ( )
2 2
pq pq
sin 𝑝 - sin 𝑞 = 2cos ( ) . sin ( )
2 2
pq pq
𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑝+𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑞 = 2𝑐𝑜𝑠 ( ). 𝑐𝑜𝑠 ( )
2 2
pq pq
𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑝- 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝑞 = -2sin ( ) . sin ( )
2 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Exercices Corrigés D'algorithmiqueDocument24 pagesExercices Corrigés D'algorithmiqueOverDoc88% (26)
- Carte Mémoire Tle D-2Document125 pagesCarte Mémoire Tle D-2Aida Mbodji90% (20)
- Examen Math2 Énoncé&Corrigé 1 LEDocument4 pagesExamen Math2 Énoncé&Corrigé 1 LEAla Ben AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ofppt: Examen de Fin de ModuleDocument4 pagesOfppt: Examen de Fin de ModuleJust to Try it100% (1)
- MAT1730 MAT1732 Notes de CoursDocument1 039 pagesMAT1730 MAT1732 Notes de CoursEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Details Et Points Singuliers MenuiseriesDocument103 pagesDetails Et Points Singuliers MenuiseriesZOGO LucPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulaire TrigoDocument3 pagesFormulaire TrigoMehdi Majid100% (1)
- MPC - OPE - IT - Cahier de Charges - V0.1 (Enregistré Automatiquement)Document37 pagesMPC - OPE - IT - Cahier de Charges - V0.1 (Enregistré Automatiquement)Dokat O5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul Trigonometrique Resume de Cours 1Document1 pageCalcul Trigonometrique Resume de Cours 1Mahfoud Natsu100% (4)
- 1sex Res TrigonometriDocument1 page1sex Res TrigonometriQuel Que Soit BiotifPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcul Trigonometrique Resume de Cours 1Document1 pageCalcul Trigonometrique Resume de Cours 1Walid ErraPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometrie 1sm NJBDocument1 pageTrigonometrie 1sm NJBAl Amine DiopPas encore d'évaluation
- Formules Trigonometriques 1 4Document1 pageFormules Trigonometriques 1 4ahmed tounsiPas encore d'évaluation
- TrigonométrieDocument6 pagesTrigonométrieArmandPas encore d'évaluation
- Sujet Bac 2023 Guinee Niger MathsDocument5 pagesSujet Bac 2023 Guinee Niger Mathsmr.4chiffrePas encore d'évaluation
- Epreuve Maths Concours Officiers Eaa 2018Document2 pagesEpreuve Maths Concours Officiers Eaa 2018Faticha Tichounei Chanei80% (5)
- Serie Révision Algèbre-Analyse Axlou Toth 1S1Document3 pagesSerie Révision Algèbre-Analyse Axlou Toth 1S1el hadji malick Dioum100% (11)
- Serie Dérivées Et Primitives TS1 WWW - Axloutoth.snDocument3 pagesSerie Dérivées Et Primitives TS1 WWW - Axloutoth.snTokyo 65Pas encore d'évaluation
- TD Maths CerferDocument2 pagesTD Maths CerferkaoenergiepPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours 2bac Biof 2023-2024 Abdel1Document56 pagesCours 2bac Biof 2023-2024 Abdel1jabarPas encore d'évaluation
- Devoir de Synthèse N°1 - Math - 3ème Technique (2011-2012) MR Horri NizarDocument2 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°1 - Math - 3ème Technique (2011-2012) MR Horri NizarMalek HarroumPas encore d'évaluation
- 2DDL 1Document2 pages2DDL 1hamzabenaldjia22Pas encore d'évaluation
- M.ka TS 2Document102 pagesM.ka TS 2Daro DiopPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie Equations Inequations Et Systemes 1S1 1S3 WWW - Axloutoth.snDocument7 pagesSerie Equations Inequations Et Systemes 1S1 1S3 WWW - Axloutoth.snthierno Diallo100% (2)
- Notions de Logique Exercices Non Corriges 7Document2 pagesNotions de Logique Exercices Non Corriges 7negroshima8120% (1)
- Fiche D'exercices Sur Primitives Et Calcul Integral-2 PDFDocument2 pagesFiche D'exercices Sur Primitives Et Calcul Integral-2 PDFMaryam Abdou Madougou100% (1)
