Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rev Odont Stomat 2015 44 p83-95
Transféré par
heraelodiaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Rev Odont Stomat 2015 44 p83-95
Transféré par
heraelodiaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’enregistrement de
l’occlusion en fonction
de la difficulté prothétique
Première partie :
situations cliniques simples
Recording the occlusion according
J.-F. CARLIER to prosthetic difficulty
Part I
simple clinical cases
J.-F. CARLIER. Ancien assistant hospitalo-universitaire UFR de Reims, chargé de cours en occlusodontie, président du Collège national d’occlusodontologie.
La restauration de dents manquantes ou délabrées par des éléments The restoration of decayed or missing teeth with
prothétiques vise à reproduire la fonction masticatrice du patient, en créant prosthetic elements aims at re-creating the patient’s
masticatory function, and thus creating a morphology
la morphologie la plus proche de celle des dents originelles. Les caracté- that will be as much as possible the same as the
ristiques occlusales telles que la forme et la position des cuspides, la morphology of the original teeth. The occlusal
profondeur des sillons, les rapports de distances aux déterminants de characteristics such as the shape and the position of
l’occlusion et les notions d’angles influencent de manière décisive la cusps, the depth of grooves, relationships of distances
fonction masticatrice. Si le projet prothétique concerne toute ou partie to the determinants of occlusion and notions of angles,
d’une arcade, les conditions anatomo-fonctionnelles devront être recréées have a major impact on the masticatory function. If the
prosthetic project concerns the full arch or just a part of
pour retrouver les critères morphologiques des dents à restaurer. S’il it, the functional anatomical conditions will have to be
concerne seulement un élément appartenant à cette arcade, la reproduction re-created to find the morphological criteria of the teeth
des caractéristiques anatomiques des dents voisines suffit pour reconstruire to be restored. If it only concerns one element of the
par mimétisme la morphologie optimale de cette dent, conditionnant arch, the reproduction of the anatomic characteristics of
l’intégration dans le système existant. Selon la quantité et la qualité des the adjacent teeth is enough to reproduce the optimal
informations perdues, la méthode d’enregistrement de l’occlusion doit morphology of this tooth, determining the integration
in the existing system. According to the quantity and
mettre en œuvre des moyens adaptés pour retrouver ces informations et the quality of information loss, the recording method of
apporter l’assurance que tous les paramètres des fonctions occlusales the occlusion must seek appropriate means to get this
seront rétablis. information back and ensure that all the parameters of
the occlusal functions will be restored.
Plusieurs critères détermineront le choix de la méthode à utiliser : le type Several criteria can help us choose the appropriate
method: the type and the quality of the occlusal
et la qualité des fonctions occlusales à enregistrer, la position de référence
functions to be recorded, the mandibular reference
mandibulaire, le type d’empreinte qui servira à réaliser la restauration position, the type of impression that will be used to
prothétique et, enfin, le type de simulateur à utiliser. design the prosthetic restoration and finally, the type
of simulator to be used.
SOUMIS POUR PUBLICATION LE 29/12/2014 – ACCEPTÉ POUR PUBLICATION LE 13/02/2015
83 ROS – MAI 2015 Rev Odont Stomat 2015;44:83-95 MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
LES FONCTIONS OCCLUSALES OCCLUSAL FUNCTIONS
Chaque dent participe au système manducateur par ses fonctions Each tooth takes part in the manducatory system with
its occlusal functions (Orthlieb et al., 1996, Orthlieb,
occlusales (Orthlieb et coll., 1996 ; Orthlieb, 2000) de centrage, de calage et 2000) of centring, wedging and guidance, which define
de guidage, qui définissent une position mandibulaire stable, sans a stable mandibular position, free of any muscular or
contraintes musculaires ou articulaires et le guidage harmonieux et articular constraints, as well as the efficient and
économe des excursions mandibulaires lors de la mastication (fig. 1). harmonious guidance of the mandibular movements
during chewing (fig. 1).
Fig. 1. Chaque dent participe au système selon une ou plusieurs
des trois fonctions : de calage, de centrage ou de guidage.
(Docs Gold).
Fig. 1. Each tooth takes part in one or several of the 3 functions
of the system. Wedging - Centring - Guidance (docs Gold).
Selon sa position sur l’arcade, elle participe à l’une ou l’autre de ces According to its position on the arch, a tooth participates
fonctions, ou à plusieurs simultanément. Lorsque les dents résiduelles sont in one or several of these functions simultaneously.
en nombre suffisant et dans leur état originel, il est facile d’en déduire la When there are enough residual teeth in their original
position mandibulaire du patient et les caractéristiques de la fonction state, it is easy to gather from these the patient’s
mandibular position and the characteristics of the
masticatrice pour les reproduire. En revanche, dès que l’état des dents masticatory function in order to reproduce them.
résiduelles ne le permet pas ou que leur nombre est insuffisant, une position However, when the condition and/or the number of
mandibulaire de référence fiable, reproductible, doit être définie pour residual teeth cannot help, a reliable and reproducible
rétablir et simuler les données manquantes pendant toutes les phases du reference mandibular position must be defined in order
traitement. to restore and simulate the missing data during all the
stages of the treatment.
LA POSITION DE RÉFÉRENCE REFERENCE POSITION
La restauration prothétique doit s’intégrer dans un système neuro- The prosthetic restoration must be integrated into a
musculaire complexe, dont il est essentiel de pouvoir déterminer et de complex neuromuscular system, from which it is
retrouver le référentiel (Laurent et coll., 2000) à tout moment d’un essential to be able to determine and find the system
traitement, en clinique comme au laboratoire. of reference (Laurent et al., 2000) at any stage of the
treatment, both in the dental office and the laboratory.
La reconstruction peut être faite dans l’occlusion du patient si elle The reconstruction can be made in the patient’s
représente une occlusion d’intercuspidation maximale (OIM) fonctionnelle occlusion, if it is a functional and natural maximal
naturelle, adaptée au vieillissement des structures dentaires, sans intercuspal occlusion (MIO), adapted to the ageing of
altération de la position de fermeture habituelle. L’OIM fonctionnelle dental structures, with no alteration of the usual closing
présente au minimum trois couples de dents pluricuspidées répartis sur position. The functional MIO shows at least three
couples of multi-cusped teeth distributed on the arch,
l’arcade, sans déviation transversale cliniquement observable. Dans cette with no clinically observable transversal deviation. In
situation clinique, l’affrontement des modèles est suffisant pour obtenir this clinical situation, the sole occlusal intermeshing of
une position reproductible et stable (fig. 2a). upper teeth and lower teeth can be used to obtain a
84 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
Lorsque l’OIM semble inconfortable ou inconstante et que la restauration stable and reproducible position (fig. 2a).
envisagée est de faible étendue, une analyse occlusale préprothétique est When the MIO seems uncomfortable or unstable, and
the envisaged restoration is small, a pre-prosthetic
réalisée pour rétablir la stabilité de la position mandibulaire, évaluer la occlusal analysis is carried out to restore the stability
faisabilité d’une équilibration et revenir à une situation simple, décrite of the mandibular position, assess the feasibility of an
précédemment. equilibration, and return to a simple situation, previously
Lorsque la préparation des dents supports est susceptible d’éliminer des described.
structures dentaires de calage qui assuraient la stabilité de l’OIM, la When the preparation of support teeth is likely to
reconstruction prothétique doit alors renforcer l’OIM et pérenniser une eliminate wedging dental structures that provide the
MIO stability, the prosthetic reconstruction must then
situation occlusale non pathogène. La technique d’enregistrement de strengthen the MIO, and maintain a nonpathogenic
l’occlusion employée doit compenser la perte d’informations due à la occlusal pattern. The technique used to record the
préparation des dents supports et faire appel à un matériau occlusion must compensate for information loss due to
d’enregistrement interposé entre les dents préparées (fig. 2b et 2c). the preparation of supporting teeth and use a recording
material placed between the prepared teeth (fig. 2b, c).
