Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Adaptation Posologique Antibiotiques Ir
Adaptation Posologique Antibiotiques Ir
Transféré par
mayna minouCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Adaptation Posologique Antibiotiques Ir
Adaptation Posologique Antibiotiques Ir
Transféré par
mayna minouDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
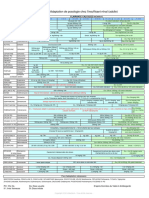
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
CLAIRANCE CALCULEE (mL.min-1)
Posologie usuelle
Spécialités DCI 0 à 10 11 à 15 16 à 20 21 à 30 31 à 40 41 à 50 51 à 60 >60
chez le patient normorénal
PENICILLINES (+INHIBITEURS BETA LACTAMASES)
1g/8h 1g puis 750mg/24h 1g puis 500mg/8h
CLAMOXYL PO Amoxicilline 1g/12h 1g puis 500mg/24h 1g puis 500mg/12h Pas d'adaptation posologique, Dmax = 6g/24h
2g/8h 1,5g/24h 3g/24h
100mg/kg/24h 25mg/kg/24h 50mg/kg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique,
CLAMOXYL IV Amoxicilline
200mg/kg/24h 50mg/kg/24h 100mg/kg/24h pour poso élevée, réaliser un suivi des concentrations plasmatiques
Amox + 1g/8h 1g puis 750mg/24h 1g puis 500mg/8h Pas d'adaptation posologique
AUGMENTIN PO
Ac clavulanique 2g/8h 1,5g/24h 3g/24h L'adaptation de la posologie s'effectue en fonction de l'amoxicilline
1g puis 500mg/12h
Amox + 1 g puis 500 mg /24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
AUGMENTIN IV 1g/8h Autres posos non
Ac clavulanique Autres posos non applicables L'adaptation de la posologie s'effectue en fonction de l'amoxicilline
applicables
12 à 24 MUI/j en 6 injections
EXTENCILLINE Benzathine 2MUI/4h (Cl 30-44)
ou 0,5 MUI/6h 1MUI/4h Pas d'adaptation posologique
(NSFP) benzylpénicilline 3MUI/4h (Cl 45-50)
en administration continue
50 mg/kg/jour (PO)
ORBENINE Cloxacilline Du/2 Pas d'adaptation posologique, Dmax = 4g/j
100 à 200 mg/kg/jour (IV)
BRISTOPEN Oxacilline Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
Phénoxymethyl-
ORACILLINE 1 MUI/8h Non donnée Pas d'adaptation posologique
pénicilline
PIPERACILLINE
Pipéracilline 4g/8h 3 à 4 g/12h 3 à 4 g/8h Pas d'adaptation posologique
PANPHARMA
Pipéracilline
TAZOCILLINE 4g/8h 3 à 4 g/12h 3 à 4 g/8h Pas d'adaptation posologique
+ Tazobactam
400 mg puis
SELEXID Pivmecillinam 400mg/8-12h 400 mg puis 200mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
200mg/8-12h
Pas d'adaptation
250mg/kg/24h
TICARPEN Ticarcilline 2g/24h 5g/12h 5g/8h posologique, Dmax :15-
(ticarcilline)
20g/24h
Pas d'adaptation
250mg/kg/24h
CLAVENTIN Ticarcilline + AC 1,5g/100mg /24h 3g/200 mg/12h 3g ou 5g/200 mg /8h posologique, Dmax :15-
(ticarcilline)
20g/24h
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 1 Copyright MedQual®
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
CLAIRANCE CALCULEE (mL.min-1)
Posologie usuelle
Spécialités DCI 0 à 10 11 à 15 16 à 20 21 à 30 31 à 40 41 à 50 51 à 60 >60
chez le patient normorénal
CEPHALOSPORINES
250mg/8h
ALFATIL Céfaclor 250-500mg/24h 250-500mg/12h Pas d'adaptation posologique, Dmax : 1500mg/24h
ou 375mg LP/12h
750mg/8-12h (Cl : <5ml/min)
KEFANDOL (NSFP) Céfamandole 3g/j, Dmax: 1,5g/4h 1,5g/6h (Cl 24-49 ml/min) Pas d'adaptation posologique
750mg/6h (Cl : 6-24ml/min)
500 mg puis
500 mg/72h (Cl<5ml/min)
CEFACIDAL 500 mg puis 250 mg/12h 500 mg puis 250 mg/6h
Céfazoline 0,5-1g/8-12h 500mg puis 250 mg/36h Pas d'adaptation posologique
(NSFP) ou 500 mg/24h ou 500 mg/12h
ou 500mg/48-72h (Cl 5-
10ml/min)
Céfépime 2g/12h 500 mg/24h 1 g/24h 2 g/24h