- Exercice ExponentielleDocument3 pagesExercice ExponentielleRobert Urias Mahuclo TOSSAPas encore d'évaluation
- Logique Serie SM FRDocument2 pagesLogique Serie SM FRFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFE100% (1)
- Logique Serie SM FRDocument2 pagesLogique Serie SM FRنور هدىPas encore d'évaluation
- FICHE DE TDs DE MATHS (1ère D) (TRIGONOMETRIE)Document2 pagesFICHE DE TDs DE MATHS (1ère D) (TRIGONOMETRIE)desireeetoaPas encore d'évaluation
- TP TrigoDocument2 pagesTP TrigomichelprincesimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Series 01Document1 pageSeries 01تفعيل الي بايPas encore d'évaluation
- Formules TrigonometriquesDocument8 pagesFormules Trigonometriquesbarryhamadounallaye1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cours 2bac Biof 2023-2024 Omar Elkhayam(1)Document56 pagesCours 2bac Biof 2023-2024 Omar Elkhayam(1)elouahdaniabdelwahedPas encore d'évaluation
- Série Fonction Logarithme NépérienDocument2 pagesSérie Fonction Logarithme NépérienSeydina WadePas encore d'évaluation
- Sujet Math 2019 CorrigerDocument5 pagesSujet Math 2019 CorrigerdiayeloupPas encore d'évaluation
- Ana 10Document21 pagesAna 10Fadi DaouPas encore d'évaluation
- DM3 Corrig C3 A9Document12 pagesDM3 Corrig C3 A9justedjenontin9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fiche Nâ°1Document3 pagesFiche Nâ°1karispaul24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Série N°1 1S2LBD2023Document2 pagesSérie N°1 1S2LBD2023falilouPas encore d'évaluation
- CP TrigoDocument1 pageCP Trigoamadougadji07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Devoir de Synthèse N°1 - Math Limites, Continuité Et Trigonométrie - 3ème Technique (2014-2015) MR Salah HannachiDocument3 pagesDevoir de Synthèse N°1 - Math Limites, Continuité Et Trigonométrie - 3ème Technique (2014-2015) MR Salah HannachiAhmed AminePas encore d'évaluation
- BAC 1 Exercices en Logique MathématiquesDocument1 pageBAC 1 Exercices en Logique MathématiquesSte ExpertisePas encore d'évaluation
- Intégrales 4ème MathématiquesDocument9 pagesIntégrales 4ème MathématiquesIbrahima Diagne DiengPas encore d'évaluation
- Sougane Exo Fonctions Logarithmes-Fonctions Exponentielles-1Document8 pagesSougane Exo Fonctions Logarithmes-Fonctions Exponentielles-1Anges bryce mouchiPas encore d'évaluation
- TD N°1 Limites, Continuité Et Dérivation-1Document3 pagesTD N°1 Limites, Continuité Et Dérivation-1Samba SallPas encore d'évaluation
- Devoir Maion N°4Document1 pageDevoir Maion N°4Redouan AfoulloussePas encore d'évaluation
- corrigé TD 3Document11 pagescorrigé TD 3kiwanmarylynn3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Formulaire Trigo b2Document2 pagesFormulaire Trigo b2exaucemuland3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution de Fiche TD4Document6 pagesSolution de Fiche TD4star1coachPas encore d'évaluation
- Cycle INGENIEUR - MathsDocument1 pageCycle INGENIEUR - MathsGide BaniekPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapitre 2 - Varietes Et Coordonnees Geometrie I-1Document8 pagesChapitre 2 - Varietes Et Coordonnees Geometrie I-1hessoul100% (1)
- Epreuves- types Maths-BCST 2022 Questionnaire - Copie (2)Document21 pagesEpreuves- types Maths-BCST 2022 Questionnaire - Copie (2)Patrick NdayisabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ana 13Document18 pagesAna 13Smail RCAPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiche TD 2nde C Decembre 2023Document10 pagesFiche TD 2nde C Decembre 2023Gabriel OlajidePas encore d'évaluation