La position mandibulaire est une position d’occlusion adaptative poten- The mandibular position is a potentially pathogenic
tiellement pathogène (fig. 2c). Elle peut être stable mais décentrée dans adaptive occlusal position (fig. 2c). It may be stable but
le plan sagittal, transversal ou vertical (anomalie de centrage). Elle peut decentered in the sagittal, transversal or vertical plane
être une position mandibulaire, centrée ou non (anomalie de calage), deve- (centring anomaly). It may be a mandibular position,
nue instable par des pertes de substance dentaire, fracture, abrasion, carie, centered or not (wedging anomaly), that has become
édentation, ou des restaurations coronaires iatrogènes. Quand le délabre- unstable due to losses of dental substance, fracture,
abrasion, caries, edentulation, or iatrogenic coronal
ment des dents résiduelles est important ou lorsque l’étendue de la restorations. When residual teeth are deeply decayed
reconstruction a supprimé toutes les informations propres aux fonctions or when the extent of the reconstruction has erased all
occlusales du patient, il n’est plus possible de retrouver une OIM stable et the information specific to the patient’s occlusal functions,
reproductible (fig. 2d). La détermination de la position mandibulaire fait it is no longer possible to find a stable and reproducible
appel à la référence articulaire du patient, obtenue par une manipulation MIO, (fig. 2d) The determination of the mandibular
position is related to the patient’s articular reference,
mandibulaire recherchant le relâchement musculaire du patient, en rota- obtained with a mandibular manipulation aiming at the
tion pure. patient’s muscular relaxation, in pure rotation.
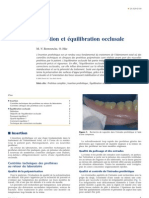
a b Fig. 2. Positions de référence
a. L’OIM du patient est maintenue. b. L’OIM doit être renforcée.
c. OIM potentiellement pathogène après préparation des dents
supports. d. L’ORC est la position de référence en l’absence
d’OIM. (Docs M. Laurent)
Fig. 2. Reference positions
a. Patient’s MIO is preserved - b. MIO must be strengthened -
c. Potentially pathogenic MIO after preparation of the support
teeth - d. The occlusion in centric relation is the reference
position in the absence of MIO. Docs M. Laurent.
c d
85 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
La relation centrée (RC) est définie par une situation condylienne de réfé- The Centric Relation (CR) is defined with a reference
rence correspondant à une coaptation bilatérale condylo-disco-temporale condylar position corresponding to a simultaneous, high,
bilateral temporal-disc-condyle coaptation, obtained
haute, simultanée, obtenue par contrôle non forcé, réitérative dans un with unforced control, repeatable in a given period of
temps donné, pour une posture corporelle donnée et enregistrable à par- time, in a specific body posture that is recordable from
tir d’un mouvement de rotation pure de la mandibule (CNO, 2001). a movement of pure rotation of the mandible. (CNO,
L’enregistrement de la relation intermaxillaire (RIM) en ORC est obtenu obli- 2001). The recording of the intermaxillary relationship
gatoirement par l’interposition entre les arcades d’un matériau (IMR) in CR is necessarily performed by placing between
d’enregistrement en épaisseur suffisante pour éliminer toute participation the arches a recording material thick enough to
eliminate any dental participation in the recording. The
dentaire à cet enregistrement. L’authenticité de la position mandibulaire accuracy of the mandibular position is increased with
est accrue par le montage des modèles complets sur un articulateur, grâce the set-up of the entire models on an articulator using
à un arc facial de transfert (fig. 3). a facebow transfer (fig. 3).
Cette position de référence articulaire est d’autant plus nécessaire quand This articular reference position is all the more
les restaurations prothétiques participent à la stabilisation d’une position necessary when the prosthetic restorations participate
in the stabilization of a therapeutic position, either by an
thérapeutique, soit par une augmentation de la DVO, soit par la création increase of the OVD, or by the creation of a new
d’une nouvelle relation articulaire stabilisée (Duminil, 2013) (fig. 4). stabilized articular relation (Duminil, 2013) (fig. 4).
Fig. 3. La relation centrée (RC), définie par une situation
condylienne de référence, reproduit la position mandibulaire lors
du montage des modèles complets sur un articulateur, grâce à
un arc facial de transfert. (Docs Gold)
Fig. 3. Centric relation (CR), defined by a reference condyle
situation reproduces the mandibular position during the setting
up of the complete models on an articulator, using a facebow
transfer (docs GOLD).
Fig. 4. La position de référence articulaire est indispensable
quand les restaurations prothétiques stabilisent une position
thérapeutique avec augmentation de la DVO. (Docs G. Duminil)
Fig. 4. The articular reference position is essential when the
prosthetic restorations stabilize a therapeutic position with an
increase of the OVD. Docs G. Duminil.
86 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
LE TYPE D’EMPREINTE TYPE OF IMPRESSION
Le choix de la technique de prise d’empreinte, partielle, mordue, arcade The choice of the technique of impression - partial, bite,
complète, dépend évidemment des réponses données aux interrogations full-arch – naturally depends on the answers given to
the following questions:
suivantes :
What are the required data to recreate the dental
– Quelles sont les données nécessaires pour recréer la morphologie dentaire? morphology?
Les dents non concernées par le projet prothétique sont autant d’indica- Teeth that are not concerned with the prosthetic project
teurs précieux pour le prothésiste dentaire lors de la phase d’élaboration are precious indicators for the dental technician during
the elaboration phase of the restoration in the laboratory.
de la restauration au laboratoire. Même si la zone à restaurer est de faible Even when the area to be restored is small, it may be
étendue, il peut être avantageux de réaliser une empreinte complète pour useful to make a full-arch impression in order to achieve
obtenir une harmonisation avec les morphologies des dents controlaté- a harmonization with the morphologies of contralateral
rales en volume, hauteur cuspidienne et orientation. teeth in volume, cusp height and orientation.
Is the mandibular wedging preserved on the working
– Le calage mandibulaire est-il conservé sur le modèle de travail ? cast?
Quelle que soit la zone à reconstruire, le contrôle du calage mandibulaire Whatever the zone to reconstruct, it must be possible to
doit pouvoir être fait à tout moment. Une empreinte sectorielle pour réaliser check the mandibular wedging at any time. A partial
une prothèse terminale d’arcade est source de problèmes d’occlusion, soit impression to make an arch terminal prosthesis may
par l’impossibilité de respecter les courbes fonctionnelles, soit par la sous- generate occlusion problems, either due to the impos-
occlusion liée à l’absence de butée distale à la restauration, en particulier sibility to respect the functional curves, or to the
sub-occlusion connected to the absence of distal abutment
lorsque le modèle de travail est monté sur un occluseur en plastique. to the restoration, in particular when the working cast is
L’absence de calage sur la face palatine d’une canine maxillaire proscrit set on a plastic occluder. The absence of wedging on
l’empreinte sectorielle pour la réalisation de restaurations sur les the palatal face of a maxillary canine bans the partial
prémolaires. impression in the making of restorations on premolars.