AXEPIM Céfépime Pas d'adaptation posologique
2g/8h 1g/24h 1g/12h 1g/8h
infection sévère
OROKEN Céfixime 200mg/12h 200 mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
Pas d'adaptation
CLAFORAN (NSFP) Céfotaxime 1-2g/8h 750mg-1,5g/24h 750mg-1,5g/12h 1-2g/12h
posologique
1-2g/8h
MEFOXIN (NSFP) Céfoxitine 0,5-1g/24-48h 1 à 2g/12-24h 1 à 2g/8-12h Pas d'adaptation posologique
(3-6g par jour)
Pas d'adaptation
ORELOX Cefpodoxime 100-200mg/12h 100 à 200 mg/24h 100 -200 mg/12-24h
posologique
ZINFORO Ceftaroline 600mg/12h 200 mg/12h 300 mg/12h 400 mg/12h Pas d'adaptation posologique
Ceftazidime
2g/8h 1g/24h 2g/24h 2 g/12h
/Discontinu Pas d'adaptation
FORTUM
Ceftazidime posologique
2g puis 6g/24h non évalué 2 g puis 1 g/24h 2 g puis 3 g/24h
/Continu
MABELIO Ceftobiprole 500mg/8h 250mg/24h 250mg/12h 500mg/12h Pas d'adaptation posologique
Ceftolozane
ZERBAXA 1g/0,5g/8h 500mg/250mg puis 100mg/50mg/8h 250mg/125mg/8h 500mg/250mg/8h Pas d'adaptation posologique
+ Tazobactam
ROCEPHINE Céftriaxone 1-2g/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique, risque d'inéfficacité si diminution posologie
ZINNAT PO Céfuroxime 250-500 mg/12h 250 à 500 mg/48h 250 à 500 mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posplogique
ZINNAT IV Céfuroxime 2-6g/24h 1000mg/48h 1000mg/24h 2g/24h
Pas d'adaptation
NEGABAN Témocilline 2g/8-12h 500mg/24h 1g/24h 1g/12h
posologique
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 2 Copyright MedQual®
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
CLAIRANCE CALCULEE (mL.min-1)
Posologie usuelle
Spécialités DCI 0 à 10 11 à 15 16 à 20 21 à 30 31 à 40 41 à 50 51 à 60 >60
chez le patient normorénal
CARBAPENEMES
INVANZ Ertapénem 1g/24h 500mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
Si Cl<5 non administré Pas d'adaptation
TIENAM Imipénème 2-4g/24h 1 à 2g /24h 1,5-2g/24h (Cl 40-70)
0,5 à 1g/24h posologique
MERONEM Méropénem 1-2g/8h 500mg-1g/12h 1-2g/12h Pas d'adaptation posologique
MONOBACTAME
2g puis
AZACTAM Aztréonam 2g puis 250-500 mg/8-12h 2g puis 500mg-1g/8h Pas d'adaptation posologique
3-6g/24h
MACROLIDES, LINCOSAMIDES ET STREPTOGRAMINES
ZITHROMAX Azythromycine Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
ZECLAR IV/PO Clarithromycine 500mg-1g/24h 250 à 500 mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
DALACINE Clindamycine Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
ERYTHROCINE Erythromycine 1g/8-12h 500-750mg/8-12g Pas d'adaptation posologique
JOSACINE Josamycine Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
500mg/6-8h (PO) 500mg/12-24h 500mg/8-12h Pas d'adaptation
LINCOCINE (NSFP) Lincomycine
600mg/8-12h (IV) 600mg/24h 600mg/12-24h posologique
MOSIL Midécamycine Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
PYOSTACINE Pristinamycine Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
RULID Roxithromycine 150mg/12h 150mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
ROVAMYCINE Spiramycine Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
KETEK Telithromycine 800mg/24h Pas en 1ère intention : alterner de 800 mg et 400 mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
AMINOSIDES
20-30mg/kg Aucun schéma posologique garantissant à la fois une bonne efficacité et une bonne tolérance en cas d'insuffisance rénale. En cas de situation clinique
AMIKLIN (NSFP) Amikacine
en perf de 30 min justifiant l'administration, la posologie unitaire ne doit pas être diminuée.