- Notions de Logique Exercices Non Corriges 1Document1 pageNotions de Logique Exercices Non Corriges 1chaymaezitouni7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notions de Logique Exercices Non Corriges 1Document1 pageNotions de Logique Exercices Non Corriges 1Khadija AkenouPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie Polynômes Apprentissage 1S1 RenfDocument4 pagesSerie Polynômes Apprentissage 1S1 Renfel hadji malick Dioum100% (1)
- Trigonometrie PDFDocument6 pagesTrigonometrie PDFShayma HammamiPas encore d'évaluation
- SUJET BAC 2023 GUINEE NIGER MathsDocument7 pagesSUJET BAC 2023 GUINEE NIGER MathsJean Michael AttemenePas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Trigonometrie Hyperbolique Corrige PDFDocument7 pages14 Trigonometrie Hyperbolique Corrige PDFاميرة النومPas encore d'évaluation
- Généralités Sur Les Fonctions NumériquesDocument2 pagesGénéralités Sur Les Fonctions NumériquesTaha El KouitPas encore d'évaluation
- COMPOSITION DE LA 1ère PERIODE 2022Document1 pageCOMPOSITION DE LA 1ère PERIODE 2022Adama DembePas encore d'évaluation
- Série limites et continuité 1S1Document4 pagesSérie limites et continuité 1S1Jaaw LufaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex de Révision TCDocument1 pageEx de Révision TCEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Etude Analytique Du Cercle Serie D Exercices 1Document2 pagesEtude Analytique Du Cercle Serie D Exercices 1El Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- SERIE 1 LN Les CoursDocument2 pagesSERIE 1 LN Les CoursEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nombres Complexes: 2° BAC .Sc. PhysiqueDocument2 pagesNombres Complexes: 2° BAC .Sc. PhysiqueEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Image IntervalleDocument2 pagesImage IntervalleEl Mehdi Belbacha100% (1)
- Blanc 7 2pc SVTDocument1 pageBlanc 7 2pc SVTEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie Derivabilite 1ere SMSXDocument1 pageSerie Derivabilite 1ere SMSXEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Diagnostiques 2BAC MATHS 2021 - 2022 LA JOCDocument2 pagesTest Diagnostiques 2BAC MATHS 2021 - 2022 LA JOCEl Mehdi Belbacha83% (6)
- Cours Calcule VectorielDocument5 pagesCours Calcule VectorielEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Diagnostique TC Biof 2021Document3 pagesTest Diagnostique TC Biof 2021El Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Image IntervalleDocument2 pagesImage IntervalleEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bilans TC LajocondeDocument3 pagesBilans TC LajocondeEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Serie 1sm Suites (2bac)Document1 pageSerie 1sm Suites (2bac)El Mehdi Belbacha100% (1)
- Manti 9Document1 pageManti 9El Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- ExpoDocument4 pagesExpoEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- TORSEURSDocument14 pagesTORSEURSEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysec00 PDFDocument93 pagesAnalysec00 PDFYoucef Br'sPas encore d'évaluation
- Fonction NumeriqueDocument3 pagesFonction NumeriqueEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Suites Fakri PDFDocument2 pagesSuites Fakri PDFMomoMassiaPas encore d'évaluation
- SuitesDocument1 pageSuitesEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- PL Avancée Nombres EntiersDocument41 pagesPL Avancée Nombres EntiersEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobydick Freestyles ParolesDocument3 pagesMobydick Freestyles ParolesEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elpr PDFDocument0 pageElpr PDFEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elpr PDFDocument0 pageElpr PDFEl Mehdi BelbachaPas encore d'évaluation
