Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Anemie Bouskraoui
Transféré par
Mohammed Boumlik0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
79 vues1 pageAnemie Bouskraoui
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentAnemie Bouskraoui
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
79 vues1 pageAnemie Bouskraoui
Transféré par
Mohammed BoumlikAnemie Bouskraoui
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
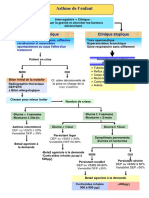
L’anémie chez l’enfant
Définition Mécanisme défaut de production
Tx Hb par rapport à la VN pour l’age excès de pertes
< 14g/dl Nné < 12g /dl enfant
Anémie mal tolérée(signe de
gravité) transfusion en urgence
Démarchediagnostique
Démarche diagnostique
Interrogatoire Ex clinique Ex compl
Age ,sexe,origine Paleur,ictère NFS :VGM , CCMH
Début HPSM,tr phanere Ferritinémie
Atcd pers RSP ,Sd hemor FS ,CTF
Atcd fam Signes : Réticulocytes
Alimentation Myélogramme
neuro,card-resp
Frottis sg,
Géophagie … Electro Hb
Hgie ext,ictère
…
…
NFS
VGM CCMH
AHM ANM ANN
VGM CCMH VGM CCMH VGM CCMH
Ferritinémie Déficit en vit B12 ou réticulocytes
Acide folique
tx tx nl ou tx an rég tx an arég
carence martiale anémie inflam an hemol hgie aigue
carence d’apport thalassémie Triade : anémie, ictère ,SPM
saignt chronique Myélog
malabsorption -corpos : déficit en G6PD
géophagie sphérocytose aplasie IRC
drépanocytose envahiss endo
-extracorp :auto immune
infect,toxique
Ait ouzdi zohair
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Q 068 AnemieDocument3 pagesQ 068 AnemietoufikPas encore d'évaluation
- QCM HématoDocument12 pagesQCM Hématoyousrabel99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anémie Microcytaire RésuméDocument2 pagesAnémie Microcytaire Résumézara100% (1)
- AnemiesDocument6 pagesAnemiesNawres SMATIPas encore d'évaluation
- Anémies Hémolytiques Congénitales (1) (DR AHMIDATOU)Document67 pagesAnémies Hémolytiques Congénitales (1) (DR AHMIDATOU)Feriel AePas encore d'évaluation
- 272 SplénomégalieDocument3 pages272 SplénomégalieJulien CoguicPas encore d'évaluation
- Tableau Recapitulatif Hemato-Oncologie MeulemanDocument4 pagesTableau Recapitulatif Hemato-Oncologie MeulemanSarah MignotPas encore d'évaluation
- Anémie Hémolytique RésuméDocument3 pagesAnémie Hémolytique RésumézaraPas encore d'évaluation
- FMC 04Document31 pagesFMC 04Abdelmadjid NebegPas encore d'évaluation
- Leuce Mies Aigue S.Document5 pagesLeuce Mies Aigue S.waliddaasPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - Les Anémies RégénérativesDocument14 pages3 - Les Anémies RégénérativesBen minaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mon Carnet HématoDocument42 pagesMon Carnet Hématoyas mine100% (5)
- LVR HematopediatrieDocument125 pagesLVR HematopediatrieFlamant RosePas encore d'évaluation
- Sémiologie en HématologieDocument4 pagesSémiologie en HématologieVictoire SIMIERPas encore d'évaluation
- Q 029 Syndrome Inflammatoire Biologique PersistantDocument3 pagesQ 029 Syndrome Inflammatoire Biologique PersistantYou NesPas encore d'évaluation
- Generalités Sur Les AnémiesDocument23 pagesGeneralités Sur Les AnémiesMor NgomPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - FDT Rappel Et Glomérulopathies P2 - NoblesDocument2 pages1 - FDT Rappel Et Glomérulopathies P2 - NoblesRamzi RzPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Media1818043488375350718Document4 pagesLocal Media1818043488375350718Farouk DjenienPas encore d'évaluation
- 28 Anemie de L'enfantDocument75 pages28 Anemie de L'enfantDefne TopalPas encore d'évaluation
- Anémie MicrocytaireDocument6 pagesAnémie MicrocytairezaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Généralités Sur Les Anémies 2019Document58 pagesGénéralités Sur Les Anémies 2019Sana SghirPas encore d'évaluation
- 095 Polyradiculonévrite Aiguë Inflammatoire (Syndrome de Guillain-Barré)Document2 pages095 Polyradiculonévrite Aiguë Inflammatoire (Syndrome de Guillain-Barré)Chloé ThépenierPas encore d'évaluation
- 161 - DysmyélopoïèseDocument4 pages161 - DysmyélopoïèseeltouffuPas encore d'évaluation
- VaquezDocument25 pagesVaquezZakaria InhafPas encore d'évaluation
- Ascite (BERKANE)Document1 pageAscite (BERKANE)Mi RyPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemie Chez L'enfant - 2024Document11 pagesAnemie Chez L'enfant - 2024latifahima05Pas encore d'évaluation