GENTALLINE Aucun schéma posologique garantissant à la fois une bonne efficacité et une bonne tolérance en cas d'insuffisance rénale. En cas de situation clinique
Gentamicine 3-8mg/kg
(NSFP) justifiant l'administration, la posologie unitaire ne doit pas être diminuée.
STREPTOMYCINE Aucun schéma posologique garantissant à la fois une bonne efficacité et une bonne tolérance en cas d'insuffisance rénale. En cas de situation clinique
Streptomycine 0,5-1,5g/j
PANPHARMA justifiant l'administration, la posologie unitaire ne doit pas être diminuée.
Aucun schéma posologique garantissant à la fois une bonne efficacité et une bonne tolérance en cas d'insuffisance rénale. En cas de situation clinique
NEBCINE Tobramycine 3-8mg/kg
justifiant l'administration, la posologie unitaire ne doit pas être diminuée.
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 3 Copyright MedQual®
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
CLAIRANCE CALCULEE (mL.min-1)
Posologie usuelle
Spécialités DCI 0 à 10 11 à 15 16 à 20 21 à 30 31 à 40 41 à 50 51 à 60 >60
chez le patient normorénal
FLUOROQUINOLONES
Pas d'adaptation
CIFLOX PO Ciprofloxacine 500-750mg/12h 500-750mg/12-24h
posologique
Pas d'adaptation
CIFLOX IV Ciprofloxacine 400mg/8-12h 400mg/24h 400 mg/12h
posologique
500 mg Pas d'adaptation
TAVANIC IV/PO Levofloxacine 500mg/12-24h 500 mg puis 125-250mg/48h 500mg puis 250mg/12-24h
puis 250mg/24-48h posologique
IZILOX Moxifloxacine Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
NOROXINE Norfloxacine 400mg/12-24h 400mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
200mg/12h 200mg / 48h 200mg/24h
400mg/12h 400mg/48h 400mg/24h
OFLOCET IV/PO Ofloxacine Pas d'adaptation posologique
400mg PU 400mg PU 400mg PU
200mg/8h 150mg/24h 100mg/8h
GLYCOPEPTIDES
1500mg en 1 perf ou
XYDALBA Dalbavancine 1000mg 1perf ou 750mg puis 375 mg 7j après Pas d'adaptation posologique
1000mg puis 500mg 7j ap
Pas d'adaptation
VANCOMYCINE Vancomycine 30mg/kg/24h D(mg/24h) = (Clairance [mL/min] x 15) + 150 en attente des taux sériques
posologique
6mg/kg/12h
6 mg/kg/12h 3 inj puis 2mg/kg/24h 6 mg/kg/12h 3 inj puis 3mg/kg/24h
puis 6mg/kg/24h Pas d'adaptation
TARGOCID Teicoplanine
12mg/kg/12h puis posologique
12mg/kg/12h 3-5 inj puis 4mg/kg/24h 12mg/kg/12h 3-5 inj 6mg/kg/24h
12mg/kg/24h
TETRACYCLINES
VIBRAVEINEUSE
(IV) Doxycycline Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
VIBRAMYCINE (PO)
Il est théoriquement nécessaire d'adapter la posologie chez le patient insuffisant rénal.
TETRALYSAL Lymécycline 300mg/12h Toutefois, en l'absence de données, il est impossible de formuler des recommandations précises sur l'adaptation de la posologie de la lymécycline
chez ces patients.