Do teeth to reconstruct participate in the mandibular
– Les dents à reconstruire participent-elles au guidage mandibulaire ? guidance?
Le concept occlusal choisi selon des critères cliniques impose la méthode The occlusal concept chosen according to clinical
d’empreinte. Une fonction de groupe, comme dans le cas d’un parodonte criteria provides the impression method. A group
affaibli, nécessite le montage des modèles en articulateur, plus pratique à function, like in the case of a weakened periodontium,
réaliser avec une empreinte globale qu’avec une empreinte sectorielle. La requires the setting up of models on an articulator,
création des pentes de guidage des prothèses assurant le guidage which is easier to make with a global impression than
with a sectorial impression. The creation of guidance
antérieur n’est envisageable que si les modèles de travail sont complets slopes for the prostheses providing the anterior guidance
pour évaluer la qualité de la désocclusion postérieure. can only be achieved when working casts are full-arch
in order to assess the quality of the posterior disocclusion.
– Comment enregistrer précisément la relation intermaxillaire ?
Au-delà de l’étendue du projet prothétique, il est essentiel de s’interroger How can the intermaxillary relationship be accurately
recorded?
sur la façon d’enregistrer et de reproduire les critères fonctionnels de Besides the size of the prosthetic project, it is necessary
l’occlusion pour déterminer le type d’empreinte à réaliser, globale ou to wonder about the methods of recording and
partielle. Ce choix est primordial si la situation clinique impose un reproducing the functional criteria of occlusion in order
enregistrement de la relation intermaxillaire avec ou sans dispositif de to determine the type of impression to take – i.e global
transfert de l’occlusion (fig. 5a). Une empreinte partielle est insuffisante si or partial. This choice is essential if the clinical context
elle est disposée sur un occluseur souple, mais peut être satisfaisante si elle requires a recording of the intermaxillary relationship
with or without an occlusal transfer system (fig. 5a). A
est placée en situation sur un articulateur (fig. 5b et 5c). partial impression is not sufficient if it is set up on a
Une position de référence mandibulaire en RC impose une empreinte flexible occluder, but it may be suitable if it is correctly
globale des deux arcades et le transfert sur articulateur du modèle placed on an articulator (fig. 5b, c).
maxillaire par un arc facial (fig. 5d). A mandibular reference position in CR requires a global
impression of both arches and the transfer of the maxillary
model on an articulator with a facebow (fig. 5d).
87 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
a b Fig. 5. a. Le recours à dispositif d’enregistrement nécessite une
empreinte complète. b. Un modèle partiel monté en OIM sur un
occluseur souple est insuffisant. c. Le modèle partiel peut être
satisfaisant sur un articulateur. d. Le choix de la RC impose une
empreinte globale.
Fig. 5. a. The use of a recording device requires a full-arch
impression. b. A partial model set up in MIO on a flexible occluder
is not enough. c. The partial model can be adequate on an
articulator. d. The choice of CR requires a global impression.
c d
LE MATÉRIAU SUPPORT D’ENREGISTREMENT THE SUPPORT MATERIAL OF RECORDING
The recording of the IMR is made in a stable and
L’enregistrement de la RIM est effectué sur une situation stable et clinically reproducible context: consequently, the
reproductible cliniquement, c’est-à-dire qu’en toutes circonstances le practitioner must always be able to check his/her
praticien doit pouvoir contrôler son enregistrement, soit immédiatement recording, either immediately after making it or later, to
après l’avoir réalisé, soit à distance pour contrôler les pièces revenues du control the parts that come back from the laboratory. It
requires to use a material with a dimensional stability
laboratoire. Cela nécessite d’utiliser un matériau dont la stabilité dimension- which will be preserved after the removal of the recording
nelle est conservée après la désinsertion de l’enregistrement et lorsqu’il and then later, when subjected to manipulations
est soumis aux manipulations tout au long de la phase de laboratoire throughout the laboratory phase (Valentin, Morin, 1977).
(Valentin-Morin, 1977). Il doit présenter une précision de surface permettant It must feature a surface accuracy allowing to check the
de vérifier la qualité du repositionnement des modèles de travail et un adequacy of the repositioning of working casts as well
as a small temperature interval to facilitate its shaping
intervalle de température réduit pour en faciliter sa mise en œuvre (cires). (waxes).
L’enregistrement étant soumis à de fortes variations de température, de la The recording being subjected to high variations of
température buccale à celle du stockage, a fortiori celle du laboratoire de temperature - from oral temperature to storage
prothèse, on choisira un produit résistant à la déformation et présentant un temperature, and particularly the temperature in the
prosthetic laboratory -, we will choose a material which
fluage minimal (Ogolnick, 1997). is resistant to deformation, with a minimal creep
Même si la position de référence choisie est réputée stable, il est difficile (Ogolnick, 1997).
pour le patient de maintenir une position d’occlusion sans fatigue et sans Even if the chosen reference position is considered stable,
risque de déplacement, la prise du matériau doit être rapide (max. 90”). it is difficult for the patient to maintain a position of
occlusion with no fatigue and without moving, the setting
Selon ces critères, les cires molles (modelling-wax, horse bite wax) sont of the material must thus be fast (90 seconds max).
totalement à proscrire pour effectuer un enregistrement occlusal. Les According to these criteria, soft wax (modelling-wax,
élastomères (Memosil®, Futar®, Jet bite®) seront réservés aux situations horse bite wax) must be avoided to make an occlusal
cliniques stables avec l’OIM pour position de référence, car nous n’avons recording. Elastomers (Memosil®, Futar®, Jet bite®) will
be used in stable clinical situations with MIO as the
pas à craindre la perforation du support d’enregistrement, elle est même reference position, because we do not have to fear the
souhaitée. Les cires chargées de poudre métallique (Aluwax®) ou les cires perforation of the recording medium – it is actually a
dures (Moyco®), rebasées ou non à la pâte d’oxyde de zinc (TempBond®, good thing. Wax containing powdered metal (Aluwax®)
Bite Registration paste®) sont des matériaux spécialement conçus pour or hard wax (Moyco®), rebased or not with zinc oxide
paste (TempBond®, Bite Registration paste®) are
des enregistrements occlusaux et doivent à ce titre être privilégiés (Santoni materials that have been especially developed for
et coll., 1998). Les résines acryliques (GC Pattern®, Pi-Ku-Plast®, Resinlay®), occlusal recordings and must thus be favored (Santoni
utilisées essentiellement pour des contrôles de précision, présentent et al., 1998). Acrylic resins (GC Pattern®, Pi-Ku-Plast®,
l’avantage d’être très adhérentes au support d’enregistrement et résistantes Resinlay®), mainly used to check the accuracy, present
88 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
sous de faibles épaisseurs. Les maquettes d’occlusion utilisées dans les the advantage to be highly adherent to the recording
cas d’édentement important doivent obéir aux mêmes principes, rigides au medium and resistant with low thicknesses. Models of
occlusion used in the cases of extensive edentulation
niveau de la base d’appui sur la fibro-muqueuse pour assurer leur stabilité have to meet the same requirements, i.e they must be
lors de l’enregistrement, et lors du repositionnement sur les modèles de rigid at the support basis on the fibro-mucous membrane
travail et indéformables au niveau de la surface d’enregistrement après to provide their stability during the recording and during
leur désinsertion (Schittly, 1995). the repositioning on the working casts, and must keep
their shape on the recording surface after removal.