- ABREVIATIONS PREPECN EmisDocument7 pagesABREVIATIONS PREPECN EmisAlpha ZeroPas encore d'évaluation
- I-11-200-Etat de Choc FICHEDocument1 pageI-11-200-Etat de Choc FICHENemo LuPas encore d'évaluation
- Item 122 Polyradiculonevrite Aiguë Inflammatoire (Syndrome de Guillain-Barre)Document2 pagesItem 122 Polyradiculonevrite Aiguë Inflammatoire (Syndrome de Guillain-Barre)MEDEDINEPas encore d'évaluation
- Aplasie Médullaire RésidanatDocument26 pagesAplasie Médullaire RésidanatFarah OHDPas encore d'évaluation
- I-10-165-Maladie de Vaquez FICHEDocument1 pageI-10-165-Maladie de Vaquez FICHENemo LuPas encore d'évaluation
- I 10 165 Maladie de Vaquez FICHEDocument1 pageI 10 165 Maladie de Vaquez FICHENemo LuPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 CAT Anémie DIU Nov2012Document58 pages23 CAT Anémie DIU Nov2012Med KhezPas encore d'évaluation
- .Thrombopénie RIDocument1 page.Thrombopénie RIImene HouriPas encore d'évaluation
- Item 208 Hémogramme Chez L'adulte - Martingale 20Document5 pagesItem 208 Hémogramme Chez L'adulte - Martingale 20AbuSabha MousaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Conduite A Tenir Devant Une Anemie de L'enfantDocument11 pages20 Conduite A Tenir Devant Une Anemie de L'enfantBenzaoui DjemanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Q 104 TVPDocument4 pagesQ 104 TVPLahcen BoulahcenPas encore d'évaluation
- Anémie Hémolytique Acquise RésuméDocument2 pagesAnémie Hémolytique Acquise Résumézara50% (2)
- Module Biologie Humaine S5 Cours D Hématologie Du PR Nouzha Bouamoud TD2Document48 pagesModule Biologie Humaine S5 Cours D Hématologie Du PR Nouzha Bouamoud TD2Oumar SourabiePas encore d'évaluation
- Image Code Couleur TubesDocument2 pagesImage Code Couleur TubesFairouz Tou100% (2)
- 8 - Purpura Thrombopénique ImmunologiqueDocument13 pages8 - Purpura Thrombopénique Immunologiquesnousi MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Anémies CarentiellesDocument35 pagesAnémies Carentiellesmkdqhp8rwdPas encore d'évaluation
- Anémies Ferriprives Pr. HamazDocument55 pagesAnémies Ferriprives Pr. HamazzakariaePas encore d'évaluation
- AnémiesDocument1 pageAnémiesjey writesPas encore d'évaluation
- Atcd:: 1 TotalDocument5 pagesAtcd:: 1 TotalSifou KrPas encore d'évaluation
- 3b - Anã©mies Microcytaires SuiteDocument42 pages3b - Anã©mies Microcytaires SuiteLidvina FirquetPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 - IRC de L - Adulte PR ARZOURDocument46 pages11 - IRC de L - Adulte PR ARZOURHOUSSEYN GHOZLANEPas encore d'évaluation
- Syndromes Myélodysplasiques DiagnosticDocument37 pagesSyndromes Myélodysplasiques DiagnosticChrist michel EssimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Livre Hematologie Pediatrique Mise A JourDocument145 pagesLivre Hematologie Pediatrique Mise A Jouratbamina11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anémie VFDocument36 pagesAnémie VFSoufiane AROUFI0% (1)
- CIVDDocument3 pagesCIVDAndry RijaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anémies HémolytiquesDocument4 pagesAnémies Hémolytiquesboutefal imene100% (1)
- 181 Réaction Inflammatoire OK 2Document1 page181 Réaction Inflammatoire OK 2kgtdPas encore d'évaluation
- Anémies de L'enfant 22-23Document63 pagesAnémies de L'enfant 22-23Zakaria MaounPas encore d'évaluation
- Bilan SanguinDocument2 pagesBilan Sanguinclohey0812Pas encore d'évaluation
- Q 300 Goutte-ChondrocalcinoseDocument4 pagesQ 300 Goutte-ChondrocalcinoseAmine OuanayaPas encore d'évaluation
- HémolyseDocument16 pagesHémolysezaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Les Syndromes GlomérulairesDocument9 pagesLes Syndromes GlomérulairesNour-El ImanePas encore d'évaluation
- Cahier de StageDocument10 pagesCahier de StageMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- QCM Residanat 2010Document7 pagesQCM Residanat 2010Mohammed Boumlik100% (2)
- QCM Dr. Kerbaol Neurologie PédiatriqueDocument17 pagesQCM Dr. Kerbaol Neurologie PédiatriqueMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- Examen Hemato Session Principale 2010Document26 pagesExamen Hemato Session Principale 2010Mohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- Révision de NépphroDocument2 pagesRévision de NépphroMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- QCM +++Document5 pagesQCM +++Mohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- L'essentiel en NéphroDocument3 pagesL'essentiel en NéphroMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- Rsca 1Document9 pagesRsca 1Mohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- ThyroïdeDocument3 pagesThyroïdeMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- QCM PneumoDocument52 pagesQCM PneumoLe Médecin85% (13)