MYNOCINE (NSFP) Minocycline Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
TYGACIL Tigécycline Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 4 Copyright MedQual®
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
CLAIRANCE CALCULEE (mL.min-1)
Posologie usuelle
Spécialités DCI 0 à 10 11 à 15 16 à 20 21 à 30 31 à 40 41 à 50 51 à 60 >60
chez le patient normorénal
SULFAMIDES
80-100mg/kg/24h 20-25mg/kg/24h 40-50mg/kg/24h
BACTRIM Cotrimoxazole 400/800/24h 400/80mg/96h 400/80mg/48h Pas d'adaptation posologique
800/160mg/8-12h 800/160mg/48h 800/160mg/24h
Le RCP de l'Adiazine® préconise une réduction de dose dès 89 ml/min. Toutefois, il n'existe à notre connaissance aucune recommandation précise
Ttt curatif : 4 -6 g/j
ADIAZINE Sulfadiazine concernant l'adaptation des doses en fonction du degré d'insuffisance rénale. Par conséquent, en l'absence de données, il est impossible de formuler
Ttt préventif : 2 g/j
des recommandations.
IMIDAZOLES
500mg/8h 250 mg/8 -12h
250mg/6h 250mg/12h
FLAGYL Métronidazole Pas d'adaptation posologique
750mg/8h 375mg/8h
500mg/12h 500mg/24h
TIBERAL Ordinazole Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
FASIGYNE Tinidazole Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
PHENICOLES
Pas d'adaptation
THIOPHENICOL Thiamphénicol 500-1000mg/ 8h 500mg/48h 500mg/24h 500mg/12h
posologique
AUTRES
FUCIDINE PO/IV Acide Fusidique Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
Traitement par voie orale, la colistine n'est pas absorbée dans la circulation systémique
COLIMYCINE PO Colistine PO 100 000 à 150 000 UI/kg/j
et il n'est pas nécessaire d'adapter la posologie chez le patient insuffisant rénal.
COLIMYCINE IV Colistine IV 9 MUI puis 9 MUI/j 9 MUI puis 3,5 MUI/j 9 MUI puis 4,5-5,5 MUI/j 9 MUI puis 5,5-7,5 MUI/j Pas d'adaptation posologique
CUBICIN Daptomycine 6-8mg/kg/24h 6-8mg/kg/48h Pas d'adaptation posologique
DIFICLIR Fidaxomicine Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
Pas d'adaptation
FOSFOCINE IV Fosfomycine 4g/6-12h 2g/48h 4g/36-48h 4g/12-24h
posologique
600mg/12h 600mg/24h
ZYVOXID Linézolide Pas d'adaptation posologique
600mg/8h Non renseigné
L’utilisation de la nitrofurantoïne chez le patient insuffisant rénal dont le DFG est inférieur à 60 ml/min reste controversée.
FURADANTINE Nitrofurantoïne 100mg/8h En effet, chez le patient insuffisant rénal, l'excrétion urinaire de la nitrofurantoïne sous forme active est diminuée.
Il peut y avoir une accumulation systémique des métabolites de la nitrofurantoïne avec un risque de neuropathie sensitive périphérique.
SIVEXTRO Tédizolide Toutes posologies Pas d'adaptation posologique
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 5 Copyright MedQual®
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
CLAIRANCE CALCULEE (mL.min-1)
Posologie usuelle
Spécialités DCI 0 à 10 11 à 15 16 à 20 21 à 30 31 à 40 41 à 50 51 à 60 >60
chez le patient normorénal
ANTITUBERCULEUX
DEXAMBUTHOL Ethambutol 15-20mg/kg/j 15-20 mg/kg/48h Pas d'adaptation posologique
RIMIFON Isoniazide 3-5mg/kg/24h 3-5mg/kg/24h; Dmax: 200 mg/24h Pas d'adaptation posologique
PIRILENE Pyrazinamide 30 mg/kg/j PU 30 mg/kg/48h Pas d'adaptation posologique
Rifampicine 8-12 mg/kg Espacement individuel des doses selon Pas d'adaptation
RIFADINE Espacement indispensables des doses e e
Si fortes doses 20-30 mg/kg/j la rifampicinémie au 2 ou 3 jour posologique
Méthode de calcul Cockroft-Gault :
Femme : Cl créat = 1,04 x poids x (140-âge/ [créat plasma])
Homme : Cl créat = 1,23 x poids x (140-âge/[créat plasma])
PO : Per os Du : Dose usuelle PU: Prise Unique
IV : intra veineuse Di : Dose initiale NSFP : ne se fait plus D'après les données du Vidal Hoptimal et GPR - Document MedQual©
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 6 Copyright MedQual®
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 7 Copyright MedQual®