(Schittly, 1995).
LES SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES SIMPLE CLINICAL SITUATIONS
RESTAURATIONS UNITAIRES POSTÉRIEURES POSTERIOR SINGLE-TOOTH RESTORATIONS
In the case of one or two intermediate elements to
Dans la situation d’un ou deux éléments intercalaires à reconstruire, les reconstruct, the prosthetic elements will be integrated
éléments prothétiques seront intégrés dans l’OIM de référence, à condition into the M.I.O of reference, provided however that teeth
toutefois que les dents limitant la restauration ne soient pas délabrées ou adjacent to the restoration are not decayed or do not
présentent des restaurations inadéquates susceptibles de reproduire une have inadequate restorations likely to reproduce a
occlusion pathogène. pathogenic occlusion.
Le prothésiste dentaire peut déduire des morphologies des dents voisines The dental technician can deduce from the morphology
of the adjacent teeth the location of the palatal and
la situation des pointes cuspidiennes vestibulaires et palatines par buccal cusp tips thanks to the alignment of the occlusal
l’alignement des lignes occlusales, l’orientation des sillons cuspidiens lines, the orientation of cusp grooves defining the
définissant les trajectoires en latérotrusion et évaluer l’angle cuspidien à laterotrusive movements; he/she can also evaluate the
reproduire. cusp angle to be reproduced.
Une empreinte sectorielle sera suffisante, sauf si la restauration doit inclure A partial impression is sufficient, except when the
restoration includes the canine. This specific case will
la canine. Cette situation est abordée plus loin. be described later.
Par définition, l’OIM nécessite des contacts dento-dentaires, son By definition, the MIO requires dento-dental contacts,
enregistrement exige l’absence de tout matériau interposé entre les dents its recording requires the absence of any material
définissant l’OIM. L’objectif étant de reproduire la situation clinique au placed between the teeth defining the MIO. Since the
laboratoire, une carte occlusale (Davies, 2006) recense les contacts goal is to reproduce the clinical situation in the
occlusaux constatés en bouche lors de l’OIM qui doivent être retrouvés sur laboratory, an occlusal mapping (Davies, 2006) lists the
occlusal contacts noticed in mouth during MIO which
les modèles affrontés manuellement (fig. 6). Cela suppose que le modèle de must be found on by the occlusal intermeshing of casts
travail doit être toiletté des bulles de coulée et taillé pour éliminer les (fig. 6). This implies that the working cast must be
traînages de plâtre lors de l’empreinte. cleared of any casting bead and cut to eliminate smears
of plaster during the impression.
Fig. 6. Sur les modèles affrontés manuellement, les marques
correspondent à celles observées en bouche. (Docs J.-P. Ré)
Fig. 6. On the occlusal intermeshing of the casts, the markings
refer to those observed in mouth. Docs J.-P. Ré.
89 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
Cependant, pour simplifier la mise en occluseur de ces modèles sectoriels, However, in order to make easier the placement of the
une clé de silicone occlusale, a minima, est réalisée pour maintenir les partial models in the occluder, an occlusal silicone key,
a minima, is made to hold the models in place, after
modèles, après s’être assuré qu’elle comporte des perforations objectivant checking the key contains perforations objectifying
les points de contacts observés en bouche (fig. 7). contact points observed in mouth (fig. 7).
Le traitement du mordu au laboratoire nécessite une préparation réduisant The treatment of the bite registration in the laboratory
au maximum les erreurs de repositionnement. Les empreintes de fonds de requires a preparation reducing as much as possible the
sillons et des embrasures seront éliminées pour ne conserver que les errors of repositioning. The impression of the bottom of
grooves and embrasures will be eliminated to keep cusp
pointes cuspidiennes. Cette préparation du mordu facilite le contrôle visuel tips only. The preparation of the bite registration
du repositionnement des modèles de travail dans la clé (fig. 8). facilitates the visual control of the repositioning of the
working casts in the key (fig. 8).
7 8
Fig. 7. L’enregistrement par une clé de silicone facilite le montage du modèle sur Fig. 8. Les perforations de la clé de silicone indiquent les contacts en OIM. (Docs
occluseur. (Docs O. Laplanche) O. Laplanche)
Fig. 7. The recording with a silicone key facilitates the setting up of the model on Fig. 8. Perforing of the silicone key indicates the contacts in MIO. Docs O. Laplanche.
an occluder. Docs O. Laplanche.
It is possible to pour directly the plaster into the silicone
Il est possible de couler directement le plâtre dans la clé de silicone repo- key repositioned on the model. However, this technique
sitionnée sur le modèle. Cette technique présente l’inconvénient de salir stains the working model, and may generate unwanted
le modèle de travail et de s’exposer à des coulures de plâtre indésirables si drips of plaster if the key is not perfectly stable on the
model.
la clé n’est pas parfaitement stable sur le modèle. Impressions in the bite registration is an ambitious
Les empreintes en mordu constituent une technique ambitieuse, puisqu’on technique, because we have to record at the same time
doit enregistrer en un seul temps l’arcade avec ses préparations, l’arcade the arch with its preparations, the antagonist arch and
antagoniste et l’occlusion (Dawson, 1992). L’insertion d’une masse de the occlusion (Dawson, 1992). The insertion of a silicone
silicone sur un secteur de l’arcade induit un réflexe de mastication qui tend mass in one part of the arch triggers a chewing reflex
which tends to shift the mandible into working position.
à déporter la mandibule en position travaillante. Il est très difficile de It is very difficult to check in which position the patient
contrôler dans quelle position le patient a mordu lors de l’empreinte. Parfois, has bitten during the impression. Sometimes, the
le porte-empreinte lui-même induit une erreur de positionnement par un impression tray itself induces a positioning error
appui douloureux sur les tissus voisins. Enfin, il y a obligatoirement du through painful pressure on neighboring tissues.
matériau ou de la toile occlusale interposés entre les dents définissant Besides, there is necessarily some material or a piece
of occlusal cloth between teeth defining the MIO. After
l’OIM. Après désinsertion de l’empreinte en mordu, le contrôle de la position removal of the bite impression, it is extremely difficult to
mandibulaire est très difficile, à moins de recenser les perforations control the mandibular position, unless the occlusal
occlusales dans l’empreinte. Ces perforations occlusales doivent être les perforations in the impression are counted. These
mêmes que les points d’OIM observés en bouche. Dans un second temps, occlusal perforations must be the same as the points of
il est prudent de réaliser un nouvel enregistrement en déposant un filet de MIO observed in mouth. It is better to proceed to a
second registration by placing an occlusal silicone mold
silicone d’occlusion (Futar®, Luxabite®) que le prothésiste pourra utiliser (Futar®, Luxabite®) that the dental technician can use to
pour le contrôle de l’occlusion, après assemblage sur l’occluseur. control the occlusion, after the set up on the occluder.