- SuitefoncDocument2 pagesSuitefoncAhmed RafiqiPas encore d'évaluation
- CG SVX039C FR 260 To 710 KWDocument88 pagesCG SVX039C FR 260 To 710 KWKhadija Fekih salemPas encore d'évaluation
- OGC Chap 3Document46 pagesOGC Chap 3Lengani Kader EvaricePas encore d'évaluation
- Informatique Et Societe QuebecDocument9 pagesInformatique Et Societe QuebecKalinatsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Informatique - Cours de XML - 124 Slides (Jacques Le Maitre) (Universite de Toulon)Document124 pagesInformatique - Cours de XML - 124 Slides (Jacques Le Maitre) (Universite de Toulon)bec souhilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theorie Des EnsemblesDocument10 pagesTheorie Des EnsemblesKhadija Ben MiledPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation EGFIDocument33 pagesPresentation EGFIbelkakarim98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Business Plan MfruitierDocument24 pagesBusiness Plan Mfruitierahmed hamza khabouzePas encore d'évaluation
- PowerWheels f150Document28 pagesPowerWheels f150celso marquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide LPKF 1 1Document7 pagesGuide LPKF 1 1abdo tmPas encore d'évaluation
- DSI1 - BDR - Contrôle #1 - Semestre 2 - 2020-2021 - CorrigéDocument2 pagesDSI1 - BDR - Contrôle #1 - Semestre 2 - 2020-2021 - CorrigéFattane RayhanePas encore d'évaluation
- Organigramme AIFE Dec 2023Document1 pageOrganigramme AIFE Dec 2023Adam ArbyPas encore d'évaluation
- R7 - Armare Pardoseli Extras - 7 PDFDocument1 pageR7 - Armare Pardoseli Extras - 7 PDFCristi RanjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Polycopie TP GE 2023Document51 pagesPolycopie TP GE 2023mariam.ouaaabedPas encore d'évaluation
- Systèmes MécatroniquesDocument44 pagesSystèmes MécatroniquesBOURAS Ihabe - بوراس إيهابPas encore d'évaluation
- Examencours 2ST Math5Document12 pagesExamencours 2ST Math5Denilson JosemirPas encore d'évaluation
- Limpact de La Digitalisation Sur La PerfDocument77 pagesLimpact de La Digitalisation Sur La PerfOumaima ElPas encore d'évaluation
- OCS Inventory & GLPI V.2 Installation Sur ... - OCS Inventory NGDocument22 pagesOCS Inventory & GLPI V.2 Installation Sur ... - OCS Inventory NGgnu slimPas encore d'évaluation
- Pistolet de Massage Musculaire, Cotsoco Massage GuDocument2 pagesPistolet de Massage Musculaire, Cotsoco Massage GuorelcreppyPas encore d'évaluation
- FeuilletageDocument28 pagesFeuilletageKarim AlamiPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 14001 2015 Partie VI Gérer Les RisquesDocument23 pagesISO 14001 2015 Partie VI Gérer Les RisquesGhassen DhouibiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cours SM en Ligne-ConvertiDocument72 pagesCours SM en Ligne-ConvertiAnfel CPas encore d'évaluation
- تصحيح اختبار الفصل الثالث -اللغة الفرنسية -الأولى ثانوي علوم تجريبيةDocument1 pageتصحيح اختبار الفصل الثالث -اللغة الفرنسية -الأولى ثانوي علوم تجريبية12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCC 1 0 0 FRDocument31 pagesMCC 1 0 0 FRDenis SpeicherPas encore d'évaluation
- L'Architecture D'u Routeur Et Les Commandes IOSDocument23 pagesL'Architecture D'u Routeur Et Les Commandes IOSomar ouhguaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4. Essais MecaniquesDocument9 pagesCH 4. Essais MecaniquesSimo Magri100% (2)
- Diplômes Et FormationsDocument1 pageDiplômes Et FormationsmohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 Identite VisuelleDocument10 pages06 Identite VisuelleOliver VADELEUXPas encore d'évaluation