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 8 Copyright MedQual®
Adaptation posologique des principaux Antibiotiques
à la fonction rénale (adulte)
Fiche n° 2018-ADAPTATION-POSOLOGIE-INSUFFISANT-RENAL Page 9 Copyright MedQual®
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Etude de La Pharmacocinétique-Toxicocinétique Du ParacétamolDocument10 pagesEtude de La Pharmacocinétique-Toxicocinétique Du ParacétamolMariem YahyaPas encore d'évaluation
- QCM Geriatrie20202021Document25 pagesQCM Geriatrie20202021r.bouthir.altoekoPas encore d'évaluation
- Les AisDocument20 pagesLes AisfarracygmailcomPas encore d'évaluation
- RSA Phénothiazines NeuroleptiquesDocument24 pagesRSA Phénothiazines Neuroleptiquesأبو عبد الرحمن وجديPas encore d'évaluation
- Posologie Des Medoc PedDocument16 pagesPosologie Des Medoc PedisoPas encore d'évaluation
- OrdonanceDocument7 pagesOrdonanceboukhartaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nalador 1Document68 pagesNalador 1Lami SouPas encore d'évaluation
- Medicaments D UrgencesDocument31 pagesMedicaments D UrgencesAhmed MarwanPas encore d'évaluation
- PROLACTINEDocument2 pagesPROLACTINENawar YalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antimitotiques (Resume)Document4 pagesAntimitotiques (Resume)Mar OuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotiques - Antibiotherapie - Antifongiques12 (Enregistré Automatiquement)Document29 pagesAntibiotiques - Antibiotherapie - Antifongiques12 (Enregistré Automatiquement)Tissi NzonouPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 - ATB Partie 01Document35 pages9 - ATB Partie 01Amirouche MezhoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardio4an Td-Gestion Anticoagulants2021gueddoudjDocument53 pagesCardio4an Td-Gestion Anticoagulants2021gueddoudjمحمد أمين دريسيPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecrit Cours Les Antidiarrheiques1Document18 pagesEcrit Cours Les Antidiarrheiques1malick SemourPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification Des ATB (Tableau)Document4 pagesClassification Des ATB (Tableau)Maria BslhPas encore d'évaluation
- TSHDocument2 pagesTSHHicham_bennyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Item 291 - Traitement CancerDocument8 pagesItem 291 - Traitement CancerNarimènePas encore d'évaluation
- Bêta 2-Microglobuline: - Chez Les Patients Infectés Par Le Virus de L'immunodéficience Humaine (VIH) : Elle Est UnDocument3 pagesBêta 2-Microglobuline: - Chez Les Patients Infectés Par Le Virus de L'immunodéficience Humaine (VIH) : Elle Est UnLilou Ṧṹpeř MaboullPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Anticoagulants..Document41 pagesLes Anticoagulants..Paul Fathead100% (1)
- Sympathomimetiques Pharmacologie Et Indications TherapeutiquesDocument17 pagesSympathomimetiques Pharmacologie Et Indications TherapeutiquesPaul FatheadPas encore d'évaluation
- AntalgiquesDocument11 pagesAntalgiquesRima LettreuchPas encore d'évaluation
- 44 Focus Cas Cliniques de Biochimie 2Document2 pages44 Focus Cas Cliniques de Biochimie 2Soumia DoukhiPas encore d'évaluation
- 14-AnTibiothérapie (Polycopié) PDFDocument10 pages14-AnTibiothérapie (Polycopié) PDFhoudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti CancereuxDocument10 pagesAnti Cancereuxhadj mohamed salehPas encore d'évaluation
- PharmacocinétiqueDocument24 pagesPharmacocinétiqueMed AliPas encore d'évaluation
- AminosidesDocument80 pagesAminosideskhouloud gazzehPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Anti-AsthmatiquesDocument7 pagesLes Anti-AsthmatiquesLahcen ElmoumouPas encore d'évaluation
- Travaux Dirigés Pharmacocinétiques L3 2019Document3 pagesTravaux Dirigés Pharmacocinétiques L3 2019Alexandre Kpangny BéniPas encore d'évaluation
- 7a d1 Ue4 Cours 12 Sémiologie Néphrologique RonéoDocument10 pages7a d1 Ue4 Cours 12 Sémiologie Néphrologique RonéoSofia RhellabPas encore d'évaluation