90 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
RESTAURATION UNITAIRE TERMINALE D’ARCADE TERMINAL SINGLE-TOOTH RESTORATIONS
Dans cette situation clinique, la dent à reconstruire étant plus proche de OF THE ARCH
l’ATM, axe de rotation de la mandibule, que du guidage antérieur, la In this clinical situation, the tooth to be reconstructed
being closer to the TMJ, the mandibular axis of rotation,
morphologie occlusale est essentiellement soumise aux valeurs des than to the anterior guide, the occlusal morphology is
déterminants postérieurs (Duminil et coll., 2013). La position de référence mainly subjected to the values of the posterior
est bien l’OIM du patient. Une empreinte de l’arcade complète est determinants (Duminil et al., 2013). The reference
préférable, car des informations essentielles à la fonction sont situées sur position is the patient’s MIO. A full-arch impression is
le secteur controlatéral, notamment le type de guidage. preferable, because essential information about the
function is located in the contralateral sector, in
Le modèle complet est monté en OIM sur un articulateur, réglé sur des particular the type of guidance.
valeurs moyennes, qui remplit le simple rôle d’occluseur. Dans ces The whole model is placed in MIO on an articulator, set
conditions, le prothésiste peut intégrer la restauration dans les courbes to average values, which is simply used as an occluder.
d’occlusion sagittale et transversale, exploiter les structures de guidage In these conditions, the dental technician can integrate
des dents voisines et ainsi éviter de créer des interférences non the restoration into the curves of sagittal and
travaillantes (fig. 9). transverse occlusion, use the structures of guidance of
the neighboring teeth and thus avoid creating non-
working interferences (fig. 9).
Fig. 9. La coiffe est réalisée sur un modèle complet monté sur
articulateur. (Docs J.-P. Ré)
Fig. 9. The capping is made on a complete model set up on
articulator. Docs J.-P. Ré.
TROIS DENTS POSTÉRIEURES (PETIT BRIDGE)
THREE POSTERIOR TEETH (SMALL BRIDGE)
Lorsque les dents antagonistes sont intègres, on privilégiera l’utilisation When the antagonist teeth are healthy, we will use
de tables d’enregistrement occlusales sectorielles réalisées à l’aide de cire sectorial occlusal registration tables made with a double
Moyco® en double épaisseur adaptée à la dimension du secteur préparé layer of Moyco® wax fitted to the size of the prepared
(fig. 10). La cire est réchauffée à 52 °C et est adaptée sur les moignons sector (fig. 10). Wax is heated to 52°C and adapted on
préparés en bouche, puis le patient se place en OIM. La profondeur des dies prepared in mouth; the patient is then placed in
MIO. The depth of the indentations must be limited to
indentations doit être limitée aux pointes cuspidiennes, la cire ne doit pas cusp tips, the wax does not have to coat the
recouvrir les dents voisines. L’enregistrement est ensuite rebasé à l’aide de neighboring teeth. The registration is then rebased with
pâte oxyde de zinc-eugénol (TempBond®) alors que le patient retrouve son zinc oxide eugenol paste (TempBond®) while the patient
OIM. Cet enregistrement présente toutes les qualités nécessaires de finds back his/her MIO. This registration features all the
précision et de rigidité (fig. 11). La stabilité des modèles complets montés necessary requirements of accuracy and rigidity (fig. 11).
en OIM est augmentée par cette table sectorielle, dont le parfait The stability of the whole models set up in MIO is
increased with this sectorial table - its perfect
repositionnement sur le modèle positif unitaire peut être contrôlé grâce au repositioning on the single-tooth positive model can be
lavis de TempBond® (fig. 12). checked with the TempBond® wash (fig. 12).
91 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
10 11
Fig. 10. Une table occlusale est ajustée sur les moignons préparés pour enregistrer
l’OIM du patient. (Docs M. Laurent)
Fig. 10. An occlusal table is fitted on the prepared dies to register the patient’s
MIO. Docs M. Laurent.
Fig. 11. Une table occlusale rebasée à la pâte ZnO enregistre avec précision le calage
en OIM. (Docs M. Laurent)
Fig. 11. An occlusal table with ZnO paste accurately records the wedging in MIO.
Docs M. Laurent.
Fig. 12. Le lavis de pâte ZnO atteste de la précision du montage des modèles sur
articulateur.
Fig. 12. The ZnO wash paste gives highlights the accuracy of the setting up of the
models on articulator.
12
Dans une seconde étape, une plus grande précision peut être obtenue en In a second step, a greater accuracy may be achieved
réenregistrant l’OIM sur l’armature confectionnée sur des modèles de by registering again the MIO on the framework made on
working casts in occlusal intermeshing. The adjustment
travail en affrontement simple. L’ajustage de l’armature sur les piliers est of the framework on the abutments is checked first with
préalablement vérifié par la technique du fit-checker et une petite quantité the fit-checker technique and a small quantity of
de résine calcinable (Resinlay® ou GC Pattern®) est déposée au pinceau sur calcinable resin (Resinlay® or GC Pattern®) is put on the
l’armature (fig. 13). Le patient se replace en OIM pendant la polymérisation. framework with a brush (fig.1 3). The patient is in MIO
Il est essentiel de n’enregistrer que l’empreinte des pointes cuspidiennes during polymerization. It is essential to record only the
antagonistes pour pouvoir contrôler le repositionnement du modèle sur impression of the antagonist cusp tips to be able to
check the repositioning of the model on the articulator
l’articulateur (fig. 14). (fig. 14).
RESTAURATION UNITAIRE ANTÉRIEURE ANTERIOR SINGLE-TOOTH RESTORATION
Cette situation clinique est différente selon que l’incisive participe au This clinical situation is different whether the incisor
guidage au même titre que les autres dents antérieures ou qu’elle assure participates in the guidance in the same way as the
other anterior teeth or whether it mainly contributes to
essentiellement le guidage en propulsion. the guidance in the propulsion movement.
Les modèles issus d’une empreinte complète sont montés en OIM par The models made from a full-arch impression are
affrontement direct des modèles sur un articulateur, réglé sur des valeurs directly placed on an articulator in MIO, set to standard
standards (pente condylienne à 50 °C) (Hobo-Takayama, 1997). values (condyle slope at 50°C) (Hobo, Takayama, 1997).
Cette procédure permet de contrôler le guidage antérieur en propulsion, This procedure allows to control the anterior guidance
pour s’assurer de l’absence d’interférence antérieure et construire une in propulsion, to check the absence of any anterior
interference and make a purely sagittal guidance
trajectoire de guidage purement sagittale, avec une participation identique movement, with a similar participation to the contralateral
à la dent controlatérale (fig. 15). tooth (fig. 15).
Dans le cas d’un guidage uniformément réparti sur l’ensemble du groupe In the case of a guidance evenly distributed on the
incisivo-canin, l’empreinte pourra être partielle et l’enregistrement de la whole canine-incisor group, the impression may be
partial and the recording of the MIR will be made with a
92 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
13 14
Fig. 13. Un apport de résine déposé sur l’armature enregistre avec précision la Fig. 14. La résine déposée sur l’armature permet de contrôler la précision de
position mandibulaire. (Docs M. Laurent) l’enregistrement sur les modèles.