- 5256 100720 DiabeteDocument6 pages5256 100720 DiabeteMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- 81 OeilrougeetdouloureuxDocument2 pages81 OeilrougeetdouloureuxMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- Parcours Physio Pharmaco Cours 1Document19 pagesParcours Physio Pharmaco Cours 1Mohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- 7164 111006 Osteomyelite ErreurDocument8 pages7164 111006 Osteomyelite ErreurMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- Exemple JDB 2e Cycle 20111Document10 pagesExemple JDB 2e Cycle 20111Mohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthme Enfant BouskraouiDocument1 pageAsthme Enfant BouskraouiMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- Crise D Asthme BouskraouiDocument1 pageCrise D Asthme BouskraouiMohammed BoumlikPas encore d'évaluation
- Local Media1818043488375350718Document4 pagesLocal Media1818043488375350718Farouk DjenienPas encore d'évaluation
- Diaporama Pascal ChaibiDocument34 pagesDiaporama Pascal Chaibikarika hélinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Les LymphomesDocument127 pages5 Les LymphomesMyriam BenkiranePas encore d'évaluation
- Hemato4an Td-Cat AnemieDocument16 pagesHemato4an Td-Cat AnemieCh HPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification Et Index Pronostiques Des Hémopathies MalignesDocument124 pagesClassification Et Index Pronostiques Des Hémopathies Malignesnigel faragePas encore d'évaluation
- Aide Memire D'hematologieDocument266 pagesAide Memire D'hematologiesa kaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemie DPDocument14 pagesAnemie DPsifessalamPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 CAT Anémie DIU Nov2012Document58 pages23 CAT Anémie DIU Nov2012Med KhezPas encore d'évaluation
- HyperQCM Clinique HematologieDocument75 pagesHyperQCM Clinique Hematologiemhiche100% (1)
- Cytologie Des Hemopathies Malignes Ed1 V1-DéverrouilléDocument153 pagesCytologie Des Hemopathies Malignes Ed1 V1-Déverrouillémohamed.benjdidia100% (2)
- 1-Myélémie 3ème Année PharmacieDocument18 pages1-Myélémie 3ème Année Pharmaciehanane elPas encore d'évaluation
- LES LEUCEMIES 3e Me Anne e InfirmiersDocument54 pagesLES LEUCEMIES 3e Me Anne e InfirmiersSamy MechtiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sémiologie en HématologieDocument4 pagesSémiologie en HématologieVictoire SIMIERPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPO - CAT Devant Une AnémieDocument29 pagesTOPO - CAT Devant Une AnémiemacysannyPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperqcmclinique-Hematologie PDFDocument27 pagesHyperqcmclinique-Hematologie PDFDoctoresse AsmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Purpura Thrombopénique ImmunologiqueDocument13 pages8 - Purpura Thrombopénique Immunologiquesnousi MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- AnémieDocument7 pagesAnémiemivoc29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anomalies de GRDocument25 pagesAnomalies de GRImen KrichenPas encore d'évaluation
- Astuces Cas Cliniques (GC)Document2 pagesAstuces Cas Cliniques (GC)TarekPas encore d'évaluation
- Anomalies GRDocument27 pagesAnomalies GRsami aidaPas encore d'évaluation
- B8 HemopathiesDocument2 pagesB8 HemopathiesYaakoub RMPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyt 2016 2Document24 pagesCyt 2016 2laboratoire du gharbPas encore d'évaluation
- PMC 1-Lymphome de BurkittDocument39 pagesPMC 1-Lymphome de Burkittfjxpfjkg4xPas encore d'évaluation
- Hémogramme PathologiqueDocument7 pagesHémogramme PathologiqueAymenPas encore d'évaluation
- I-10-163-Leucémies Lymphoïdes Chroniques FICHEDocument1 pageI-10-163-Leucémies Lymphoïdes Chroniques FICHENemo LuPas encore d'évaluation
- Gammapathies MonoclonalesDocument28 pagesGammapathies MonoclonalesDumas TchibozoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 HématimétrieDocument3 pages1 HématimétrieNova FlowerPas encore d'évaluation
- Item 163 Leucemies Lymphoïdes Chroniques PDFDocument1 pageItem 163 Leucemies Lymphoïdes Chroniques PDFAmine DounanePas encore d'évaluation