- Les AnticoagulantsDocument30 pagesLes AnticoagulantsHossam naimPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - ProteinurieDocument21 pages2 - ProteinurieSofia RhellabPas encore d'évaluation
- PheochromocytomeDocument2 pagesPheochromocytomeElbordjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Anticoagulants 2011Document53 pagesAnticoagulants 2011Abryda Ania AityPas encore d'évaluation
- Schéma Biosynthèse Des StéroïdesDocument2 pagesSchéma Biosynthèse Des StéroïdesIsmael100% (1)
- Polydipsie Et PolyurieDocument3 pagesPolydipsie Et PolyurieDoc OdocPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploration Des Insuffisances Renales 2017Document9 pagesExploration Des Insuffisances Renales 2017kimoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dosage de L'hémoglobine A1cDocument9 pagesDosage de L'hémoglobine A1cKadri BrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Atb StaphDocument10 pagesAtb StaphFanny Grosso100% (1)
- Hemoglobine GlyqueeDocument4 pagesHemoglobine GlyqueeChahine MansouriPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacodynamie Et Interactions MédicamenteusesDocument19 pagesPharmacodynamie Et Interactions MédicamenteusesChaima FatnassiPas encore d'évaluation
- FIBRINOGENEDocument2 pagesFIBRINOGENEKha LedPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Antiparasitaires UEHDocument60 pagesLes Antiparasitaires UEHSalomon JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Prescription Des AINS BisDocument8 pagesPrescription Des AINS BisbayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Médicaments de L'hémostaseDocument10 pagesLes Médicaments de L'hémostaseLahcen ElmoumouPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunoglobuline Monoclonale Et Orientation DiagnostiqueDocument7 pagesImmunoglobuline Monoclonale Et Orientation DiagnostiqueabdellahPas encore d'évaluation
- Les BarbituriquesDocument1 pageLes BarbituriquesGHERMI .MPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytotoxiques (Anticancéreux)Document12 pagesCytotoxiques (Anticancéreux)Annab TakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Antidiabetiques FMPRDocument43 pagesAntidiabetiques FMPRYasmine BoustajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Polycopié Cours Bactériologie MédicaleDocument47 pagesPolycopié Cours Bactériologie MédicaleSaid BenakliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chimiothérapie AntiviraleDocument43 pagesChimiothérapie AntiviraleRania Ranou0% (1)
- 14 - Heterosides-CardiotoniquesDocument7 pages14 - Heterosides-CardiotoniquesSk CissePas encore d'évaluation
- Les AntiulcereuxDocument2 pagesLes AntiulcereuxFeriel FerielPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapies Ciblees Ma PrésentationDocument18 pagesTherapies Ciblees Ma PrésentationAbdelhalim BensidhoumPas encore d'évaluation
- Med 3an qcm1 ImmunoDocument8 pagesMed 3an qcm1 ImmunoBouchra Perle De DiamantPas encore d'évaluation
- Les AINS Et Les CorticoïdesDocument7 pagesLes AINS Et Les CorticoïdesLahcen ElmoumouPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Anti-ThyroperoxydaseDocument2 pagesAc Anti-Thyroperoxydasemenadi el mouatezPas encore d'évaluation
- MICROALBUMINEDocument3 pagesMICROALBUMINECheikh Ismaïla BAPas encore d'évaluation
- Méthodes Pharmacocinétiques D - Adaptation de PosologieDocument3 pagesMéthodes Pharmacocinétiques D - Adaptation de PosologieDoc OdocPas encore d'évaluation
- QE HEMATO BELMEKKI - REPONSES-convertiDocument7 pagesQE HEMATO BELMEKKI - REPONSES-convertiNada Amrani100% (1)
- Transfusion SanguineDocument2 pagesTransfusion SanguineNazih Bio100% (1)
- Adaptation de Posologie Chez Linsuffisant RénalDocument1 pageAdaptation de Posologie Chez Linsuffisant RénalBerkane DjamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Démarche Qualité AllemagneDocument109 pagesDémarche Qualité AllemagneKoross MohsinePas encore d'évaluation