Fig. 13. Some resin put on the framework accurately records the mandibular Fig. 14. The resin put on the framework allows to check the accuracy of the
position. Docs M. Laurent. recording on the models.
Fig. 15. La coiffe participe au guidage comme toutes les dents antérieures.
Fig. 15. The capping participates in the guidance like all the anterior teeth.
15
RIM sera obtenu par une clé de silicone sur un modèle antagoniste partiel silicone key on a partial antagonist model limited to the
réduit aux dents antérieures. La clé de silicone permet de reproduire l’angle anterior teeth. The silicone key allows to reproduce the
inter-incisif et de positionner les modèles en OIM sur un occluseur simple. interincisal angle and to place the models in MIO on a
Puisque le guidage antérieur est conservé par les dents adjacentes, les simple occluder. Since the anterior guidance is still
trajectoires sont implicites. made by the adjacent teeth, trajectories are implicit.
Things are different in Class II division 2 clinical
Il en est autrement dans les situations cliniques en classe II division 2 (fig. 16), situations (fig. 16), where central incisors perform the
où les incisives centrales assurent le guidage en propulsion et participent propulsion guidance, but also participate in the
également au guidage en latérotrusion (fig. 17). Le montage d’un modèle laterotrusive movement (fig. 17). The setting up of a
complet en articulateur est nécessaire pour obtenir le profil correct e la complete model onto the articulator is necessary to
face palatine par une table incisive personnalisée dans cette situation. Une obtain the adequate profile of the palatal face with an
incisal guide table specific to this situation. Some Kerr
masse de pâte de Kerr verte est réchauffée dans un bain à 52 °C et green paste is warmed in a 52°C bath and solidarized
solidarisée à la flamme sur la table incisive de l’articulateur. La table est with flame on the incisal guide table of the articulator.
modelée progressivement par le pointeau incisif durant les mouvements The table is gradually modelled by the incisal needle
de propulsion et de latérotrusion exécutés par manipulation en translation during the propulsion and laterotrusive movements
des boîtiers condyliens (fig. 18). performed by a translational manipulation of condylar
boxes (fig. 18).
93 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
16 17
Fig. 16. Seules les incisives centrales assurent le guidage antérolatéral. Fig. 17. La coiffe complète le guidage avec la dent controlatérale.
Fig. 16. Only the central incisors perform the anterolateral guide. Fig. 17. The capping completes the guide with the contralateral tooth.
Fig. 18. La table incisive réalisée sur articulateur reproduit l’enveloppe des trajec-
toires de guidage. (Docs J.-P. Ré)
Fig. 18. The incisal guide table made on articulator reproduces the envelope of the
guidance movements. Docs J.-P. Ré.
18
RESTAURATION UNITAIRE CANINE CANINE SINGLE-TOOTH RESTORATION
L’observation clinique de l’occlusion permet d’évaluer le rôle fonctionnel de The clinical observation of the occlusion allows to
assess the functional role of the canine to be restored
la canine à restaurer et d’en déterminer le profil occlusal le plus approprié and to determine the occlusal profile which is the most
à la situation. Quand la canine peut assurer l’essentiel des fonctions de suitable to the case. When the canine can perform the
guidage, une empreinte sectorielle est suffisante. Une clé de silicone main part of the functions of guidance, a sectorial
permet l’enregistrement de la RIM et stabilise le montage en OIM du modèle impression is sufficient. A silicone key enables the
partiel antagoniste. Le guidage canin est obtenu soit en majorant la pente registration of the IMR and stabilizes the set-up of the
antagonist partial model in MIO. The canine guidance is
palatine par rapport à la pente cuspidienne de la première prémolaire, soit achieved either by increasing the palatal slope with
par une clé de silicone de la face palatine de la couronne provisoire après regard to the cusp slope of the first premolar or with a
validation clinique de son rôle de protection dans les différentes trajectoires silicone key of the palatal face of the provisional crown
excentrées. after clinical validation of its protective role in the
various off-centered movements.
Dès que le support parodontal est affaibli et que les fonctions de guidage When the periodontal bone support is weak, and the
functions of guidance must be distributed on the
doivent être réparties sur les secteurs antérieurs et latéraux, une empreinte anterior and lateral sectors, a complete impression is
complète est requise. Les modèles seront placés sur l’articulateur dans la required. The models will be placed on the articulator in
position d’OIM par simple affrontement. Le profil de la face palatine de la MIO position by simple occlusal intermeshing of upper
canine vient s’intégrer dans la fonction de groupe définie par les dents teeth and the lower teeth. The profile of the canine
adjacentes. palatal face gets integrated into the group function
defined by the adjacent teeth.
94 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
O C C L U S O D O N T I E
L’ENREGISTREMENT DE L’OCCLUSION EN FONCTION DE LA DIFFICULTÉ PROTHÉTIQUE. PREMIÈRE PARTIE : SITUATIONS CLINIQUES SIMPLES
Ces différentes situations cliniques sont réputées simples, car les These various clinical situations are said to be simple
informations nécessaires au rétablissement ad integrum des fonctions because the information needed to restore ad integrum
the occlusal functions are located in the immediate
occlusales sont situées à proximité immédiate de la zone à restaurer et vicinity of the zone to be restored and easily
facilement transposable sans faire appel à des dispositifs complexes, dont transposable without using complex devices, the
la manipulation est souvent à l’origine d’erreurs. Même si cela semble simple manipulation of which often generates errors. Even if it
à réaliser, l’enregistrement de la RIM demande de la rigueur à la clinique, seems easy to perform, the recording of IMR requires a
dans le contrôle de la position enregistrée, et au laboratoire de prothèse, lot of rigor both in the dental office, particularly in the
dans le traitement des enregistrements, dans la conservation des control of the recorded position, and in the prosthesis
laboratory, in the processing of the recordings, the
informations et la stabilité des dispositifs souvent réduits et fragiles. Ces preservation of the information and the stability of the
situations feront essentiellement référence à la position d’OIM, à condition devices which is often low and fragile. These situations
toutefois que celle-ci ne présente pas un caractère pathogène. essentially refer to the position of MIO, provided
nevertheless that this position is not pathogenic.
Demande de tirés-à-part :
Dr Jean-François CARLIER – drjfcarlier@orange.fr Traduction : Marie Chabin
3, rue Léon-Tassin, 02880 BUCY-LE-LONG.
BIBLIOGRAPHIE
ORTHLIEB J.D., LAPLANCHE O., PRECKEL E.B. – La fonction DAWSON P.E. – Les problèmes de l’occlusion. Évaluation, SCHITTLY J., BOREL J.C., EXBRAYAT J. – L’occlusion en
occlusale et ses dysfonctionnements. Réal clin 1996 72:131- diagnostic et traitement. CdP, Paris 1992. Cat ? prothèse partielle amovible. Réal Clin 1995 6: 447-465. Cat ?
143. Cat ?
DUMINIL G., LAPLANCHE O., RÉ J.P., CARLIER J.F. – L’occlusion VALENTIN C.M. MORIN – L'intercuspidation maximale : examen
ORTHLIEB J.D. – La fonction de guidage : un modèle biomé- tout simplement. ID Paris 2013 205:221. Cat ? clinique des caractères de l'intercupisdation maximale. Cah
canique pour un concept thérapeutique. Cah Prothèse Prothèse 1982 38: 101-114. Cat ?
2004128:55–64. Cat ? HOBO S., TAKAYAMA H. – oral rehabilitation,clinical determintation
of occlusion. Tokyo - Quintessence publishing 1997. Cat ? Wirth C.G., Alpin A.W. – An improved interocclusal record of
ORTHLIEB J.D. – Gnathologie fonctionnelle : Volume 1 et 2 : centric relation. J Prosth Dent 1974. Cat ?
occlusion et reconstruction prothétique. coll Memento. LAURENT M., LABORDE G., ORTHLIEB J.D. – Choix et de la
Éditions CDP 2010. Cat ? position de référence in Manuel d'occlusodontie Pratique.
cdp PARIS 2000 79-84. Cat ?
CNO. Occlusodontologie : lexique. Paris: Quintessence
International 2001. Cat ? OGOLNICK R. – Les materiaux d'enregistrement de la relation
intermaxillaire. Cah prothèse 1997 100:15-22. Cat ?
DAVIES S.J., GRAY R.J., AL-ANI M.Z., SLOAN P., WORTHINGTON
H. – Inter - and intra - operator reliability of the recording of SANTONI P., BISCARAT F., TAVITIAN P. – Étude de trois
occlusal contacts using’occlusal sketch’acetate technique. matériaux d'enregistrement de la relation centrée. Cah
Br Dent J 2002; 193: 397-400. Cat ? prothèse 1998 103:57-63. Cat ?
95 ROS – MAI/MAY 2015
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Le langage au bout des doigts: Les liens fonctionnels entre la motricité et le langageD'EverandLe langage au bout des doigts: Les liens fonctionnels entre la motricité et le langagePas encore d'évaluation
- Pro AmovibleDocument6 pagesPro Amovibleenima67% (3)
- EMC Orthlieb Fonctions Occlusales 2013Document12 pagesEMC Orthlieb Fonctions Occlusales 2013Mezmaz Fadhela ManarPas encore d'évaluation
- Occlusion en Prothèse FixéeDocument5 pagesOcclusion en Prothèse FixéeMeriem MeddahPas encore d'évaluation
- DownloadDocument10 pagesDownloadbilal balbziouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Paralliliseur PapDocument8 pagesParalliliseur Paplydia khalfaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Occlusionmontagedesdents 2004Document24 pagesOcclusionmontagedesdents 2004Fatiha BensbaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Le Manuel Du Résident - DentisterieDocument484 pagesLe Manuel Du Résident - DentisterieOthmane LazrakPas encore d'évaluation
- EMC Articulation Dentodentaire Et FonctionDocument16 pagesEMC Articulation Dentodentaire Et FonctionMezmaz Fadhela ManarPas encore d'évaluation
- DVOdeterminantOrthliebRC2013 PDFDocument7 pagesDVOdeterminantOrthliebRC2013 PDFSamuel Flores CalderonPas encore d'évaluation
- LocatorDocument8 pagesLocatorChokri SahbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Coronoplasties Occlusales PréprothétiquesDocument13 pagesCoronoplasties Occlusales PréprothétiquesRenboh GuezPas encore d'évaluation
- Finition Stabilite Et HarmonieDocument33 pagesFinition Stabilite Et Harmoniediana100% (1)
- EMC GoutDocument14 pagesEMC Goutamira benhamoudaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 L'occlusion en Prothèse ConjointeDocument9 pages3.1 L'occlusion en Prothèse ConjointeMi NaPas encore d'évaluation
- La Prothèse CompositeDocument5 pagesLa Prothèse CompositeStar LilyaPas encore d'évaluation
- ProtheseDocument11 pagesProtheseanony100% (1)
- Spvol5n2p129-144Document16 pagesSpvol5n2p129-144smt66zd62xPas encore d'évaluation
- Démarche DiagnostiqueDocument8 pagesDémarche Diagnostiquem6njjpmdj8Pas encore d'évaluation
- TheseDocument2 pagesThesejaboubadrPas encore d'évaluation
- Spvol8n3p165-181Document17 pagesSpvol8n3p165-181smt66zd62xPas encore d'évaluation
- Ancrage Et OdfDocument19 pagesAncrage Et OdfdadahinePas encore d'évaluation
- Les Reconstitutions Corono-RadiculairesDocument14 pagesLes Reconstitutions Corono-RadiculairesKaouter100% (1)
- Entretien Avec Hugo de ClerckDocument28 pagesEntretien Avec Hugo de ClerckHafaifa TaiebPas encore d'évaluation
- Restauration Fonctionnelle Par Ajustement Occlusal Functional Restoration by Occlusal AdjustmentDocument17 pagesRestauration Fonctionnelle Par Ajustement Occlusal Functional Restoration by Occlusal Adjustmentboorin1989Pas encore d'évaluation
- L'Occlusion Bilatérale EquilibréeDocument11 pagesL'Occlusion Bilatérale EquilibréeMi Na100% (1)
- Rebasage en Prothèse TotaleDocument5 pagesRebasage en Prothèse TotaleAhlem RaddaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Comment Faire Uninlay-Onlay EsthetiqueDocument10 pagesComment Faire Uninlay-Onlay EsthetiqueJacques AlbertiniPas encore d'évaluation
- SP Anthogyr PACSI Max DefDocument8 pagesSP Anthogyr PACSI Max DefChokri SahbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestion Des Moyens de Rétention Au Service de L'esthétique en PAPMDocument9 pagesGestion Des Moyens de Rétention Au Service de L'esthétique en PAPMAhlem RaddaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Temporisation en Implantologie PDFDocument3 pagesTemporisation en Implantologie PDFRamzy ChekriPas encore d'évaluation
- Extraction Des Dents Incluses Dents de SagesseDocument10 pagesExtraction Des Dents Incluses Dents de SagesseAlex OuchatPas encore d'évaluation
- RCvol24n3p237 246Document10 pagesRCvol24n3p237 246Dhiaeddine OuasliPas encore d'évaluation
- CAT Inclusion PalatineDocument8 pagesCAT Inclusion Palatinerola bouamaraPas encore d'évaluation
- @ Conseils Pratiques en Occlusodontie - SOPDocument5 pages@ Conseils Pratiques en Occlusodontie - SOPAna PopescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Alladin PDFDocument8 pagesAlladin PDFazizgoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Crête FlottanteDocument13 pagesCrête FlottanteAlia FerchichiPas encore d'évaluation
- 02) Traitment Des Édentement DistauxDocument8 pages02) Traitment Des Édentement DistauxNorelimane OuchenePas encore d'évaluation
- Choix D'un Concept en ImplontologieDocument26 pagesChoix D'un Concept en Implontologienesrine eljPas encore d'évaluation
- Articlerubrique Pia RelectureauteurcopieDocument13 pagesArticlerubrique Pia RelectureauteurcopiesousourimePas encore d'évaluation
- Aos 2013265 P 04Document15 pagesAos 2013265 P 04ElbordjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Simon2006 PDFDocument12 pagesSimon2006 PDFSai KrupaPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Occlusions Pathologiques - Physiologie Et TraitementDocument7 pagesLes Occlusions Pathologiques - Physiologie Et TraitementFamilly KouiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Reconstitutions Lecorono-RadiculairesDocument8 pagesLes Reconstitutions Lecorono-RadiculairesKaouterPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthodfr 160001Document16 pagesOrthodfr 160001Hanadi BelghalemPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestion Du Profil D'émergence en Implantologie (PDFDrive)Document13 pagesGestion Du Profil D'émergence en Implantologie (PDFDrive)tamouza chaouiPas encore d'évaluation