- Phenobarbital Posologie Nourisson - Recherche GooDocument1 pagePhenobarbital Posologie Nourisson - Recherche GooCristal Fangue TchounkePas encore d'évaluation
- Calcichew d3 Article 30 Referral Annex I II III - FRDocument13 pagesCalcichew d3 Article 30 Referral Annex I II III - FRRavaka Harivololona AndrianaivojaonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ou Acheter Du Cialis Sans Ordonnancecwgky PDFDocument2 pagesOu Acheter Du Cialis Sans Ordonnancecwgky PDFeyecast82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Item 188 - Atteinte Respiratoire Connectivite-Vascularite - Pdf#viewer - Action DownloadDocument3 pagesItem 188 - Atteinte Respiratoire Connectivite-Vascularite - Pdf#viewer - Action DownloadbibouPas encore d'évaluation
- Gna FMCDocument8 pagesGna FMCtina harratPas encore d'évaluation
- Cas Clinique PyomètreDocument23 pagesCas Clinique PyomètreMichelle HasegawaPas encore d'évaluation
- PRICE LIST FortaDocument32 pagesPRICE LIST FortaRidho SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- N. SAMALEA-pharmacologie - Médicaments Complémentaires À L'anesthésieDocument35 pagesN. SAMALEA-pharmacologie - Médicaments Complémentaires À L'anesthésie5zkwnrwvmkPas encore d'évaluation
- These: Universite de OuagadougouDocument130 pagesThese: Universite de OuagadougouSk CissePas encore d'évaluation
- Memoire OunisDocument132 pagesMemoire Ounissarra.henoudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction Pharmaco. Generale m1 s1 G.PDocument13 pagesIntroduction Pharmaco. Generale m1 s1 G.PHamdaoui dounia100% (1)
- Recommandation Acidocetose DiabetiqueDocument7 pagesRecommandation Acidocetose DiabetiqueAssi HachinPas encore d'évaluation
- CarbocaineDocument1 pageCarbocainemarie christine cheuzevillePas encore d'évaluation
- Infections Des Voies BiliairesDocument6 pagesInfections Des Voies BiliairesMahefa Serge RakotozafyPas encore d'évaluation
- These72 18Document139 pagesThese72 18Abdourasck GOUMANEHPas encore d'évaluation
- II/ Nature de La Barrière Capillaire GlomérulaireDocument9 pagesII/ Nature de La Barrière Capillaire Glomérulaireahmed AlayoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Antalgiques Non MorphiniquesDocument39 pagesLes Antalgiques Non Morphiniquestessa grayPas encore d'évaluation
- Profil Epidemiologique Et Cytologique Des Leucemies Aiguës Chez L'Enfant Etude Retrospective (Juin 2012-Mai 2014)Document168 pagesProfil Epidemiologique Et Cytologique Des Leucemies Aiguës Chez L'Enfant Etude Retrospective (Juin 2012-Mai 2014)TuccoPas encore d'évaluation
- PharmacologieDocument34 pagesPharmacologieScribdTranslationsPas encore d'évaluation
- I-6-65-Bases Neurophysiologiques Et Évaluation D'une Douleur Aiguë Et ChroniqueDocument11 pagesI-6-65-Bases Neurophysiologiques Et Évaluation D'une Douleur Aiguë Et ChroniqueTaxo HaPas encore d'évaluation
- II-222 Anémie Par Carence MartialeDocument9 pagesII-222 Anémie Par Carence MartialeAro MandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap SNVDocument21 pagesChap SNVOumayma SETTOURIPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyponatrémie 2020Document11 pagesHyponatrémie 2020Lorlyna Mandzeyi100% (2)
- Temps Thrombine PDFDocument2 pagesTemps Thrombine PDFBac 2018Pas encore d'évaluation
- CONNAISSANCE DU MEDICAMENT Partie 2Document45 pagesCONNAISSANCE DU MEDICAMENT Partie 2Estelle MkoungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ostéochimionécrose Maxillo-Mandibulaire EtDocument6 pagesOstéochimionécrose Maxillo-Mandibulaire EtDonia BlrsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ulcère GastroduodénalDocument66 pagesUlcère Gastroduodénalsabiou amadouPas encore d'évaluation
- Trauma Cranien CCDocument38 pagesTrauma Cranien CCQuentin KesslerPas encore d'évaluation