- Indiquer L'orthodontieDocument8 pagesIndiquer L'orthodontieChiguer RedouanePas encore d'évaluation
- Les Empreinte en Prothese Partiel AdjointeDocument9 pagesLes Empreinte en Prothese Partiel AdjointeNorelimane OuchenePas encore d'évaluation
- Le Rôle de Lorthodontiste Dans La Chirurgie OrthognatiqueDocument8 pagesLe Rôle de Lorthodontiste Dans La Chirurgie OrthognatiqueMeriem AbadliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aos 2016275 Article 3Document10 pagesAos 2016275 Article 3anonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Equilibration PDFDocument10 pagesEquilibration PDFasma tiouitPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapport Clinique: Enregistrement Piézographique de La Zone Neutre, Chez Un Patient Souffrant de Spasmes Musculaires InvolontairesDocument6 pagesRapport Clinique: Enregistrement Piézographique de La Zone Neutre, Chez Un Patient Souffrant de Spasmes Musculaires InvolontairesYasmine BenPas encore d'évaluation
- Rehabilitation Neuro Occlusale Application en Orthopedie DentoDocument8 pagesRehabilitation Neuro Occlusale Application en Orthopedie DentoAmina Aissa DilmiPas encore d'évaluation
- L'occlusion en Prothèse Totale AdjointeDocument2 pagesL'occlusion en Prothèse Totale AdjointeTellab MariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prothèse Complète Immédiate: M.-V. Berteretche, O. HüeDocument11 pagesProthèse Complète Immédiate: M.-V. Berteretche, O. HüeAbdelkhalek BouararaPas encore d'évaluation
- Résorption Alvéolaire Et Montage Des Dents en Prothèse Totale. A.hamiziDocument17 pagesRésorption Alvéolaire Et Montage Des Dents en Prothèse Totale. A.hamiziStar LilyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Polycope OcclusionDocument37 pagesPolycope Occlusiontaha el idrissiPas encore d'évaluation
- Léquilibration OcclusaleDocument10 pagesLéquilibration Occlusaleasma tiouitPas encore d'évaluation
- Insertion Et ÉquilibrationDocument12 pagesInsertion Et Équilibrationgougou84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fonctions OcclusalesDocument4 pagesFonctions Occlusaleshadil chebliPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthlieb RCmyostabilisee CDP1412008Document10 pagesOrthlieb RCmyostabilisee CDP1412008Jonathan Héctor Mendoza SaldivarPas encore d'évaluation
- Scdpha TD 2004 Flechon AntoineDocument160 pagesScdpha TD 2004 Flechon AntoineNassima BELILPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide de L'animationDocument2 pagesGuide de L'animationAnna Matras100% (1)
- Interception DDM Bilan InterceptifDocument9 pagesInterception DDM Bilan InterceptifBen Kbaier FatenPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Références Esthétiques Et FonctionellesDocument4 pages1-Références Esthétiques Et FonctionellesNjimaZidiPas encore d'évaluation
- E7-Cavité D'accès EndoDocument3 pagesE7-Cavité D'accès EndobergeronPas encore d'évaluation
- L'Implantologie Chirurgicale Et Prothétique: La Pratique Au QuotidienDocument362 pagesL'Implantologie Chirurgicale Et Prothétique: La Pratique Au QuotidienmohmoamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Parodontite MTCDocument4 pagesParodontite MTCOudottePas encore d'évaluation
- Système D'orthodontie Linguale Individualisé: J.-S. Simon, C. Galletti, D. WiechmannDocument16 pagesSystème D'orthodontie Linguale Individualisé: J.-S. Simon, C. Galletti, D. Wiechmannmaxillo.arrasPas encore d'évaluation
- Questionnaire MédicalDocument1 pageQuestionnaire Médicalbrice lemairePas encore d'évaluation
- Eval Voc Prefixe Suffixe Syn Anto HomoDocument7 pagesEval Voc Prefixe Suffixe Syn Anto HomoSiham LouizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Odonto 2021 RemionDocument87 pagesOdonto 2021 Remionlina rayenePas encore d'évaluation
- MTRL SereniteDocument1 pageMTRL Serenitejacques albertPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibioprophylaxie 48 Heuresversusantibiotherapie 7 Joursdanslapreventiondelinfectiondusiteoperatoireapresextractionsdentairessimples MASSALEYKYetal 2Document12 pagesAntibioprophylaxie 48 Heuresversusantibiotherapie 7 Joursdanslapreventiondelinfectiondusiteoperatoireapresextractionsdentairessimples MASSALEYKYetal 2Hichem HalladjPas encore d'évaluation
- Examen Clinique.2docxDocument15 pagesExamen Clinique.2docxBoűmřãh FōüĀdPas encore d'évaluation
- Abces Parodontal, Syndrome Du Septum, GingivorragiesDocument71 pagesAbces Parodontal, Syndrome Du Septum, GingivorragiesCloud MindPas encore d'évaluation
- Santé Bucco Dentaire Et Population À RisqueDocument9 pagesSanté Bucco Dentaire Et Population À RisqueMayssa BourenanePas encore d'évaluation
- Radiologie Médicale - Techniques de Manipulations-1Document279 pagesRadiologie Médicale - Techniques de Manipulations-1Anas IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- La Prise de Teinte Numérique Par Le DR Walter DevotoDocument1 pageLa Prise de Teinte Numérique Par Le DR Walter DevotohachemPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 N°4Document84 pages2018 N°4Houssam ElhousniPas encore d'évaluation
- Généralités en Prothese DentaireDocument5 pagesGénéralités en Prothese DentaireAsma Asma0% (1)
- 3 Les ArticulateursDocument59 pages3 Les ArticulateursImene ChlPas encore d'évaluation
- La Radiographie en Endodontie:: Incidences Développement Lecture de ClichésDocument46 pagesLa Radiographie en Endodontie:: Incidences Développement Lecture de Clichésmohamed rayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Imagerie en Odontologie PediatriqueDocument25 pagesImagerie en Odontologie PediatriqueNéhémie Tembwa Kipupa ÉdouardiPas encore d'évaluation
- Article Revue Odf 2016Document28 pagesArticle Revue Odf 2016Hafaifa TaiebPas encore d'évaluation
- QCM Et Cas Clinique Pour Résidanat Chirurgie DentaireDocument29 pagesQCM Et Cas Clinique Pour Résidanat Chirurgie DentaireBouch RaPas encore d'évaluation
- La Contention Et La RécidiveDocument10 pagesLa Contention Et La RécidiveAimen FeknousPas encore d'évaluation
- Chirurgie EndodontiqueDocument4 pagesChirurgie EndodontiqueMeriem ImenePas encore d'évaluation
- Megard Sonia 20220321 1307Document2 pagesMegard Sonia 20220321 1307Sonia MegardPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023-05-23 11-12-56 - Devis ConventionnelDocument1 page2023-05-23 11-12-56 - Devis Conventionnelhubert.gondard05Pas encore d'évaluation